Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Solve Numerical example.
From the given data set, determine angular dispersion by the prism and dispersive power of its material for extreme colours. nR = 1.62 nV = 1.66, δR = 3.1°
उत्तर
Given: nR = 1.62, nV = 1.66, δR = 3.1°
To find: i. Angular dispersion (δVR)
ii. Dispersive power (ωVR)
Formula: i. δ = A (n − 1)
ii. δVR = δV − δR
iii. ω =
Calculation: From formula (i),
δR = A(nR − 1)
∴ A =
∴ δV = A(nV − 1) = 5 × (1.66 − 1) = 3.3°
From formula (ii),
δVR = 3.3 − 3.1 = 0.2°
From formula (iii),
ωVR =
= 0.0625
- Angular dispersion by prism is 0.2°
- Dispersive power of material of prism is 0.0625.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Which colour of light has a higher critical angle? Red light or green light.
What do you understand by the deviation produced by a prism? Why is it caused?
A light ray does not bend at the boundary in passing from one medium to the other medium if the angle of incident is ______.
Draw diagram to illustrate the total internal reflection.
In the given figure PQ and PR are the two light rays emerging from an object P. The ray PQ is refracted as QS.
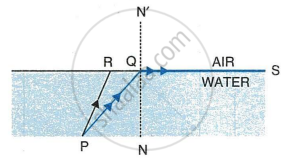
- State the special name given to the angle of incidence ∠PQN of the ray PQ.
- What is the angle of refraction for the refracted ray QS?
- Name the phenomenon that occurs if the angle of incidence ∠PQN is increased.
- The ray PR suffers partial reflection and refraction on the water-air surface. Give reason.
- Draw in the diagram the refracted ray for the incident ray PR and hence show the position of image of the object P by the letter P’ when seen vertically from above.
Define critical angle for a given medium.
Plot a graph between
Angle of incidence versus angle of reflection,
Plot a graph between
Sine of angle of incidence versus sine of angle of refraction,
In the following figure, show two rays A and B travelling from water to air. If the critical angle for water- air surface is 48°, complete the ray diagram showing the refracted rays for each. State conditions when the ray will suffer total internal reflection.

Name the principle on the basis of which optical fibres work.
Why do diamonds sparkle?
How are critical angles related to the refractive index of the medium?
Images formed by totally reflecting prisms are brighter than the image formed by ordinary reflected light, why?
What is meant by the statement, ‘the critical angle for diamond is 24°’?
Draw a diagram, properly labelled, to illustrate the use of a total reflecting prism (a right-angled isosceles prism) to turn a ray of light through 180°. Name an instrument in which this device is used.
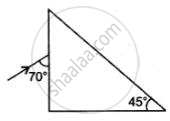
Complete the following diagram to show the path of the ray of a single colour in the diagram as if enters in and emerges out of the prism. Mark the angles wherever necessary. (Critical angle for glass = 42°).
A ray of light is incident as a normal ray on the surface of separation of two different mediums. What is the value of the angle of incidence in this case?
Answer the following question.
Define the critical angle of incidence and obtain an expression for it.
Answer the following question.
Describe the construction and working of an optical fibre.
Solve Numerical example.
A monochromatic ray of light is incident at 37° on an equilateral prism of refractive index 3/2. Determine angle of emergence and angle of deviation. If angle of prism is adjustable, what should its value be for emergent rays to be just possible for the same angle of incidence?
Which one of the following is NOT the correct formula for refractive index of glass w.r.t. air (aμg) (i = angle of incidence, r = angle of refraction)
For total internal reflection to take place, the angle of inddence i and the refractive index µ of the medium must satisfy the inequality ____________.
Optical fibre communication uses the principle of ______.
A bundle of glass threads, each of which is capable of transmitting messages using light waves is called ______.
What is a mirage? How does it occur?
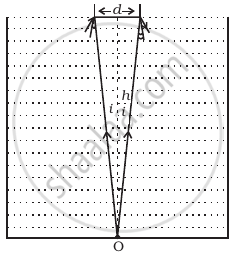
A jar of height h is filled with a transparent liquid of refractive index µ (Figure). At the centre of the jar on the bottom surface is a dot. Find the minimum diameter of a disc, such that when placed on the top surface symmetrically about the centre, the dot is invisible.
A ray of light passes from vacuum into a medium of refractive index µ, the angle of incidence is found to be twice the angle of refraction. Then the angle of incidence is ______.
State two differences between normal reflection and total internal reflection.
