Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Choose the correct option.
Angles of deviation for extreme colours are given for different prisms. Select the one having maximum dispersive power of its material.
विकल्प
7°, 10°
8°, 11°
12°, 16°
10°, 14°
उत्तर
7°, 10°
Explanation:
Dispersive power for thin prism is,
ω = `(δ_"V"-δ_"R")/(((δ_"V"+δ_"R")/2)`
∴ For values in option (A),
ω = `(10-7)/(((10+7)/2))=6/17` = 0.35
For values in option (B),
ω = `(11-8)/(((11+8)/2))=6/19` = 0.31
For values in option (C),
ω = `(16-12)/(((16+12)/2))=2/7` = 0.28
For values in option (D),
ω = `(14-10)/(((14+10)/2))=1/3` = 0.33
Thus, value of ω is maximum for prism with angles of deviations, 7°, 10°.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What do you understand by the deviation produced by a prism? Why is it caused?
Two isosceles right-angle glass prisms P and Q are placed near each other as shown in Fig. Complete the path of the light ray entering the prism P till it emerges out of the prism Q.
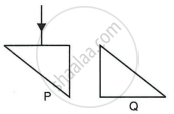
Prove the statement.
A rainbow is the combined effect of the refraction, dispersion, and total internal reflection of light.
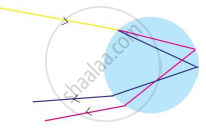
i) Observe the given figure and answer the following questions.
a) Identify and write the natural process shown in the figure.
b) List the phenomena which are observe in this process.
c) Redraw the diagram and show above phenomena in it.
The observation made by Swarali while doing the experiment is given below. Based on these write answers to the questions:
Swarali found that the light ray travelling from the denser medium to rarer medium goes away from the normal. If the angle of incidence (i) is raised by Swarali, the angle of refraction (r) went on increasing. However, after certain value of the angle of incidence the light ray is seen to return back into the denser medium.
Questions:
- What is the specific value of∠i called?
- What is the process of reflection of incident rays into denser medium called?
- Draw the diagrams of three observations made by Swarali.
(i) Define critical angle.
(ii) State one important factor which affects the critical angle of a given medium.
Make the correct choices for each of the following :
Total Internal reflection takes place when
(where ∠i = angle of incidence, ∠r = angle of refraction, ∠C = critical angle)
In the following figure, show two rays A and B travelling from water to air. If the critical angle for water- air surface is 48°, complete the ray diagram showing the refracted rays for each. State conditions when the ray will suffer total internal reflection.

How does a ray of light bend when it travels from when it is normal to the interface of the two media.
Can light be ‘piped’ like sound in a doctor’s stethoscope?
Images formed by totally reflecting prisms are brighter than the image formed by ordinary reflected light, why?
What is meant by the term ‘critical angle’?
Draw a diagram, properly labelled, to illustrate the use of a total reflecting prism (a right-angled isosceles prism) to turn a ray of light through 180°. Name an instrument in which this device is used.
PQ and PR are two light rays emerging from the object as shown in the figure below:
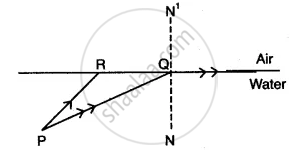
(i) What is the special name given to the angle of incidence (∠PQN) of ray PQ?
(ii) Copy the ray diagram and complete it to show the position of the image of the object P when seen obliquely from above.
(iii) Name the phenomenon that occurs if the angle of incidence ∠PQN is increased still further.
Answer the following question.
Explain ‘mirage’ as an illustration of refraction.
Answer the following question.
Under what conditions are total internal reflection possible? Explain it with a suitable example.
Observe the given figure and write appropriate phenomenon of light in the box.

Critical angle of light passing from glass to air is maximum for ____________.
A green light is incident from the water to the air-water interface at the critical angle `(theta)`. Select the correct statement
The angle of minimum deviation produced by a thin glass prism in air is 'δ'. If that prism is immersed in water, the angle of minimum deviation will be ______.
( aμg = refractive index of glass w.r.t, air aμw = refractive index of water w.r.t. air)
The twinkling effect of star light is due to ______.
The angle of incidence at which the angle of refraction is Q£ is called the critical angle.
Define the critical angle.
What is the phenomenon used in optical fiber? Explain.
A ray of light passes from vacuum into a medium of refractive index µ, the angle of incidence is found to be twice the angle of refraction. Then the angle of incidence is ______.
The angle made by incident ray of light with normal of the reflecting surface is called ______.
- Assertion (A): Propagation of light through an optical fibre is due to total internal reflection taking place at the core-cladding interface.
- Reason (R): Refractive index of the material of the cladding of the optical fibre is greater than that of the core.
An endoscope uses optic fiber to transmit high resolution images of internal organs without loss of information. The principle of light that is used by the optic fiber is based on ______.
