Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
![Frank solutions for Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 2 - Light Frank solutions for Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 2 - Light - Shaalaa.com](/images/physics-part-2-english-class-10-icse_6:39af211da77c495e91d1cf4305988990.PNG)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 2: Light
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 2 of CISCE Frank for Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE.
Frank solutions for Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE 2 Light Exercise 2.1 i [Page 88]
State Snell'S Law.
-
- the angle of refraction and
- the angle of deviation for the ray?
Plot a graph between
Angle of incidence versus angle of reflection,
Plot a graph between
Sine of angle of incidence versus sine of angle of refraction,
Plot a graph between
Angle of incidence versus angle of refraction.
The refractive index of water respect to air is `4/3`. calculate the refractive index of air with respect to water.
Define the term refractive index of a medium. What do you understand by the statement 'the refractive index of glass is 1.5 for white light'?
Define the term angle of deviation.
If a light ray does not undergo, refraction at the boundary between two media, the angle of incidence is:
0°
45°
60°
90°
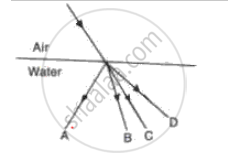
A ray of light passes from air to water. In fig. 39, which of the ray A, B, C and D is the correct refracted ray?
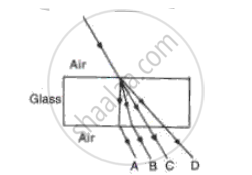
In the fig. name the ray which represents the correct path of light while passing through a glass block.
Which of the following has the highest refractive index:
Glass
Water
Diamond
Ruby
Frank solutions for Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE 2 Light Exercise 2.1 ii [Page 89]
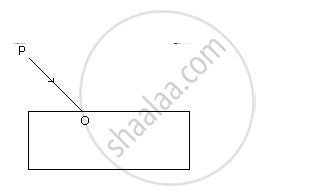
In the fig., PO is a ray of light incident on a rectangular glass block.
(a) Complete the path of the ray through the block.
(b) In the diagram, mark the angle of incidence (i) and the angle of refraction (r) at the first interface. How is the refractive index of glass related to the angles I and r?
(c) Mark angle of emergence by the letter e. How are the angles i and e related?
(d) Which two rays are parallel to each other? Name them.
(e) Indicate in the diagram the lateral displacement between the emergent ray and the incident ray.
- red light,
- blue light?
Fill in the blank to complete the following sentence:
When light travels from a rarer to a denser medium, it bends ...........
Draw an í- `delta` graph for a mono chromatic raY through a glass prism of a plane and mark
(i) `delta` m, the angle of mínimum devíation
(íí) Any two values of i for which value of `delta` ís same.
Frank solutions for Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE 2 Light Exercise 2.2 i [Page 101]
Draw neat diagram to show the
Convergent action of a convex lens,
Draw neat diagram to show the
Divergent action of concave lens
Define the term principal axis of a lens.
Frank solutions for Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE 2 Light Exercise 2.2 ii [Page 102]
State the condition of the following:
A lens has both its focal lengths equal.
State the condition of the following:
A ray passes undeviated through the lens.
Fig shows a lens as a combination of a glass block and two prisms.
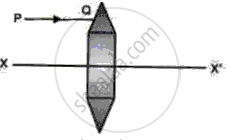
(i) Name the lens formed by the combination.
(ii) what is the XX' called?
(iii) Complete the ray diagram and show the path of the incident ray PQ after passing through the lens.
(iv) The final emergent ray will either meet XX' at a point or appear to come from a point on XX'. what is the point called?
Fig shows a lens as a combination of a glass block and two prisms.
(i) Name the lens formed by the combination.
(ii) What is the line XX' called?
(iii) Complete the path of the incident ray PQ after passing through the lens.
(iv) The final emergent ray either meets XX' at a point or appears to come from a point on XX'. Label it as F, What is this point called?
Fig shows an object PQ placed on the principle axis of a lens L. The two foci of the kens are F1 and f2. The image formed by the lens is erect, Virtual and dimnished.
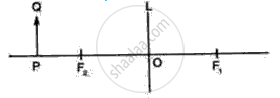
(i) Draw the outline ofthe lens L used and Named it.
(ii) Draw a ray of light starting from Q and passing through O. show the same ray after refraction by the lens.
