Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
PQ and PR are two light rays emerging from the object as shown in the figure below:
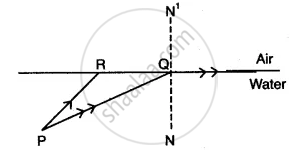
(i) What is the special name given to the angle of incidence (∠PQN) of ray PQ?
(ii) Copy the ray diagram and complete it to show the position of the image of the object P when seen obliquely from above.
(iii) Name the phenomenon that occurs if the angle of incidence ∠PQN is increased still further.
Solution
(i) Critical angle
(ii)
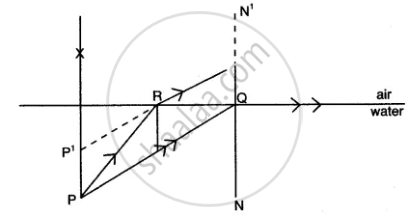
(iii) Total internal reflection of light.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
You are given prisms made of crown glass and flint glass with a wide variety of angles. Suggest a combination of prisms which will
(a) deviate a pencil of white light without much dispersion,
(b) disperse (and displace) a pencil of white light without much deviation.
State the conditions required for total internal reflection of light to take place
Write the relation between the refractive index and critical angle for a given pair of optical media?
State one factor on which a critical angle for a given pair of media depends. The critical angle for the glass-air interface is 45° for the yellow light. Will it be equal to, less than or greater than 45° for (i) red light, (ii) blue light?
Choose the correct option.
Consider the following phenomena/ applications: P) Mirage, Q) rainbow, R) Optical fibre and S) glittering of a diamond. Total internal reflection is involved in
A green light is incident from the water to the air-water interface at the critical angle `(theta)`. Select the correct statement
Total internal reflection can take place only if light is travelling from ______.
What are the examples of total internal reflection in nature?
Small air bubbles rising up a fish tank appear silvery when viewed from some particular angle is due to the ______.
