Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
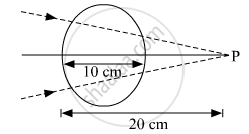
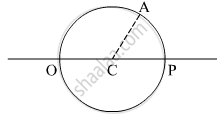
A converging beam of light travelling in air converges at a point P as shown in the figure. When a glass sphere of refractive index 1 . 5 is introduced in between the path of the beam, calculate the new position of the image. Also draw the ray diagram for the image formed.
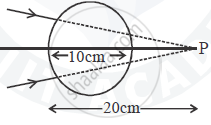
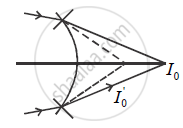
उत्तर
Case 1 : n1 = 1 n2 = 1.5
u = ∞

`1.5/V = 1/ ∞ = ((1.5 - 1))/5`
`1.5/V = 0.5/5`
V = 15 cm
case 2 :
`1/V - 1.5/15 = (1-1.5)/-5`
`1/V = 0.5/5 + 1.5/15`
`1/V = 1/20`
V = 20 cm
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A fish which is at a depth of l2 em .in water `(mu = 4/3)` is viewed by an observer on the bank of a lake. Its apparent depth as observed: by the observer is:
a) 3 cm
b) 9 cm
c) 12 cm
d) 16 cm
For the same value of angle of incidence, the angles of refraction in three media A, B and C are 15°, 25° and 35° respectively. In which medium would the velocity of light be minimum?
Is the formula "Real depth/Apparent depth = μ" valid if viewed from a position quite away from the normal?
Why does a diamond shine more than a glass piece cut to the same shape?
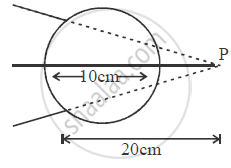
A converging beam of light traveling in air converges at a point P as shown in the figure. When a glass sphere of refractive index 1⋅5 is introduced in between the path of the beam, calculate the new position of, the image. Also, draw the ray diagram for the image formed.
What is relative refractive index?
A concave mirror of focal length 'f1' is placed at a distance 'd' from a convex lens of focal length 'f2'. A parallel beam of light coming from infinity parallel to principal axis falls on the convex lens and then after refraction falls on the concave mirror. If it is to retrace the path, the distance 'd' should be ______.
For a rectangular slab, refraction takes place at ______.
Consider an extended object immersed in water contained in a plane trough. When seen from close to the edge of the trough the object looks distorted because ______.
- the apparent depth of the points close to the edge are nearer the surface of the water compared to the points away from the edge.
- the angle subtended by the image of the object at the eye is smaller than the actual angle subtended by the object in air.
- some of the points of the object far away from the edge may not be visible because of total internal reflection.
- water in a trough acts as a lens and magnifies the object.