(iii) Draw another ray from Q Which is incident parallel to the principle axis and show how it emerges after refraction from the lens.
(iv) Locate the final image formed.
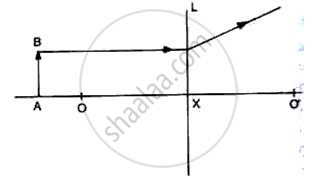
Refer to fig
(i) Name the lens L.
(ii) What are the points O, O' called?
(iii) Complete the diagram to form the image of the object AB.
(iv) Write three characteristics of the image.
Frank solutions for Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE 2 Light Exercise 2.2 iii [Page 103]
Express power of a concave lens of focal length 50 cm with its sign.
Frank solutions for Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE 2 Light Exercise 2.2 iv [Page 110]
Frank solutions for Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE 2 Light Exercise 2.3 i [Page 109]
Name the radiations of wavelength
(i) Longer than 8 x 10 -7 m
(ii) shorter than 4 x 10 -7 m.
Fig shows a thin beam of white light from a source S striking on one face of a prism.
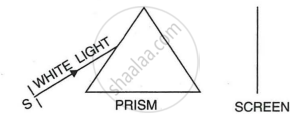
- Complete the diagram to show the effect of the prism on the beam and to show what is seen on the screen.
- If a slit is placed in between the prism and the screen to pass only the light of green colour, what will you then observe on the screen?
- What conclusion do you draw from the observation in part (b) above?
If a monochromatic beam of light undergoes minimum deviation through an equiangular prism, how does the beam pass through the prism, with respect to its base?
If white light is used in same way what change is expected in the emergent beam?
Frank solutions for Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE 2 Light Exercise 2.3 ii [Page 110]
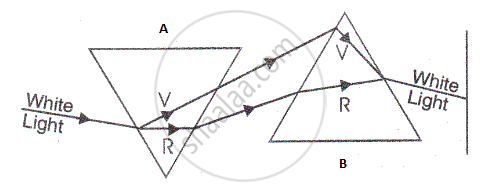
Draw a diagram to show the splitting of white light into its constituent colours.
Draw another diagram to show how the colours of spectrum of white light can be combined to give the effect of white light.
Complete the ray diagram given below to show the nature of light produced on the screen.
The completed ray diagram is as shown below:
Name the scientist who discovered
X-rays
Name the scientist who discovered Visible light
Name the scientist who discovered Microwaves
Name the scientist who discovered radio waves
Name the scientist who discovered Infra-red waves
Name the scientist who discovered Ultraviolet rays
Frank solutions for Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE 2 Light Exercise 2.3 iii [Page 145]
Frank solutions for Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE 2 Light Exercise 1 [Page 112]
Make the correct choices in the following items :
A magnified erect image is obtained when an object is positioned in front of a converging lens. The distance of the object from the lens would be
Greater than three focal lengths
Equal to two focal lengths
Between one and two focal lengtghs
equal to one focal length
Less than one focal length
Make the rrect choices in the following items :
An object is placed 50 cm from a connverging lens of focal length 30 cm. The image produced would be
lnverted and same size as the obíect
lnverted and diminished
lnverted and magnified
Erect and diminished
Erect and magnified
Make the rrect choices in the following items :
ln fig, , a real image of a point objert O is formed, Which of the following statements is true about each of the arrangements?
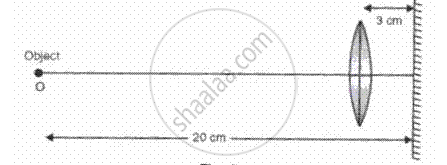
(i) The object is at the principle focus of the lens
(ii) The focal length of the lens is 17 cm
(iii) lf the mirror is moved so that it is 6 cm from the lens image will also move
Make the correct choices in the following items :
A lens used as a magnifying glass
(i) ls a diverging lens
(ii) Produces a virtual image
(iii) ls placed with the object nearer the lens than the principle focus
Make the correct choices in the following items:
lf the image can be focused on a screen it must be
errect
virtual
real
upright
coloured
Make the correct choices in the following items :
The image formed by a diverging lens, shown in fig, , is
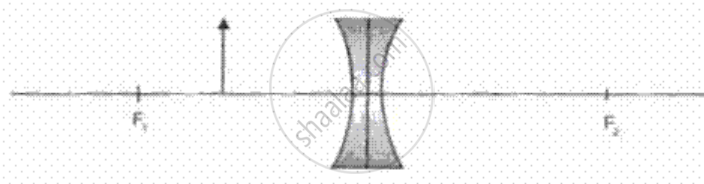
Virtual, erect, magnified
Virtual, erect, diminished
Virtual, inverted, magnified
Real, inverted, diminished
Real, upright, magnified
Make the correct choices in the following items :
A converging lens B has the same focal length as a converging lens A, but only half the diameter, Both lens are used, separately, to form two images of building on a screen. which one of the follwing statements about the images is correct?
