Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Solve Numerical example.
A monochromatic ray of light is incident at 37° on an equilateral prism of refractive index 3/2. Determine angle of emergence and angle of deviation. If angle of prism is adjustable, what should its value be for emergent rays to be just possible for the same angle of incidence?
उत्तर
By Snell’s law, in case of prism,
n = `sin("i")/sin("r"_1)`
∴ `3/2=sin(37°)/sin("r"_1)`
∴ r1 = `sin^-1(0.6018/(3//2))`
= sin−1 (0.4012)
= 23°39’
For equilateral prism, A = 60°
Also, A= r1 + r2
∴ r2 = A − r1 = 60° – 23°39’ = 36°21’
Applying snell’s law on the second surface of prism,
`1/"n"=sin("r"_2)/sin("e")`
∴ `2/3=sin(36°21’)/sin("e")`
∴ e = `sin^-1((0.5927)/(2//3))`
= sin–1 (0.889)
= 62°44’
≈ 63
For any prism,
i + e = A + δ
∴ δ = (i + e) − A
= (37 + 63) − 60
= 40°
For an emergent ray to just emerge, the angle r2’ acts as a critical angle.
∴ r2’ = `sin^-1(1/"n")`
= `sin^-1(2/3)`
= 41’48°
As, A = r1 + r2 and i to be kept the same.
⇒ A’ = r1 + r2’ = 23°39’ + 41°48’
= 65°27’
- Angle of emergence and angle of deviation in first case are 63° and 40° respectively.
- For emergent ray to just emerge with same incident angle the angle of prism should have the value of 65°27’.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
You are given prisms made of crown glass and flint glass with a wide variety of angles. Suggest a combination of prisms which will
(a) deviate a pencil of white light without much dispersion,
(b) disperse (and displace) a pencil of white light without much deviation.
Name the factors affecting the critical angle for the pair of media.
Draw the diagram of a right-angled isosceles prism which is used to make an invented image erect
Name two factors which affect the critical angle for a given pair of media. State how do the factors affect it.
In the given figure PQ and PR are the two light rays emerging from an object P. The ray PQ is refracted as QS.
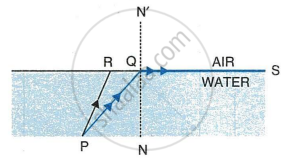
- State the special name given to the angle of incidence ∠PQN of the ray PQ.
- What is the angle of refraction for the refracted ray QS?
- Name the phenomenon that occurs if the angle of incidence ∠PQN is increased.
- The ray PR suffers partial reflection and refraction on the water-air surface. Give reason.
- Draw in the diagram the refracted ray for the incident ray PR and hence show the position of image of the object P by the letter P’ when seen vertically from above.
Two isosceles right-angle glass prisms P and Q are placed near each other as shown in Fig. Complete the path of the light ray entering the prism P till it emerges out of the prism Q.
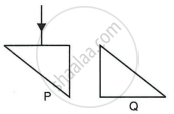
Write the necessary conditions for the phenomenon of total internal reflection to
occur ?
Write the relation between the refractive index and critical angle for a given pair of optical media?
(i) Define critical angle.
(ii) State one important factor which affects the critical angle of a given medium.
The diagram below shows a light source P embedded in a rectangular glass block ABCD of critical angle 42°. Complete the path of the ray PQ till it emerges out of the block. [Write necessary angles].
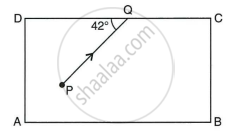
Plot a graph between
Angle of incidence versus angle of reflection,
In the following figure, show two rays A and B travelling from water to air. If the critical angle for water- air surface is 48°, complete the ray diagram showing the refracted rays for each. State conditions when the ray will suffer total internal reflection.

How does a ray of light bend when it travels from rarer to denser medium
How does a ray of light bend when it travels from when it is normal to the interface of the two media.
Write down the relationship between the critical angle and the refractive index of the medium.
How is the critical angle of a material related to its refractive index?
A ray of light is incident on a glass surface at an angle of 50° with the corresponding angle of refraction 30°. Find the value of the R.I. of glass.
A ray of light is incident as a normal ray on the surface of separation of two different mediums. What is the value of the angle of incidence in this case?
Answer the following question.
Explain ‘mirage’ as an illustration of refraction.
For the same angle of incidence, the angle of refraction in four media A, B, C and D are 25°, 30°, 35° and 40° respectively. The speed of light is least in medium ______.
The outer concentric shell in optic fiber is called ______.
Write any two uses of total internal reflection.
A green light is incident from the water to the air-water interface at the critical angle (θ). Select the correct statement.
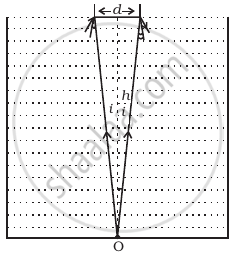
A jar of height h is filled with a transparent liquid of refractive index µ (Figure). At the centre of the jar on the bottom surface is a dot. Find the minimum diameter of a disc, such that when placed on the top surface symmetrically about the centre, the dot is invisible.
Observe the given figure of the raindrop and answer the following questions:
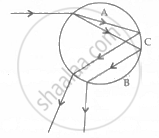
- Label A and B of the given diagram. Why colour will deviate most.
- Name the phenomenon shown in label C.
Which of the following is used in optical fibres?
An endoscope uses optic fiber to transmit high resolution images of internal organs without loss of information. The principle of light that is used by the optic fiber is based on ______.
The diagram below shows a fish in the tank and its image seen in the surface of water.

Name the phenomenon responsible for the formation of this image.
