Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A tank is filled with water to a height of 12.5 cm. The apparent depth of a needle lying at the bottom of the tank is measured by a microscope to be 9.4 cm. What is the refractive index of water? If water is replaced by a liquid of refractive index 1.63 up to the same height, by what distance would the microscope have to be moved to focus on the needle again?
उत्तर
Actual depth of the needle in water, h1 = 12.5 cm
Apparent depth of the needle in water, h2 = 9.4 cm
Refractive index of water = μ
The value of μ can be obtained as follows:
μ = `"h"_1/"h"_2`
= `12.5/9.4`
= 1.329 ≈ 1.33
Hence, the refractive index of water is about 1.33.
Water is replaced by a liquid of refractive index, μ' = 1.63
The actual depth of the needle remains the same, but its apparent depth changes. Let y be the new apparent depth of the needle. Hence, we can write the relation:
μ' = `"h"_1/"y"`
∴ y = `"h"_1/(μ"'")`
= `12.5/1.63`
= 7.67 cm
Hence, the new apparent depth of the needle is 7.67 cm. It is less than h2. Therefore, to focus the needle again, the microscope should be moved up.
∴ Distance by which the microscope should be moved up = 9.4 − 7.67 = 1.73 cm
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
- Figure shows a cross-section of a ‘light pipe’ made of a glass fibre of refractive index 1.68. The outer covering of the pipe is made of a material of refractive index 1.44. What is the range of the angles of the incident rays with the axis of the pipe for which total reflections inside the pipe take place, as shown in the figure?
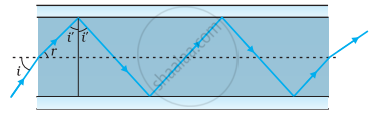
- What is the answer if there is no outer covering of the pipe?
Light incident normally on a plane mirror attached to a galvanometer coil retraces backward as shown in Figure. A current in the coil produces a deflection of 3.5° of the mirror. What is the displacement of the reflected spot of light on a screen placed 1.5 m away?

Monochromatic light of wavelength 589 nm is incident from air on a water surface. If µ for water is 1.33, find the wavelength, frequency and speed of the refracted light.
Why does a diamond shine more than a glass piece cut to the same shape?
A narrow beam of white light goes through a slab having parallel faces.
(a) The light never splits in different colours
(b) The emergent beam is white
(c) The light inside the slab is split into different colours
(d) The light inside the slab is white
Consider the situation in figure. The bottom of the pot is a reflecting plane mirror, S is a small fish and T is a human eye. Refractive index of water is μ. (a) At what distance(s) from itself will the fish see the image(s) of the eye? (b) At what distance(s) from itself will the eye see the image(s) of the fish.

Answer the following question.
Define absolute refractive index and relative refractive index. Explain in brief with an illustration for each.
A ray of light travelling in a transparent medium of refractive index n falls, on a surface separating the medium from air at an angle of incidents of 45°. The ray can undergo total internal reflection for the following n.
What is optical path? Obtain the equation for optical path of a medium of thickness d and refractive index n.
What is critical angle and total internal reflection?
Obtain the equation for critical angle.
Explain the reason for glittering of diamond.
How does an endoscope work?
A light travels through water in the beaker. The height of water column is 'h'. Refractive index of water is 'μw'. If c is velocity of light in air, the time taken by light to travel through water will ______.
The critical angle for a ray of light from glass to air is 'θ' and refractive index of glass with respect to air is 'n'. If a ray of light is incident from air to glass at an angle 'θ', then corresponding angle of refraction is ______.
Light travels from an optically denser medium 'A' into the optically rarer medium 'B' with speeds 1.8 × 108 m/s and 2.7 × 108 m/s respectively. Then critical angle between them is ______.
(µ1 and µ2 are the refractive indices of media A and B respectively.)
If `"^imu_j` represents refractive index, when a light ray goes from medium i to medium j, then the product `"^2mu_1 xx ^3mu_2 xx ^4mu_3` is equal to ______.
There are certain material developed in laboratories which have a negative refractive index (Figure). A ray incident from air (medium 1) into such a medium (medium 2) shall follow a path given by.
Three immiscible liquids of densities d1 > d2 > d3 and refractive indices µ1 > µ2 > µ3 are put in a beaker. The height of each liquid column is `h/3`. A dot is made at the bottom of the beaker. For near normal vision, find the apparent depth of the dot.