The image B formed is closer to the lens than the image formed by A.
The image B formed is bigger than the image formed by A.
The image B formed is not as sharply focused as the image formed by A
The image are of the same brightness
Both the image are real and inverted
Frank solutions for Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE 2 Light Exercise 2 [Page 113]
A pin 2 cm long is placed 12 cm away from a convex lens at right angles to the principal axis. If the focal length of the lens is 20 cm, by scale drawing find the size of the image and its magnification.
Define the term 'focus' of a lens.
Distinguish between concave and convex lens.
(a) Draw a sketch to show how a lens is able to produce an image of the sun on a paper screen.
(b)(i) Would you regard the rays from the sun as being divergent, parallel or convergent?
(ii) What is the name given to the point where such rays meet after they have passed through the lens?
(iii) How does the image of the sun sometimes burn a paper screen?
(a) What type of a lens can be used as a magnifying glass?
(b) Show by a ray diagram the formation of a real image by simple magnifying lens.
Frank solutions for Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE 2 Light Exercise 3 [Page 114]
Ray diagram for the formation of image by a magnifying glass.
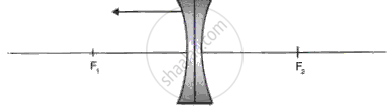
What is meant by the power of accommodation produced?
How is accommodation produced?
What type of lenses are used in spectacles worn by an old lady for knitting?
An object AB is placed in front of a convex lens as shown in fig. 4. Complete the ray diagram and obtain the image formed and state the nature of the image.

An object is placed in front of a converging lens and in front of a diverging lens as in fig.
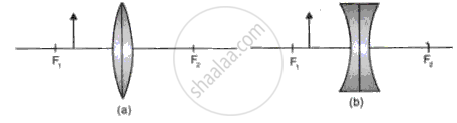
(a)Complete the ray diagram to obtain an image.
(b)Compare the nature of image formed by both the lenses in the above case.
In the following diagram ., the object and the image formed by the respective lenses are shown. Complete the ray diagram, and locate the focus. Find the focal length of the lens.

In the following diagram the object and the image formed by the respective lenses are shown. Complete the ray diagram, and locate the focus. Find the focal length of the lens.
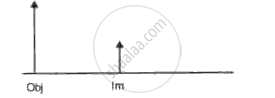
In the following diagram , the object and the image formed by the respective lenses are shown. Complete the ray diagram, and locate the focus. Find the focal length of the lens.
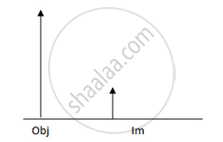
In the following diagram , the object and the image formed by the respective lenses are shown. Complete the ray diagram, and locate the focus. Find the focal length of the lens.

Frank solutions for Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE 2 Light Exercise 4 [Page 115]
| Gamma rays | D | C | Visible light | B | A |
The above table shows different parts of the electromagnetic spectrum.
(a) Identify the parts of the spectrum marked as A, B, C and D.
(b) Which of the radiations A or B has the higher frequency?
(c) State two properties which are common to all parts of the electromagnetic spectrum.
(d) Name one source of each of the radiation of electromagnetic spectrum.
(e) Name one detector for each of the radiation.
(f) Name one use of each of the radiation.
Make the correct choice for each of the following:
Which one of the following Fig correctly shows the path of the ray through the glass block?
