Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Answer the following question.
Define absolute refractive index and relative refractive index. Explain in brief with an illustration for each.
उत्तर
- Absolute refractive index of a medium is defined as the ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum to that in the given medium.
- A stick or pencil kept obliquely in a glass containing water appears broken as its part in water appears to be raised.
- As the speed of light is different in two media, the rays of light coming from water undergo refraction at the boundary separating the two media.
- Consider the speed of light to be v in water and c in air. (Speed of light in air ≈ speed of light in vacuum)
∴ refractive index of water = `"n"_"w"/"n"_"a"="n"_"w"/"n"_"vacuum"="c"/"v"` - The relative refractive index of a medium 2 is the refractive index of medium 2 with respect to medium 1 and it is defined as the ratio of the speed of light v1 in medium 1 to its speed v2 in medium 2.
∴ The relative refractive index of medium 2,
1n2 = `"v"_1/"v"_2` - Consider a beaker filled with water of absolute refractive index n1 kept on a transparent glass slab of absolute refractive index n2.
- Thus, the refractive index of water with respect to that of glass will be,
gnw = `"n"_2/"n"_1=("c"/"v"_2)/("c"/"v"_1)="v"_1/"v"_2`.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Double-convex lenses are to be manufactured from a glass of refractive index 1.55, with both faces of the same radius of curvature. What is the radius of curvature required if the focal length is to be 20 cm?
A diver under water, looks obliquely at a fisherman standing on the bank of a lake. Would the fisherman look taller or shorter to the diver than what he actually is?
Light incident normally on a plane mirror attached to a galvanometer coil retraces backward as shown in Figure. A current in the coil produces a deflection of 3.5° of the mirror. What is the displacement of the reflected spot of light on a screen placed 1.5 m away?

Determine the value of the angle of incidence for a ray of light travelling from a medium of refractive index \[\mu_1 = \sqrt{2}\] into the medium of refractive index \[\mu_2 = 1\] so that it just grazes along the surface of separation.
The refractive index of a material changes by 0.014 as the colour of the light changes from red to violet. A rectangular slab of height 2.00 cm made of this material is placed on a newspaper. When viewed normally in yellow light, the letters appear 1.32 cm below the top surface of the slab. Calculate the dispersive power of the material.
A pole of length 1.00 m stands half dipped in a swimming pool with water level 50.0 cm higher than the bed. The refractive index of water is 1.33 and sunlight is coming at an angle of 45° with the vertical. Find the length of the shadow of the pole on the bed.
A vessel contains water up to a height of 20 cm and above it an oil up to another 20 cm. The refractive indices of the water and the oil are 1.33 and 1.30 respectively. Find the apparent depth of the vessel when viewed from above.
A convex lens of focal length 20 cm and a concave lens of focal length 10 cm are placed 10 cm apart with their principal axes coinciding. A beam of light travelling parallel to the principal axis and having a beam diameter 5.0 mm, is incident on the combination. Show that the emergent beam is parallel to the incident one. Find the beam diameter of the emergent beam.
Stars twinkle due to ______.
What is optical path? Obtain the equation for optical path of a medium of thickness d and refractive index n.
What is a principle of reversibility?
Obtain the equation for apparent depth.
Why do stars twinkle?
Explain the reason for glittering of diamond.
What is mirage?
Write a note on optical fibre.
An object is immersed in a fluid of refractive index 'µ'. In order that the object becomes invisible when observed from outside, it should ______.
When a light ray is incident on a prism at an angle of 45°, the minimum deviation is obtained. If refractive index of material of prism is `sqrt2`, then angle of prism will be ______.
`sin pi/4=1/sqrt2, sin30^circ=cos60^circ=1/2`
The critical angle is maximum when light travels from ______.
`(a^mu"w"=4/3,a^mug=3/2)`
When a ray of light is incident normally on one refracting surface of an equilateral prism of refractive index 1.5, the emerging ray ______.
`[sin^-1(1/1.5)=41.8^circ]`
When a ray of light is refracted from one medium to another, then the wavelength changes from 6000Å to 4000Å. The critical angle for the interface will be ______.
A concave mirror of focal length 'f1' is placed at a distance 'd' from a convex lens of focal length 'f2'. A parallel beam of light coming from infinity parallel to principal axis falls on the convex lens and then after refraction falls on the concave mirror. If it is to retrace the path, the distance 'd' should be ______.
Light travels in two media A and B with speeds 1.8 × 108 ms−1 and 2.4 × 108 ms−1 respectively. Then the critical angle between them is:
A ray of unpolarised light is incident on the surface of glass plate of µ = 1.54 at polarising angle, then angle of refraction is
The optical density of turpentine is higher than that of water while its mass density is lower. Figure shows a layer of turpentine floating over water in a container. For which one of the four rays incident on turpentine in figure, the path shown is correct?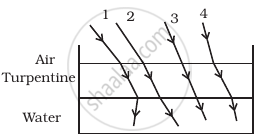
There are certain material developed in laboratories which have a negative refractive index (Figure). A ray incident from air (medium 1) into such a medium (medium 2) shall follow a path given by.
Consider an extended object immersed in water contained in a plane trough. When seen from close to the edge of the trough the object looks distorted because ______.
- the apparent depth of the points close to the edge are nearer the surface of the water compared to the points away from the edge.
- the angle subtended by the image of the object at the eye is smaller than the actual angle subtended by the object in air.
- some of the points of the object far away from the edge may not be visible because of total internal reflection.
- water in a trough acts as a lens and magnifies the object.
A beam of light travels from air into a medium. Its speed and wavelength in the medium are 1.5 × 108 ms-1 and 230 nm respectively. The wavelength of light in the air will be ______.
