Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Answer the following question.
What are the advantages of optical fibre communication over electronic communication?
Solution
Advantages:
- Broad bandwidth (frequency range): For TV signals, a single optical fibre can carry over 90000 independent signals (channels).
- Immune to EM interference: Optical fibre being electrically non-conductive, does not pick up nearby EM signals.
- Low attenuation loss: loss being lower than 0.2 dB/km, a single long cable can be used for several kilometres.
- Electrical insulator: Optical fibres being electrical insulators, ground loops of metal wires or lightning do not cause any harm.
- Theft prevention: Optical fibres do not use copper or other expensive material which are prone to be robbed.
- Security of information: Internal damage is most unlikely to occur, keeping the information secure.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Draw the diagram of a right-angled isosceles prism which is used to make an invented image erect
A light ray does not bend at the boundary in passing from one medium to the other medium if the angle of incident is ______.
Write the necessary conditions for the phenomenon of total internal reflection to
occur ?
The observation made by Swarali while doing the experiment is given below. Based on these write answers to the questions:
Swarali found that the light ray travelling from the denser medium to rarer medium goes away from the normal. If the angle of incidence (i) is raised by Swarali, the angle of refraction (r) went on increasing. However, after certain value of the angle of incidence the light ray is seen to return back into the denser medium.
Questions:
- What is the specific value of∠i called?
- What is the process of reflection of incident rays into denser medium called?
- Draw the diagrams of three observations made by Swarali.
(i) Define critical angle.
(ii) State one important factor which affects the critical angle of a given medium.
Plot a graph between
Sine of angle of incidence versus sine of angle of refraction,
Make the correct choices for each of the following :
Total Internal reflection takes place when
(where ∠i = angle of incidence, ∠r = angle of refraction, ∠C = critical angle)
Name the principle on the basis of which optical fibres work.
If a ray of light passes from medium I to medium II without any change of direction, what can be said about the refractive indices of these media (angle I is not 0)?
Images formed by totally reflecting prisms are brighter than the image formed by ordinary reflected light, why?
State one factor on which a critical angle for a given pair of media depends. The critical angle for the glass-air interface is 45° for the yellow light. Will it be equal to, less than or greater than 45° for (i) red light, (ii) blue light?
How is the critical angle of a material related to its refractive index?
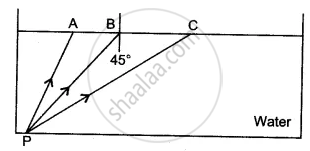
The diagram shows a point source P inside a water container. Three rays A, B, and C starting from P are shown up to the water surface. Show in the diagram the path of these rays after striking the water surface. The critical angle for the water-air pair is 48°.
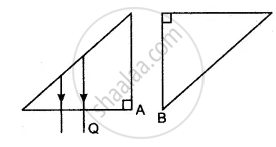
The adjacent diagram shows two right-angled isosceles prisms A and B. Complete the diagram to show the path of rays P and Q emerging out of the prism B. What principles have you used to complete the diagram?
A ray of light is incident on a glass surface at an angle of 50° with the corresponding angle of refraction 30°. Find the value of the R.I. of glass.
A spherical marble, of refractive index 1.5 and curvature 1.5 cm, contains a tiny air bubble at its centre. Where will it appear when seen from outside?
Choose the correct option.
Angles of deviation for extreme colours are given for different prisms. Select the one having maximum dispersive power of its material.
Answer the following question.
Describe the construction and working of an optical fibre.
Solve Numerical example.
A monochromatic ray of light is incident at 37° on an equilateral prism of refractive index 3/2. Determine angle of emergence and angle of deviation. If angle of prism is adjustable, what should its value be for emergent rays to be just possible for the same angle of incidence?
Solve Numerical example.
From the given data set, determine angular dispersion by the prism and dispersive power of its material for extreme colours. nR = 1.62 nV = 1.66, δR = 3.1°
The resultant `vec"R"` of `vec"P"` and `vec"Q"` is perpendicular to `vec"P"`. Also `|vec"P"|=|vec"R"|`. The angle between `vec"P"` and `vec"Q"` is ______.
[tan 45° = 1]
Which one of the following is NOT the correct formula for refractive index of glass w.r.t. air (aμg) (i = angle of incidence, r = angle of refraction)
For total internal reflection to take place, the angle of inddence i and the refractive index µ of the medium must satisfy the inequality ____________.
Total internal reflection can take place only if light is travelling from ______.
A particle is projected such that the horizontal range and vertical height are equal. Then the angle of projection is :
Optical Fibres are based on the phenomenon of dispersion.
What is a mirage? How does it occur?
Name any two phenomena which take place in the formation of a rainbow.
The diagram below shows a fish in the tank and its image seen in the surface of water.

Name the phenomenon responsible for the formation of this image.
