Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
When a ray of light travels from air to glass slab and strikes the surface of separation at 90°, then it …………….
(a) bends towards normal
(b) bends away from normal
(c) passes unbent
(d) passes in zigzag way
उत्तर
(c) passes unbent
In this case, the angle of incidence (i) is zero and so also the angle of refraction.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
When rays of light are incident on a glass slab then the incident ray and emergent ray are _________ each other.
- perpendicular
- parallel
- opposite
- concurrent
A student traces the path of a ray of light through a rectangular glass slab for the different values of angle of incidence. He observes all possible precautions at each step of the experiment. At the end of the experiment, on analyzing the measurements, which of the following conclusions is he likely to draw?
(A) ∠i = ∠e < ∠r
(B) ∠i < ∠e < ∠r
(C) ∠i > ∠e > ∠r
(D) ∠i = ∠e > ∠r
Four students P, Q, R and S traced the path of a ray of light passing through a glass slab for an angle of incidence 40° and measured the angle of refraction. The values as measured them were 18°; 22°; 25° and 30° respectively. The student who has performed the experiment methodically is
(A) P
(B) Q
(C) R
(D) S
Why do we get a spectrum of seven colors when white light is dispersed by a prism?
Explain the term absolute refractive index of a medium and write an expression to relate it with the speed of light in vacuum.
Draw a ray diagram to show the refraction of a monochromatic ray through a prism when it suffers minimum deviation
A ray of light passes from water to air. How does the speed of light change?
Observe the following figure and answer the questions given under it:
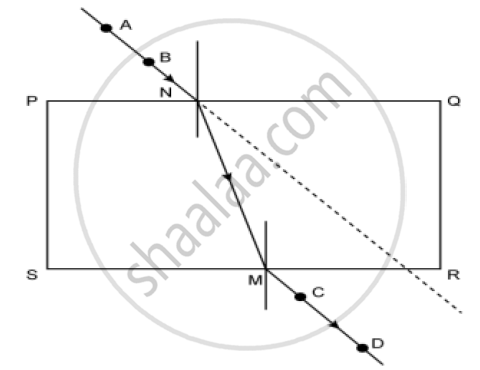
1) How many times does refraction take place in the above figure?
2) What happens to the ray of light when it passes from air to glass?
3) What happens to the ray of light when it passes from glass to air?
4) What are the rays AB and CD in the figure called?
5) Define refraction.
A ray of light passes from glass into air. The angle of refraction will be:
(a) equal to the angle of incidence
(b) greater than the angle of incidence
(c) smaller than the angle of incidence
(d) 45°
Draw diagrams to show the refraction of light from
- air to glass, and
- glass to air. In each diagram, label the incident ray, refracted ray, the angle of incidence
- and the angle of refraction (r).
How is the refractive index of a medium related to the speed of light in it?
Light of a single colour is passed through a liquid having a piece of glass suspended in it. On changing the temperature of liquid, at a particular temperature the glass piece is not seen. When is the glass piece not seen?
When a lighted candle is held in front of a thick plane glass mirror, several images can be seen, but the second image is the brightest, give reason.
How does the speed of light change when it passes from glass to water?
The diagram alongside shows the refraction of a ray of light from air to a liquid.
- Write the values of (i) angle of incidence, (ii) angle of refraction.
- Use Snell’s law to find the refractive index of liquid with respect to air.

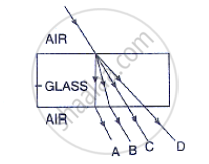
In fig 4.18, name the ray which represents the correct path of light while emerging out through a glass block.
A ray of light enters a glass slab ABDC as shown in figure and strikes at the centre O of the circular part AC of the slab. The critical angle of glass is 42°. Complete the path of the ray till it emerges out from the slab. Mark the angles in the diagram wherever necessary.

A total reflecting right angled isosceles prism can be used to deviate a ray of light through:
(a) 30° (b) 60° (c) 75° (d) 90°.
Select from the following the best experimental set-up for tracing the path of a ray of light through a glass slab: (A) I
(A) I
(B) II
(C) III
(D) IV
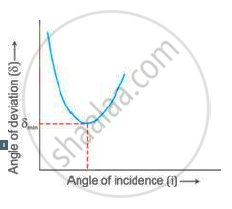
Observe the figure and write accurate conclusion regarding refraction of light.
-
- the angle of refraction and
- the angle of deviation for the ray?
Using the curve, how do you infer that for given prism, the angle of minimum deviation δmin is unique for the given light?
What should be the ratio of the speed of light through the liquid to the speed through the glass so that there is no refraction of light at the boundaries of the glass block when the system is illuminated by the light of one colour?
How is the refractive index of a medium related to its real depth and apparent depth?
Name two instruments of the total refracting prism in which is used.
In what condition a prism is said to be in the position of minimum deviation? What is the direction of the refracted ray inside the prism in this condition?
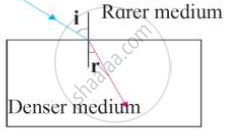
The refractive index of air with respect to glass is defined: as gµa = sin i/sin r
Write down a similar expression for aµg in terms of angle i and r.
The refractive index of air with respect to glass is defined: as gµa = sin i/sin r
If r = 90°, what is the corresponding angle i called?
After a robbery, if a window has been broken, there will be tiny particles of glass. Some of these will be found at the scene of the crime and some may be caught in the thief’s clothing. If the police can prove that these particles are identical, they have a strong case.
A method of doing this is to suspend the particles of glass in a special liquid. Light of a single colour is thrown through the liquid and the particles viewed through a microscope. The temperature of the liquid is then slowly altered. This alters the speed of light through the liquid (i.e., it alters the refractive index). At one particular temperature, the particles of glass disappear. It this happens at the same temperature for both sets of glass particles, they probably came from the same broken pane of glass.
Complete and copy the diagram to show how light bends when it travels from the liquid to the glass and back to the liquid, If the light slows down in the glass.
How will you verify the laws of refraction or how the refractive index of glass is determined in the laboratory?
A ray of light PQ is incident normally on the hypotenuse of a right-angled prism ABC as shown in the diagram given below:
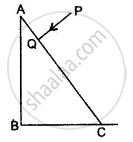
(i) Copy the diagram and complete the path of the ray PQ till it emerges from the prism.
(ii) What is the value of the angle of deviation of the ray?
(iii) Name an instrument where this action of the prism is used.
The refractive index of glass with respect to air is 1.5. What is the value of the refractive index of air with respect to glass?
Observe the figure and name the ray AB, ray CD, ray GH.