Make the correct choices for each of the following :
Total Internal reflection takes place when
(where ∠i = angle of incidence, ∠r = angle of refraction, ∠C = critical angle)
Light is going from glass to air and ∠I < ∠C
Light is going from air to glss and ∠i < ∠C
Light is going from glass to air and ∠i > ∠C
Light is going from air to glss and ∠i > ∠C
Light is going from glass to air and ∠i = ∠r
Make the correct for each of the following :
With reference to the fig, the refractive index of the glass block is
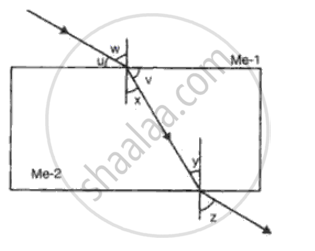
`"sin w"/"sin z"`
`"sin x"/"sin w"`
`"sin u"/"sin v"`
`"sin u"/"sin x"`
`"sin w"/"sin x"`
Make the correct choice for each of the following:
fig illustrates an experiment to determine the refractive index of glass. Which one of the following graphs would give a straight line through the origin?
∠i plotted against ∠r.
Sin i plotted against ∠r.
∠i plotted against sin D
Sin i plotted against Sin r
`1/(∠"i") " plotted against" 1/(∠"r")`
Make the correct choice for each of the following :
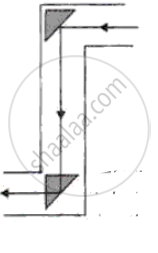
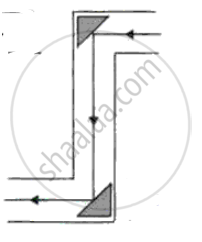
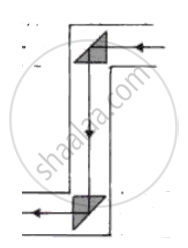
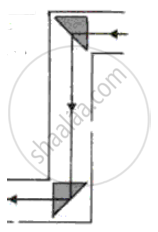
Which one of the five diagrams represents the path of a ray of light through a periscope?
Frank solutions for Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE 2 Light Exercise 5 [Page 116]
Fig. shows two rays of light Op and OQ coming from an object at the bottom of a pond, incident on the water surface.
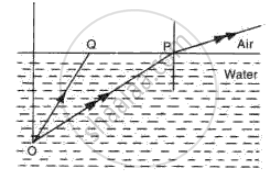
(a) Mark on the diagram
(i) The angle of incidence of ray OP,
(ii) The angle of refraction of ray Op,
(iii) The position of image of the object as seen from above.
(iv) An approximate path of the ray OQ.
(b) Explain, why do the rays of light change directions on passing from water to air.
(c) A fish in water sees everything outside the water by rays of light entering its eye in a small cone of light. Draw a diagram and explain how does this happen.
(a)A ray of light is incident at 45° on the face of
(i) A rectangular block of glass.
(ii) A 600 glass prism.
(b) Draw a sketch showing how the ray of monochromatic ray of light passes through glass in each case.
(c) With the aid of a diagram, explain how the face of a right angled prism may totally reflect incident on it.
(d) A thick plane mirror produces several faint images in addition to a prominent one. Draw a ray diagram showing how reflection and refraction produce all these images.
(e) Fig. represents a stone S at the bottom of a pond of water. Using the two rays, as shown, complete the ray diagram to show where the image of the stone appears when viewed from E.

(f) What is a''mirage'? Explain with the help of a diagram.
(g) A man observes the bottom of a swimming pool of 3 m depth. If the refractive index of water is 1.3, what is the apparent depth of water?
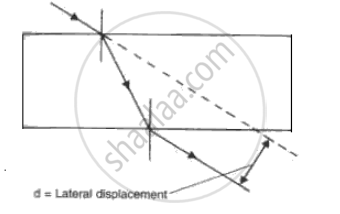
(h) When a ray of light undergoes refraction through a glass slab and when it emerges it is displaced laterally (Fig). What are the factors on which the lateral displacement depends?
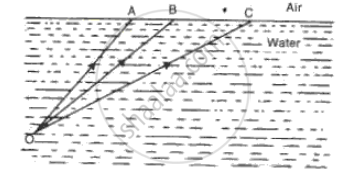
(i) Fig. shows three rays of light OA, OB and OC passing from water to air, making angles 490, 410 and 350 with the horizontal surface respectively. Draw an approximate path of the emergent ray for each. (Critical angle of water is 490.)
