Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Solution
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
In the adjacent diagram, AO is a ray of light incident on a rectangular glass slab.
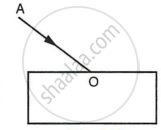
- Complete the path of the ray till it emerges out of the slab.
- In the diagram, mark the angle of incidence (i) and the angle of refraction (r) at the first interface. How is the refractive index of glass related to the angles i and r?
- Mark angles of emergence by the letter e. How are the angles i and e related?
- Which two rays are parallel to each other? Name them.
- Indicate in the diagram the lateral displacement between the emergent ray and the incident ray. State one factor that affects the lateral displacement.
The highest refractive index is of ______.
An object is viewed through a glass prism with its vertex pointing upwards. It appears to be displaced upward. Explain the reason.
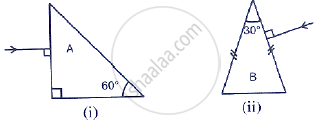
Fig 4.31 below shows a light ray of single colour incident normally on two prisms A and B. In each case draw the path of the ray of light as it enters and emerges out of the prism. Mark the angle wherever necessary.
A ray of light falls normally on the surface of a transparent glass slab. Draw a ray diagram to show its path and also mark angle of incidence and angle of emergence.
What is the correct reason for blinking / flickering of stars? Explain it.
a) The blasts in the stars.
b) Absorption of star light by the atmosphere.
c) Motion of the stars.
d) Changing refractive index of gases in the atmosphere.
A ray of light passes from water to air. How does the speed of light change?
Draw ray of light bending towards the normal while passing from glass to water. Label your diagrams.
How does the angle of deviation produced by a prism depend on the angle of incidence of light at the prism surface? Draw a graph to illustrate your answer.
Trace a ray of light incident at 30° on a surface if travelling from glass to air. What is the angle of refraction in this case? (R.I. for glass = 3/2).
