Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
- Figure shows a cross-section of a ‘light pipe’ made of a glass fibre of refractive index 1.68. The outer covering of the pipe is made of a material of refractive index 1.44. What is the range of the angles of the incident rays with the axis of the pipe for which total reflections inside the pipe take place, as shown in the figure?
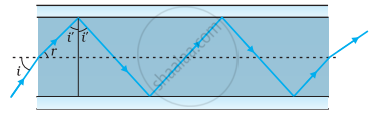
- What is the answer if there is no outer covering of the pipe?
उत्तर
(a) Refractive index of the glass fibre, μ1 = 1.68
Refractive index of the outer covering of the pipe, μ2 = 1.44
Angle of incidence = i
Angle of refraction = r
Angle of incidence at the interface = i'
The refractive index (μ) of the inner core − outer core interface is given as:
`μ = μ_2/μ_1 = 1/(sin "i'")`
`sin "i'" = (μ_1)/(μ_2)`
= `1.44/1.68`
= 0.8571
∴ i' = 59°
For the critical angle, total internal reflection (TIR) takes place only when i > i', i.e., i > 59°
Maximum angle of reflection, rmax = 90° − i' = 90° − 59° = 31°
Let, imax be the maximum angle of incidence.
The refractive index at the air-glass interface, μ1 = 1.68
We have the relation for the maximum angles of incidence and reflection as:
`μ_1 = (sin "i"_"max")/sin "r"_"max"`
sin imax = μ1 sin rmax
= 1.68 sin 31°
= 1.68 × 0.5150
= 0.8652
∴ imax = sin−1 0.8652 ≈ 60°
Thus, all the rays incident at angles lying in the range 0 < i < 60° will suffer total internal reflection
(b) If the outer covering of the pipe is not present, then:
Refractive index of the outer pipe, μ1 = Refractive index of air = 1
For the angle of incidence i = 90°, we can write Snell’s law at the air − pipe interface as:
`sin "i"/sin "r" = μ_2` = 1.68
`sin "r" = (sin 90°)/1.68 = 1/1.68`
`"r" = sin^(-1) (0.5952)`
= 36.5°
∴ i' = 90° − 36.5° = 53.5°
Since i' > r, all incident rays will suffer total internal reflection.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Double-convex lenses are to be manufactured from a glass of refractive index 1.55, with both faces of the same radius of curvature. What is the radius of curvature required if the focal length is to be 20 cm?
The refractive index of diamond is much greater than that of ordinary glass. Is this fact of some use to a diamond cutter?
A converging lens has a focal length of 20 cm in air. It is made of a material of refractive index 1·6. If it is immersed in a liquid of refractive index 1·3, find its new focal length.
For the same value of angle of incidence, the angles of refraction in three media A, B and C are 15°, 25° and 35° respectively. In which medium would the velocity of light be minimum?
A narrow beam of white light goes through a slab having parallel faces.
(a) The light never splits in different colours
(b) The emergent beam is white
(c) The light inside the slab is split into different colours
(d) The light inside the slab is white
If the light moving in a straight line bends by a small but fixed angle, it may be a case of
(a) reflection
(b) refraction
(c) diffraction
(d) dispersion.
A pole of length 1.00 m stands half dipped in a swimming pool with water level 50.0 cm higher than the bed. The refractive index of water is 1.33 and sunlight is coming at an angle of 45° with the vertical. Find the length of the shadow of the pole on the bed.
A convex lens of focal length 20 cm and a concave lens of focal length 10 cm are placed 10 cm apart with their principal axes coinciding. A beam of light travelling parallel to the principal axis and having a beam diameter 5.0 mm, is incident on the combination. Show that the emergent beam is parallel to the incident one. Find the beam diameter of the emergent beam.
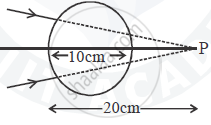
A converging beam of light travelling in air converges at a point P as shown in the figure. When a glass sphere of refractive index 1 . 5 is introduced in between the path of the beam, calculate the new position of the image. Also draw the ray diagram for the image formed.
What is optical path? Obtain the equation for optical path of a medium of thickness d and refractive index n.
What is a principle of reversibility?
Obtain the equation for apparent depth.
Why do stars twinkle?
Obtain the equation for critical angle.
A ray of light travels from air to water to glass and aga in from glass to air. Refractive index of water with respect to air is 'x' glass with respect to water is 'y' and air with respect to glass is 'z'. which one of the following is correct?
When a ray of light is refracted from one medium to another, then the wavelength changes from 6000Å to 4000Å. The critical angle for the interface will be ______.
Three immiscible liquids of densities d1 > d2 > d3 and refractive indices µ1 > µ2 > µ3 are put in a beaker. The height of each liquid column is `h/3`. A dot is made at the bottom of the beaker. For near normal vision, find the apparent depth of the dot.
A beam of light travels from air into a medium. Its speed and wavelength in the medium are 1.5 × 108 ms-1 and 230 nm respectively. The wavelength of light in the air will be ______.
