Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Figures (a) and (b) show the refraction of a ray in air incident at 60° with the normal to a glass-air and water-air interface, respectively. Predict the angle of refraction in the glass when the angle of incidence in water is 45° with the normal to a water-glass interface [Figure (c)].
 |
 |
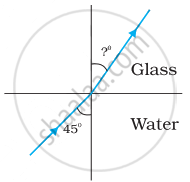 |
| (a) | (b) | (c) |
उत्तर
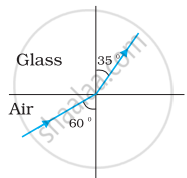
As per the given figure, for the glass-air interface:
Angle of incidence, i = 60°
Angle of refraction, r = 35°
The relative refractive index of glass with respect to air is given by Snell’s law as:
`""^"a"μ_"g" = (sin "i")/(sin "r")`
= `(sin 60°)/(sin 35°)`
= `(0.8660)/(0.5736)`
= 1.51 ......(1)
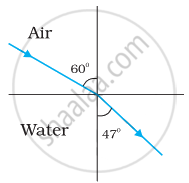
As per the given figure, for the air-water interface:
Angle of incidence, i = 60°
Angle of refraction, r = 47°
The relative refractive index of water with respect to air is given by Snell’s law as:
`""^"a"μ_"w" = (sin "i")/(sin "r")`
= `(sin 60°)/(sin 47°)`
= `(0.8660)/(0.7314)`
= 1.184 ....(2)
Using (1) and (2), the relative refractive index of glass with respect to water can be obtained as:
`""^"w"μ_"g" = (""^"a"μ_"g")/(""^"a"μ_"w")`
= `1.51/1.184`
= 1.275
The following figure shows the situation involving the glass-water interface.
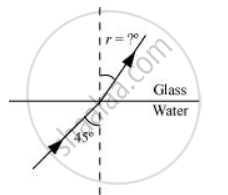
Angle of incidence, i = 45°
Angle of refraction = r
From Snell’s law, r can be calculated as:
`(sin "i")/(sin "r") = ""^"w"μ_"g"`
`(sin 45°)/sin "r"` = 1.275
sin r = `(1/(sqrt2))/1.275`
sin r = 0.5546
∴ r = `sin^(-1) (0.5546)` = 33.68°
Hence, the angle of refraction at the water-glass interface is 33.68°.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A small pin fixed on a table top is viewed from above from a distance of 50 cm. By what distance would the pin appear to be raised if it is viewed from the same point through a 15 cm thick glass slab held parallel to the table? Refractive index of glass = 1.5. Does the answer depend on the location of the slab?
Light incident normally on a plane mirror attached to a galvanometer coil retraces backward as shown in Figure. A current in the coil produces a deflection of 3.5° of the mirror. What is the displacement of the reflected spot of light on a screen placed 1.5 m away?

Monochromatic light of wavelength 589 nm is incident from air on a water surface. If µ for water is 1.33, find the wavelength, frequency and speed of the refracted light.
A fish which is at a depth of l2 em .in water `(mu = 4/3)` is viewed by an observer on the bank of a lake. Its apparent depth as observed: by the observer is:
a) 3 cm
b) 9 cm
c) 12 cm
d) 16 cm
A converging lens has a focal length of 20 cm in air. It is made of a material of refractive index 1·6. If it is immersed in a liquid of refractive index 1·3, find its new focal length.
A glass lens of refractive index 1.45 disappears when immersed in a liquid. What is the value of refractive index of the liquid?
A laser light is focussed by a converging lens. Will there be a significant chromatic aberration?
A pole of length 1.00 m stands half dipped in a swimming pool with water level 50.0 cm higher than the bed. The refractive index of water is 1.33 and sunlight is coming at an angle of 45° with the vertical. Find the length of the shadow of the pole on the bed.
Locate the image formed by refraction in the situation shown in figure.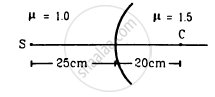
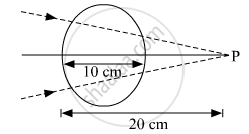
A converging beam of light traveling in air converges at a point P as shown in the figure. When a glass sphere of refractive index 1⋅5 is introduced in between the path of the beam, calculate the new position of, the image. Also, draw the ray diagram for the image formed.
What is a principle of reversibility?
What is relative refractive index?
Obtain the equation for apparent depth.
Write a short note on the prisms making use of total internal reflection.
The critical angle for a ray of light from glass to air is 'θ' and refractive index of glass with respect to air is 'n'. If a ray of light is incident from air to glass at an angle 'θ', then corresponding angle of refraction is ______.
When a ray of light is incident normally on one refracting surface of an equilateral prism of refractive index 1.5, the emerging ray ______.
`[sin^-1(1/1.5)=41.8^circ]`
A concave mirror of focal length 'f1' is placed at a distance 'd' from a convex lens of focal length 'f2'. A parallel beam of light coming from infinity parallel to principal axis falls on the convex lens and then after refraction falls on the concave mirror. If it is to retrace the path, the distance 'd' should be ______.
For a rectangular slab, refraction takes place at ______.
There are certain material developed in laboratories which have a negative refractive index (Figure). A ray incident from air (medium 1) into such a medium (medium 2) shall follow a path given by.
A beam of light travels from air into a medium. Its speed and wavelength in the medium are 1.5 × 108 ms-1 and 230 nm respectively. The wavelength of light in the air will be ______.
