Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Solve Numerical example.
From the given data set, determine angular dispersion by the prism and dispersive power of its material for extreme colours. nR = 1.62 nV = 1.66, δR = 3.1°
Solution
Given: nR = 1.62, nV = 1.66, δR = 3.1°
To find: i. Angular dispersion (δVR)
ii. Dispersive power (ωVR)
Formula: i. δ = A (n − 1)
ii. δVR = δV − δR
iii. ω = `(δ_"V"-δ_"R")/(((δ_"V"+δ_"R")/2))`
Calculation: From formula (i),
δR = A(nR − 1)
∴ A = `δ_"R"/(("n"_"R"-1))=3.1/((1.62-1))=3.1/0.62`
∴ δV = A(nV − 1) = 5 × (1.66 − 1) = 3.3°
From formula (ii),
δVR = 3.3 − 3.1 = 0.2°
From formula (iii),
ωVR = `(3.3-3.1)/(((3.3+3.1)/2))=0.2/6.4xx2=0.2/3.2=1/16`
= 0.0625
- Angular dispersion by prism is 0.2°
- Dispersive power of material of prism is 0.0625.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Draw the diagram of a right-angled isosceles prism which is used to make an invented image erect
A light ray does not bend at the boundary in passing from one medium to the other medium if the angle of incident is ______.
Write the necessary conditions for the phenomenon of total internal reflection to
occur ?
Calculate the speed of light in a medium whose critical angle is 30° ?
If a light ray does not undergo, refraction at the boundary between two media, the angle of incidence is:
How does a ray of light bend when it travels from rarer to denser medium
If a ray of light passes from medium I to medium II without any change of direction, what can be said about the refractive indices of these media (angle I is not 0)?
What is meant by the term ‘critical angle’?
A ray of light is incident as a normal ray on the surface of separation of two different mediums. What is the value of the angle of incidence in this case?
Choose the correct option.
Angles of deviation for extreme colours are given for different prisms. Select the one having maximum dispersive power of its material.
Which of the following is not involved in formation of a rainbow?
Answer the following question.
Explain ‘mirage’ as an illustration of refraction.
The angle of minimum deviation produced by a thin glass prism in air is 'δ'. If that prism is immersed in water, the angle of minimum deviation will be ______.
( aμg = refractive index of glass w.r.t, air aμw = refractive index of water w.r.t. air)
Define the critical angle.
Write any two uses of total internal reflection.
A green light is incident from the water to the air-water interface at the critical angle (θ). Select the correct statement.
The phenomena involved in the reflection of radiowaves by ionosphere is similar to ______.
A jar of height h is filled with a transparent liquid of refractive index µ (Figure). At the centre of the jar on the bottom surface is a dot. Find the minimum diameter of a disc, such that when placed on the top surface symmetrically about the centre, the dot is invisible.
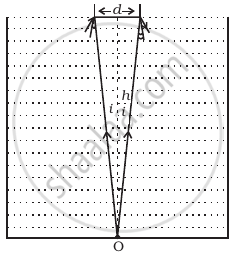
State the condition under which total internal reflection occurs. Give the mathematical expression for total internal reflection.
A given ray of light suffers minimum deviation in an equilateral prism P. Additional prism Q and R of identical shape and of the same material as P are now added as shown in the figure. The ray will now suffer ______.

Find the value of θ in the given figure.
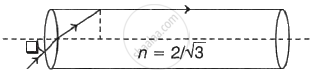
An endoscope uses optic fiber to transmit high resolution images of internal organs without loss of information. The principle of light that is used by the optic fiber is based on ______.
The diagram below shows a fish in the tank and its image seen in the surface of water.

Name the phenomenon responsible for the formation of this image.
