Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Answer the following question.
Why is prism binoculars preferred over traditional binoculars? Describe its working in brief.
उत्तर
- Traditional binoculars use only two cylinders. Distance between the two cylinders can’t be greater than that between the two eyes. This creates a limitation of the field of view.
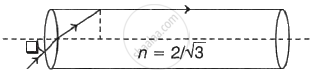
- A prism binocular has two right-angled glass prisms that apply the principle of total internal reflection.
- The incident light rays are reflected internally twice giving the viewer a wider field of view. For this reason, prism binoculars are preferred over traditional binoculars.
Working:

Prism binoculars
- The prism binoculars consist of 4 isosceles, right-angled prisms of a material having a critical angle less than 45°.
- The prism binoculars have a wider input range compared to traditional binoculars.
- The light rays incident on the prism binoculars, first get total internally reflected by the isosceles, right-angled prisms 1 and 4.
- These reflected rays undergo another total internal reflection by prisms 2 and 3 to form the final image.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Name the factors affecting the critical angle for the pair of media.
Which colour of light has a higher critical angle? Red light or green light.
A light ray does not bend at the boundary in passing from one medium to the other medium if the angle of incident is ______.
What is total internal reflection?
Draw diagram to illustrate the total internal reflection.
Total internal reflection occurs only when a ray of light passes from a ______ medium to a ______ medium.
Write the relation between the refractive index and critical angle for a given pair of optical media?
Calculate the speed of light in a medium whose critical angle is 30° ?
Prove the statement.
A rainbow is the combined effect of the refraction, dispersion, and total internal reflection of light.
If a light ray does not undergo, refraction at the boundary between two media, the angle of incidence is:
Express the refractive index μ of a medium in terms of the angle of incidence i in air and the angle of refraction r in a denser medium.
Name the factors affecting the critical angle for the pair of media.
What is meant by the term ‘critical angle’?
PQ and PR are two light rays emerging from the object as shown in the figure below:
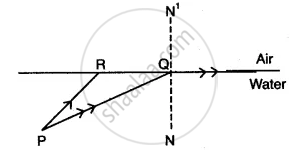
(i) What is the special name given to the angle of incidence (∠PQN) of ray PQ?
(ii) Copy the ray diagram and complete it to show the position of the image of the object P when seen obliquely from above.
(iii) Name the phenomenon that occurs if the angle of incidence ∠PQN is increased still further.
A ray of light is incident as a normal ray on the surface of separation of two different mediums. What is the value of the angle of incidence in this case?
Choose the correct option.
Angles of deviation for extreme colours are given for different prisms. Select the one having maximum dispersive power of its material.
The resultant `vec"R"` of `vec"P"` and `vec"Q"` is perpendicular to `vec"P"`. Also `|vec"P"|=|vec"R"|`. The angle between `vec"P"` and `vec"Q"` is ______.
[tan 45° = 1]
The twinkling effect of star light is due to ______.
The entire light is reflected back into the denser medium is called ______.
The outer concentric shell in optic fiber is called ______.
A bundle of glass threads, each of which is capable of transmitting messages using light waves is called ______.
The critical angle is defined as the angle of incidence at which the total internal reflection starts to occur.
The angle of incidence at which the angle of refraction is Q£ is called the critical angle.
Define the critical angle.
The angle made by incident ray of light with normal of the reflecting surface is called ______.
Find the value of θ in the given figure.