Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
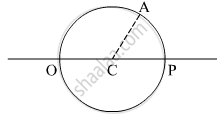
उत्तर
Point O is marked on the surface of the glass sphere, and the image of point O is being observed from point P. Let the observed distance of point O is `"d"_"observed"`, then according to the relation of apparent depth,
`"d"_"observed"/mu_"observer" = "d"_"Actual"/(mu_"Object")`
⇒ `"d"_"observed" = mu_"observer" xx "d"_"Actual"/mu_"Object"`
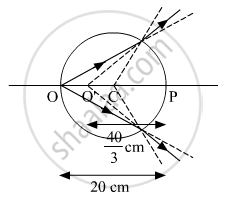
⇒ `"d"_"observed" = 1 xx (20"cm")/1.5 = 40/3 "cm"`
Hence the image of point O will form at`40/3` cm from the point P towards point O. The figure below shows the ray diagram.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
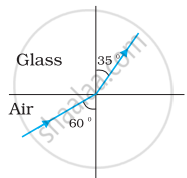
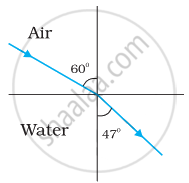
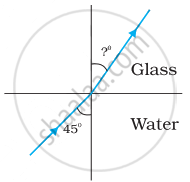
Figures (a) and (b) show the refraction of a ray in air incident at 60° with the normal to a glass-air and water-air interface, respectively. Predict the angle of refraction in the glass when the angle of incidence in water is 45° with the normal to a water-glass interface [Figure (c)].
 |
 |
 |
| (a) | (b) | (c) |
Does the apparent depth of a tank of water change if viewed obliquely? If so, does the apparent depth increase or decrease?
Monochromatic light of wavelength 589 nm is incident from air on a water surface. If µ for water is 1.33, find the wavelength, frequency and speed of the refracted light.
A narrow beam of white light goes through a slab having parallel faces.
(a) The light never splits in different colours
(b) The emergent beam is white
(c) The light inside the slab is split into different colours
(d) The light inside the slab is white
An object P is focussed by a microscope M. A glass slab of thickness 2.1 cm is introduced between P and M. If the refractive index of the slab is 1.5, by what distance should the microscope be shifted to focus the object again?
Locate the image formed by refraction in the situation shown in figure.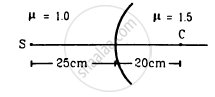
Why do stars twinkle?
What is Snell’s window?
How does an endoscope work?
Obtain the equation for radius of illumination (or) Snell’s window.
