Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Answer the following question.
Explain ‘mirage’ as an illustration of refraction.
उत्तर
- On a hot clear Sunny day, along a level road, there appears a pond of water ahead of the road. However, if we physically reach the spot, there is nothing but the dry road and water pond again appears some distance ahead. This illusion is called mirage.
- Mirage results from the refraction of light through a non-uniform medium.
- On a hot day the air in contact with the road is hottest and as we go up, it gets gradually cooler. The refractive index of air thus decreases with height. Hot air tends to be less optically dense than cooler air which results into a non-uniform medium.
- Light travels in a straight line through a uniform medium but refracts when traveling through a non-uniform medium.
- Thus, the ray of light coming from the top of an object get refracted while travelling downwards into less optically dense air and become more and more horizontal as shown in figure.
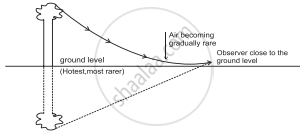
- As it almost touches the road, it bends (refracts) upward. Then onwards, upward bending continues due to denser air.
- As a result, for an observer, it appears to be coming from below thereby giving an illusion of reflection from an (imaginary) water surface.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State two conditions necessary for total internal reflection to occur.
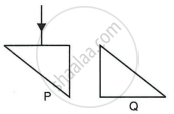
Two isosceles right-angle glass prisms P and Q are placed near each other as shown in Fig. Complete the path of the light ray entering the prism P till it emerges out of the prism Q.
Swarali has got the following observations while doing an experiment. Answer her questions with the help of observations.
Swarali observed that the light bent away from the normal, while travelling from dense medium to rarer medium. When Swarali increased the values of angle of incidence (i), the values of angle of refraction (r) went on increasing. But at a certain angle of incidence, the light rays returned into the dense medium.
So, Swarali has some questions. Answer them –
a) Name this certain value of ‘i ’. What is the value of ‘r’ at that time ?
b) Name this process of returning of light in dense medium. Explain the process.
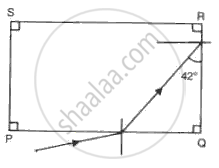
(a) A ray of monochromatic light enters glass PQRS as shown in the fig. Complete the path of ray till it emerges from the glass. (Critical angle of glass is 420).
(b) Draw diagram of a prism periscope.
(c) What are the advantages of total internal reflecting prism over plane mirror?
If a ray of light passes from medium I to medium II without any change of direction, what can be said about the refractive indices of these media (angle I is not 0)?
What is meant by the statement, ‘the critical angle for diamond is 24°’?
Draw a diagram, properly labelled, to illustrate the use of a total reflecting prism (a right-angled isosceles prism) to turn a ray of light through 180°. Name an instrument in which this device is used.
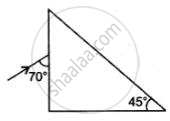
Complete the following diagram to show the path of the ray of a single colour in the diagram as if enters in and emerges out of the prism. Mark the angles wherever necessary. (Critical angle for glass = 42°).
PQ and PR are two light rays emerging from the object as shown in the figure below:
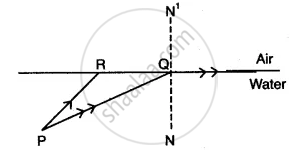
(i) What is the special name given to the angle of incidence (∠PQN) of ray PQ?
(ii) Copy the ray diagram and complete it to show the position of the image of the object P when seen obliquely from above.
(iii) Name the phenomenon that occurs if the angle of incidence ∠PQN is increased still further.
Choose the correct option.
Angles of deviation for extreme colours are given for different prisms. Select the one having maximum dispersive power of its material.
Answer the following question.
Define the critical angle of incidence and obtain an expression for it.
Answer the following question.
Describe the construction and working of an optical fibre.
Answer the following question.
Why is prism binoculars preferred over traditional binoculars? Describe its working in brief.
Solve Numerical example.
From the given data set, determine angular dispersion by the prism and dispersive power of its material for extreme colours. nR = 1.62 nV = 1.66, δR = 3.1°
For total internal reflection to take place, the angle of inddence i and the refractive index µ of the medium must satisfy the inequality ____________.
A particle is projected such that the horizontal range and vertical height are equal. Then the angle of projection is :
The entire light is reflected back into the denser medium is called ______.
What are the conditions to achieve total internal reflection?
What is the phenomenon used in optical fiber? Explain.
Write any two uses of total internal reflection.
What are the examples of total internal reflection in nature?
A Rainbow is a beautiful natural phenomenon formed because of the following:
A ray of light passes from vacuum into a medium of refractive index µ, the angle of incidence is found to be twice the angle of refraction. Then the angle of incidence is ______.
The angle made by incident ray of light with normal of the reflecting surface is called ______.
Small air bubbles rising up a fish tank appear silvery when viewed from some particular angle is due to the ______.
