Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Answer the following question.
Why is prism binoculars preferred over traditional binoculars? Describe its working in brief.
Solution
- Traditional binoculars use only two cylinders. Distance between the two cylinders can’t be greater than that between the two eyes. This creates a limitation of the field of view.
- A prism binocular has two right-angled glass prisms that apply the principle of total internal reflection.
- The incident light rays are reflected internally twice giving the viewer a wider field of view. For this reason, prism binoculars are preferred over traditional binoculars.
Working:

Prism binoculars
- The prism binoculars consist of 4 isosceles, right-angled prisms of a material having a critical angle less than 45°.
- The prism binoculars have a wider input range compared to traditional binoculars.
- The light rays incident on the prism binoculars, first get total internally reflected by the isosceles, right-angled prisms 1 and 4.
- These reflected rays undergo another total internal reflection by prisms 2 and 3 to form the final image.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
You are given prisms made of crown glass and flint glass with a wide variety of angles. Suggest a combination of prisms which will
(a) deviate a pencil of white light without much dispersion,
(b) disperse (and displace) a pencil of white light without much deviation.
Name the factors affecting the critical angle for the pair of media.
Draw diagram to illustrate the total internal reflection.
In the given figure PQ and PR are the two light rays emerging from an object P. The ray PQ is refracted as QS.
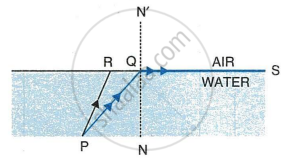
- State the special name given to the angle of incidence ∠PQN of the ray PQ.
- What is the angle of refraction for the refracted ray QS?
- Name the phenomenon that occurs if the angle of incidence ∠PQN is increased.
- The ray PR suffers partial reflection and refraction on the water-air surface. Give reason.
- Draw in the diagram the refracted ray for the incident ray PR and hence show the position of image of the object P by the letter P’ when seen vertically from above.
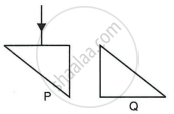
Two isosceles right-angle glass prisms P and Q are placed near each other as shown in Fig. Complete the path of the light ray entering the prism P till it emerges out of the prism Q.
Define critical angle for a given medium.
Plot a graph between
Sine of angle of incidence versus sine of angle of refraction,
If a light ray does not undergo, refraction at the boundary between two media, the angle of incidence is:
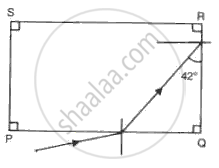
(a) A ray of monochromatic light enters glass PQRS as shown in the fig. Complete the path of ray till it emerges from the glass. (Critical angle of glass is 420).
(b) Draw diagram of a prism periscope.
(c) What are the advantages of total internal reflecting prism over plane mirror?
Name the principle on the basis of which optical fibres work.
State two advantages of using a right-angle prism as a reflector, rather than a plane mirror.
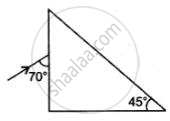
Complete the following diagram to show the path of the ray of a single colour in the diagram as if enters in and emerges out of the prism. Mark the angles wherever necessary. (Critical angle for glass = 42°).

Complete the following diagram to show the path of the ray of a single colour in the diagram as if enters in and emerges out of the prism. Mark the angles wherever necessary. (Critical angle for glass = 42°).
Choose the correct option.
Select the WRONG statement.
Which of the following is not involved in formation of a rainbow?
Answer the following question.
Explain ‘mirage’ as an illustration of refraction.
Solve Numerical example.
From the given data set, determine angular dispersion by the prism and dispersive power of its material for extreme colours. nR = 1.62 nV = 1.66, δR = 3.1°
Critical angle of light passing from glass to air is maximum for ____________.
For a ray of light, the critical angle is minimum when it travels from ______.
Optical fibre communication uses the principle of ______.
The angle of incidence at which the angle of refraction is Q£ is called the critical angle.
What are the conditions to achieve total internal reflection?
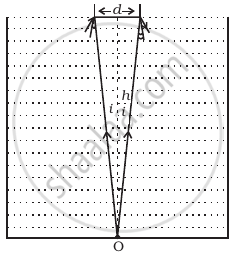
A jar of height h is filled with a transparent liquid of refractive index µ (Figure). At the centre of the jar on the bottom surface is a dot. Find the minimum diameter of a disc, such that when placed on the top surface symmetrically about the centre, the dot is invisible.
The angle made by incident ray of light with normal of the reflecting surface is called ______.
An endoscope uses optic fiber to transmit high resolution images of internal organs without loss of information. The principle of light that is used by the optic fiber is based on ______.
The diagram below shows a fish in the tank and its image seen in the surface of water.

Name the phenomenon responsible for the formation of this image.
State two differences between normal reflection and total internal reflection.