Frank solutions for Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE 2 Light Exercise 6 [Page 117]
(a) A ray of monochromatic light enters glass PQRS as shown in the fig. Complete the path of ray till it emerges from the glass. (Critical angle of glass is 420).
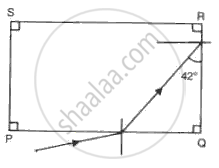
(b) Draw diagram of a prism periscope.
(c) What are the advantages of total internal reflecting prism over plane mirror?
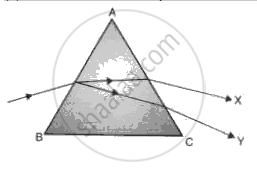
Fig. shows a ray of white light that passes through a prism and produces a spectrum.
(a) Name the phenomenon that is taking place.
(b) What colour would you see at X and Y?
(c) What radiation would you detect above X and below Y?
Frank solutions for Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE 2 Light Exercise 7 [Page 118]
Two waves A and B have wavelength 0.01 Å and 9000 Å respectively.
Name the two waves. compare the speeds of these waves when they travel in vacuum.
Frank solutions for Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE 2 Light Exercise 8 [Page 119]
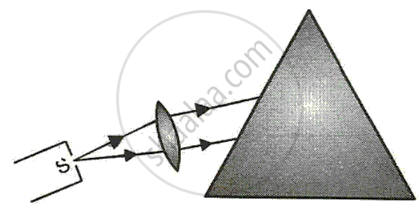
Fig shows part of the arrangement for obtaining pure spectrum.
(a) Complete thediagram and show how to obtain a pure spectrum.
(b) What are the conditions necessary for obtaining a pure spectrum?
-
- Calculate the speed of the wave.
- Name the medium through which it is traveling.
Solutions for 2: Light
![Frank solutions for Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 2 - Light Frank solutions for Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 2 - Light - Shaalaa.com](/images/physics-part-2-english-class-10-icse_6:39af211da77c495e91d1cf4305988990.PNG)
Frank solutions for Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 2 - Light
Shaalaa.com has the CISCE Mathematics Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Frank solutions for Mathematics Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE 2 (Light) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Frank textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 2 Light are Introduction to Refraction of Light, Speed of Light, Relationship Between Refractive Index and Speed of Light (µ = C/V), Refraction of Light Through a Rectangular Glass Slab, Prism, Principle of Reversibility of the Path of Light, Experimental Verification of Law of Refraction and Determination of Refractive Index of Glass, Critical Angle, Relationship Between the Critical Angle and the Refractive Index (µ = 1/ Sin C), Total Internal Reflection in a Prism, Some Consequences of Refraction of Light, Use of a Total Internal Reflecting Prism in Place of a Plane Mirror, Consequences of Total Internal Refraction, Multiple Images in a Thick Plane Glass Plate Or Thick Mirror, Refraction of Light Through a Prism, Real and Apparent Depth, Apparent Bending of a Stick Under Water, Transmission of Light from a Denser Medium (Glass Or Water) to a Rarer Medium (Air) at Different Angles of Incidence, Total Internal Reflection, Deviation Produced by a Triangular Prism, Dispersion of Light Through Prism and Formation of Spectrum, Electromagnetic Spectrum, Colour in White Light with Their Wavelength and Frequency Range, Different Radiation of Electromagnetic Spectrum, Gamma Rays, X rays, Visible Light, Micro Waves, Radio Waves, Scattering of Light and Its Types, Applications of Scattering of Light, Ultraviolet Radiations, Infrared Radiations, Magnification Due to Spherical Lenses, Concept of Lenses, Action of a Lens as a Set of Prisms, Spherical Lens, Refraction of Light Through the Equiconvex Lens and Equiconcave Lens, Guideline for Image Formation Due to Refraction Through a Convex and Concave Lens, Formation of Image by Reflection: Real and Virtual Image, Images Formed by Sperical Lenses, Concave Lens, Images Formed by Concave Lenses, Convex Lens, Images Formed by Convex Lenses, Differentiation Between Concave and Convex Lens, Sign Convention, Lens Formula, Power of a Lens, Magnifying Glass Or Simple Microscope, Experimental Determination of Focal Length of Convex Lens.
Using Frank Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE solutions Light exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Frank Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CISCE Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE students prefer Frank Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 2, Light Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE additional questions for Mathematics Physics - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.