Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Solve Numerical example.
A monochromatic ray of light is incident at 37° on an equilateral prism of refractive index 3/2. Determine angle of emergence and angle of deviation. If angle of prism is adjustable, what should its value be for emergent rays to be just possible for the same angle of incidence?
Solution
By Snell’s law, in case of prism,
n = `sin("i")/sin("r"_1)`
∴ `3/2=sin(37°)/sin("r"_1)`
∴ r1 = `sin^-1(0.6018/(3//2))`
= sin−1 (0.4012)
= 23°39’
For equilateral prism, A = 60°
Also, A= r1 + r2
∴ r2 = A − r1 = 60° – 23°39’ = 36°21’
Applying snell’s law on the second surface of prism,
`1/"n"=sin("r"_2)/sin("e")`
∴ `2/3=sin(36°21’)/sin("e")`
∴ e = `sin^-1((0.5927)/(2//3))`
= sin–1 (0.889)
= 62°44’
≈ 63
For any prism,
i + e = A + δ
∴ δ = (i + e) − A
= (37 + 63) − 60
= 40°
For an emergent ray to just emerge, the angle r2’ acts as a critical angle.
∴ r2’ = `sin^-1(1/"n")`
= `sin^-1(2/3)`
= 41’48°
As, A = r1 + r2 and i to be kept the same.
⇒ A’ = r1 + r2’ = 23°39’ + 41°48’
= 65°27’
- Angle of emergence and angle of deviation in first case are 63° and 40° respectively.
- For emergent ray to just emerge with same incident angle the angle of prism should have the value of 65°27’.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Name the factors affecting the critical angle for the pair of media.
The figure shows a ray of light falling normally on the face AB of an equilateral glass prism having refractive index`3/2`, placed in water of refractive index `4/3`.Will this ray suffer total internal reflection on striking the face AC? Justify your answer.
What do you understand by the deviation produced by a prism? Why is it caused?
State two conditions necessary for total internal reflection to occur.
Draw diagram to illustrate the total internal reflection.
Total internal reflection occurs only when a ray of light passes from a ______ medium to a ______ medium.
Prove the statement.
A rainbow is the combined effect of the refraction, dispersion, and total internal reflection of light.
Swarali has got the following observations while doing an experiment. Answer her questions with the help of observations.
Swarali observed that the light bent away from the normal, while travelling from dense medium to rarer medium. When Swarali increased the values of angle of incidence (i), the values of angle of refraction (r) went on increasing. But at a certain angle of incidence, the light rays returned into the dense medium.
So, Swarali has some questions. Answer them –
a) Name this certain value of ‘i ’. What is the value of ‘r’ at that time ?
b) Name this process of returning of light in dense medium. Explain the process.
i) Observe the given figure and answer the following questions.
a) Identify and write the natural process shown in the figure.
b) List the phenomena which are observe in this process.
c) Redraw the diagram and show above phenomena in it.
Plot a graph between
Angle of incidence versus angle of refraction.
Name the principle on the basis of which optical fibres work.
Write down the relationship between the critical angle and the refractive index of the medium.
Images formed by totally reflecting prisms are brighter than the image formed by ordinary reflected light, why?
Draw a diagram, properly labelled, to illustrate the use of a total reflecting prism (a right-angled isosceles prism) to turn a ray of light through 180°. Name an instrument in which this device is used.
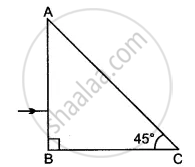
A ray of light passes through a right-angled prism as shown in the figure. State the angles of incidence at the faces AC and BC.
PQ and PR are two light rays emerging from the object as shown in the figure below:
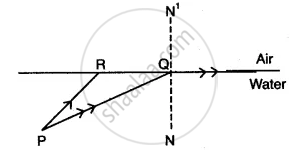
(i) What is the special name given to the angle of incidence (∠PQN) of ray PQ?
(ii) Copy the ray diagram and complete it to show the position of the image of the object P when seen obliquely from above.
(iii) Name the phenomenon that occurs if the angle of incidence ∠PQN is increased still further.
Choose the correct option.
Consider the following phenomena/ applications: P) Mirage, Q) rainbow, R) Optical fibre and S) glittering of a diamond. Total internal reflection is involved in
Choose the correct option.
Select the WRONG statement.
Choose the correct option.
Angles of deviation for extreme colours are given for different prisms. Select the one having maximum dispersive power of its material.
The resultant `vec"R"` of `vec"P"` and `vec"Q"` is perpendicular to `vec"P"`. Also `|vec"P"|=|vec"R"|`. The angle between `vec"P"` and `vec"Q"` is ______.
[tan 45° = 1]
For a ray of light, the critical angle is minimum when it travels from ______.
The entire light is reflected back into the denser medium is called ______.
Define the critical angle.
What are the conditions to achieve total internal reflection?
A ray of light passes through a prism of refractive index `sqrt2` as shown in the figure. Find:
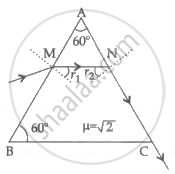
- The angle of incidence (∠r2) at face AC.
- The angle of minimum deviation for this prism.
A ray of light passes from vacuum into a medium of refractive index µ, the angle of incidence is found to be twice the angle of refraction. Then the angle of incidence is ______.
