Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Trace a ray of light incident at 30° on a surface if travelling from glass to air. What is the angle of refraction in this case? (R.I. for glass = 3/2).
Solution

For a ray of light from glass to air R.I. is denoted as gμa.
`""_"g"mu_"a"=1/(""_"a"mu_"g")`
∴ `sin"i"/sin"r′"=1/(""_"a"mu_"g")`
sin r′ = aμg × sin i
and aμg = `3/2`
∴ sin r′ = `3/2xx1/2`
= `3/4`
= 0.7500
∴ r′ = 48°36′
Angle of refraction for glass to air = 48°36′.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Explain how the formation of a rainbow occurs.
A student traces the path of a ray of light passing through a rectangular glass slab and marks the angle of incidence i, angle of refraction r and angle of emergence e, as shown.
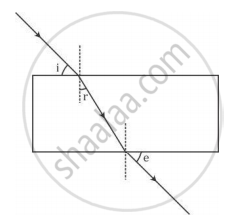
The correctly marked angle(s) is/are
(A) ∠ i only
(B) ∠ e only
(C) ∠ r only
(D) ∠ i and ∠ e
After tracing the path of a ray of light passing through a rectangular glass slab for four different values of the angle of incidence, a student reported his observations in tabular form as given below:
| S.No | ∠ i | ∠ r | ∠ e |
| I | 30° | 19° | 29° |
| II | 40° | 28° | 40° |
| III | 50° | 36° | 50° |
| IV | 60° | 40° | 59° |
The best observation is
(A) I
(B) II
(C) III
(D) IV
Which of the above wavelengths has a higher frequency?
Observe the following figure and answer the questions given under it:
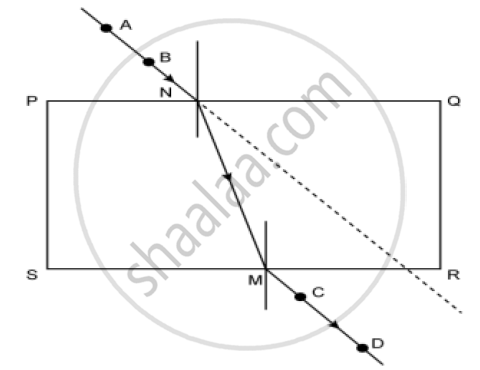
1) How many times does refraction take place in the above figure?
2) What happens to the ray of light when it passes from air to glass?
3) What happens to the ray of light when it passes from glass to air?
4) What are the rays AB and CD in the figure called?
5) Define refraction.
When a ray of light from air enters a denser medium, it ______.
Select from the following the best experimental set-up for tracing the path of a ray of light through a glass slab: (A) I
(A) I
(B) II
(C) III
(D) IV
A student has traced the path of a ray of light through a glass slab as follows. If you are asked to label 1, 2, 3 and 4, the correct sequencing of labeling ∠i, ∠e, ∠r and lateral displacement respectively is
(a) 2, 1, 3, 4
(b) 1, 2, 3, 4
(c) 1, 3, 2, 4
(d) 1, 3, 4, 2
Write a relation between the angle of incidence (i), angle of emergence (e), angle of the prism (A), and angle of deviation (d) for a ray of light passing through an equilateral prism.
In the diagram below, PQ is a ray of light incident on a rectangular glass block.
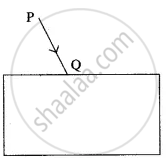
Copy the diagram and complete the path of the ray of light through the glass block. In your diagram, mark the angle of incidence by letter ‘i’ and the angle of emergence by the letter ‘e’.
