Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Solution
Factors affecting the critical angle are:
(i) The colour (or wavelength) of light.
(ii) The temperature (on changing the temperature of medium, its refractive index changes).
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
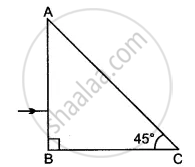
A ray of light passes through a right-angled prism as shown in the figure. State the angles of incidence at the faces AC and BC.
PQ and PR are two light rays emerging from the object as shown in the figure below:
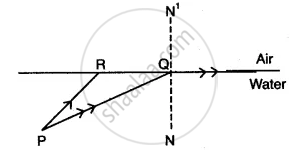
(i) What is the special name given to the angle of incidence (∠PQN) of ray PQ?
(ii) Copy the ray diagram and complete it to show the position of the image of the object P when seen obliquely from above.
(iii) Name the phenomenon that occurs if the angle of incidence ∠PQN is increased still further.
A spherical marble, of refractive index 1.5 and curvature 1.5 cm, contains a tiny air bubble at its centre. Where will it appear when seen from outside?
Choose the correct option.
Select the WRONG statement.
Answer the following question.
Define the critical angle of incidence and obtain an expression for it.
Answer the following question.
What are the advantages of optical fibre communication over electronic communication?
A green light is incident from the water to the air-water interface at the critical angle (θ). Select the correct statement.
A rectangular block of glass ABCD has a refractive index 1.6. A pin is placed midway on the face AB (Figure). When observed from the face AD, the pin shall ______.
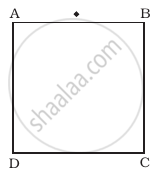
- appear to be near A.
- appear to be near D.
- appear to be at the centre of AD.
- not be seen at all.
Name any two phenomena which take place in the formation of a rainbow.
