Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Choose the correct option.
Angles of deviation for extreme colours are given for different prisms. Select the one having maximum dispersive power of its material.
Options
7°, 10°
8°, 11°
12°, 16°
10°, 14°
Solution
7°, 10°
Explanation:
Dispersive power for thin prism is,
ω = `(δ_"V"-δ_"R")/(((δ_"V"+δ_"R")/2)`
∴ For values in option (A),
ω = `(10-7)/(((10+7)/2))=6/17` = 0.35
For values in option (B),
ω = `(11-8)/(((11+8)/2))=6/19` = 0.31
For values in option (C),
ω = `(16-12)/(((16+12)/2))=2/7` = 0.28
For values in option (D),
ω = `(14-10)/(((14+10)/2))=1/3` = 0.33
Thus, value of ω is maximum for prism with angles of deviations, 7°, 10°.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Draw the diagram of a right-angled isosceles prism which is used to make an invented image erect
Angle of deviation is the angle which the ______ ray makes with the direction of ______ray.
State two conditions necessary for total internal reflection to occur.
In the following figure, show two rays A and B travelling from water to air. If the critical angle for water- air surface is 48°, complete the ray diagram showing the refracted rays for each. State conditions when the ray will suffer total internal reflection.

Name the principle on the basis of which optical fibres work.
How does a ray of light bend when it travels from rarer to denser medium
If a ray of light passes from medium I to medium II without any change of direction, what can be said about the refractive indices of these media (angle I is not 0)?
How are critical angles related to the refractive index of the medium?
State two advantages of using a right-angle prism as a reflector, rather than a plane mirror.
Name the factors affecting the critical angle for the pair of media.
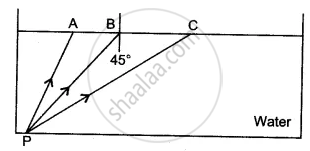
The diagram shows a point source P inside a water container. Three rays A, B, and C starting from P are shown up to the water surface. Show in the diagram the path of these rays after striking the water surface. The critical angle for the water-air pair is 48°.
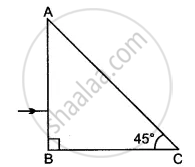
A ray of light passes through a right-angled prism as shown in the figure. State the angles of incidence at the faces AC and BC.
PQ and PR are two light rays emerging from the object as shown in the figure below:
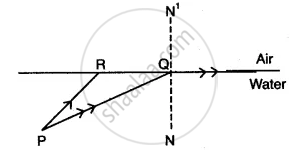
(i) What is the special name given to the angle of incidence (∠PQN) of ray PQ?
(ii) Copy the ray diagram and complete it to show the position of the image of the object P when seen obliquely from above.
(iii) Name the phenomenon that occurs if the angle of incidence ∠PQN is increased still further.
Answer the following question.
Describe the construction and working of an optical fibre.
Answer the following question.
What are the advantages of optical fibre communication over electronic communication?
Which one of the following is NOT the correct formula for refractive index of glass w.r.t. air (aμg) (i = angle of incidence, r = angle of refraction)
For total internal reflection to take place, the angle of inddence i and the refractive index µ of the medium must satisfy the inequality ____________.
For a ray of light, the critical angle is minimum when it travels from ______.
The entire light is reflected back into the denser medium is called ______.
What is a mirage? How does it occur?
A green light is incident from the water to the air-water interface at the critical angle (θ). Select the correct statement.
A ray of light incident at an angle θ on a refracting face of a prism emerges from the other face normally. If the angle of the prism is 5° and the prism is made of a material of refractive index 1.5, the angle of incidence is ______.
State the condition under which total internal reflection occurs. Give the mathematical expression for total internal reflection.
Which of the following is used in optical fibres?
Find the value of θ in the given figure.
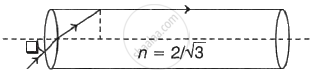
An endoscope uses optic fiber to transmit high resolution images of internal organs without loss of information. The principle of light that is used by the optic fiber is based on ______.
The diagram below shows a fish in the tank and its image seen in the surface of water.

Name the phenomenon responsible for the formation of this image.
State two differences between normal reflection and total internal reflection.
