Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Trace a ray of light incident at 30° on a surface if travelling from glass to air. What is the angle of refraction in this case? (R.I. for glass = 3/2).
उत्तर

For a ray of light from glass to air R.I. is denoted as gμa.
`""_"g"mu_"a"=1/(""_"a"mu_"g")`
∴ `sin"i"/sin"r′"=1/(""_"a"mu_"g")`
sin r′ = aμg × sin i
and aμg = `3/2`
∴ sin r′ = `3/2xx1/2`
= `3/4`
= 0.7500
∴ r′ = 48°36′
Angle of refraction for glass to air = 48°36′.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
When a ray of light travels from air to glass slab and strikes the surface of separation at 90°, then it …………….
(a) bends towards normal
(b) bends away from normal
(c) passes unbent
(d) passes in zigzag way
A student traces the path of a ray of light passing through a rectangular glass slab and marks the angle of incidence i, angle of refraction r and angle of emergence e, as shown.
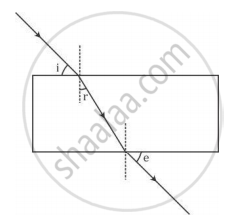
The correctly marked angle(s) is/are
(A) ∠ i only
(B) ∠ e only
(C) ∠ r only
(D) ∠ i and ∠ e
Draw a ray diagram to show the refraction of light through a glass slab and mark angle of refraction and the lateral shift suffered by the ray of light while passing through the slab.
Study the following four experimental set-ups I, II, III and IV for the experiment, "To trace the path of a ray of light through a rectangular glass slab."
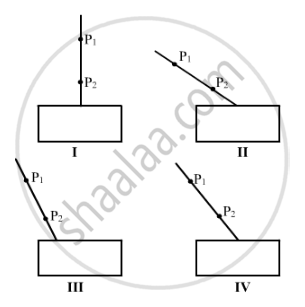
Which of the marked set-ups is likely to give best results (P1 and P2 are the positions of pins fixed on the incident ray)?
(A) I
(B) II
(C) III
(D) IV
A ray of light passes from water to air. How does the speed of light change?
“A ray of light incident on a rectangular glass slab immersed in any medium emerges parallel to itself.” Draw labelled ray diagram to justify the statement.
After tracing the path of rays of light through a glass slab for three different angles of incidence, a student measured the corresponding values angle of refraction r and angle of emergence e and recorded them in the table given below:
|
S. No. |
∠i |
∠i |
∠e |
|
I |
30° |
20° |
31° |
|
II |
40° |
25° |
40° |
|
III |
50° |
31° |
49° |
The correct observations are:
(A) I and II
(B) II and III
(C) I and III
(D) I, II and III
A ray of light falls normally on the surface of a transparent glass slab. Draw a ray diagram to show its path and also mark angle of incidence and angle of emergence.
-
- the angle of refraction and
- the angle of deviation for the ray?
The diagram shows the path of a ray of light through a rectangular glass block placed in a liquid of uniform density.

What should be the rate of the speed of light through the liquid to the speed through the glass so that there is no refraction of light at the boundaries of the glass block when the system is illuminated by the light of one colour?
