Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Observe the figure and name the ray AB, ray CD, ray GH.

उत्तर
- Ray AB - Incident ray
- Ray CD - Refracted ray
- Ray GH - Emergent ray
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
When a ray of light travels from air to glass slab and strikes the surface of separation at 90°, then it …………….
(a) bends towards normal
(b) bends away from normal
(c) passes unbent
(d) passes in zigzag way
After tracing the path of a ray of light passing through a rectangular glass slab for four different values of the angle of incidence, a student reported his observations in tabular form as given below:
| S.No | ∠ i | ∠ r | ∠ e |
| I | 30° | 19° | 29° |
| II | 40° | 28° | 40° |
| III | 50° | 36° | 50° |
| IV | 60° | 40° | 59° |
The best observation is
(A) I
(B) II
(C) III
(D) IV
In your laboratory you trace the path of light rays through a glass slab for different values of angle of incidence (∠i) and in each case measure the values of the corresponding angle of refraction (∠r) and angle of emergence (∠e). On the basis of your observations your correct conclusion is:
(a) ∠i is more than ∠r, but nearly equal to ∠e
(b) ∠i is less then ∠r, but nearly equal to ∠e
(c) ∠i is more than ∠e, but nearly equal to ∠r
(d) ∠i is less than ∠e, but nearly equal to ∠r
Draw a ray diagram to show the refraction of light through a glass slab and mark angle of refraction and the lateral shift suffered by the ray of light while passing through the slab.
A student very cautiously traces the path of a ray through a glass slab for different values of the angle of incidence (∠i). He then measures the corresponding values of the angle of refraction (∠r) and the angle of emergence (∠e) for every value of the angle of incidence. On analysing these measurements of angles, his conclusion would be
(A) ∠i > ∠r > ∠e
(B) ∠i = ∠e > ∠r
(C) ∠i < ∠r < ∠e
(D) ∠i = ∠e < ∠r
Draw the diagram given below and clearly show the path taken by the emergent ray.
A ray of light passes from water to air. How does the speed of light change?
Which colour of light travels fastest in any medium except air?
In the adjacent diagram, AO is a ray of light incident on a rectangular glass slab.
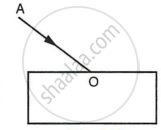
- Complete the path of the ray till it emerges out of the slab.
- In the diagram, mark the angle of incidence (i) and the angle of refraction (r) at the first interface. How is the refractive index of glass related to the angles i and r?
- Mark angles of emergence by the letter e. How are the angles i and e related?
- Which two rays are parallel to each other? Name them.
- Indicate in the diagram the lateral displacement between the emergent ray and the incident ray. State one factor that affects the lateral displacement.
A ray of light of wavelength 6600 Å suffer refraction from air to glass. Taking \[\ce{_a\mu_g = \frac{3}{2}}\], find the wavelength of light in glass.
A light ray in passing from water to a medium
(a) speeds up
(b) slows down. In each case, give one example of the medium.
The critical angle for glass-air is 45° for the light of yellow colour. State whether it will be less than, equal to, or more than 45° for (i) ref light, (ii) blue light?
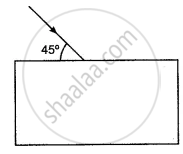
Trace the path of a ray of light incident at an angle of 45° on a rectangular glass slab. Write the measure of the angle of refraction, the angle of emergence and the lateral displacement suffered by the ray as it passes through the slab.
Select from the following the best set-up for tracing the path of a ray of light through a rectangular glass slab:
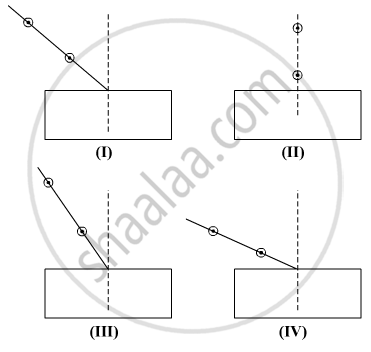
(A) I
(B) II
(C) III
(D) IV
A ray of light falls normally on the surface of a transparent glass slab. Draw a ray diagram to show its path and also mark angle of incidence and angle of emergence.
While tracing the path of a ray of light passing through a rectangular glass slab a student tabulated his observations as given below:
|
S.NO. |
∠i |
∠r |
∠e |
|
I |
60° |
40° |
61° |
|
II |
50° |
36° |
51° |
|
III |
40° |
28° |
39° |
|
IV |
30° |
20° |
31° |
The correct observations is:
(A) I
(B) II
(C) III
(D) IV
-
- the angle of refraction and
- the angle of deviation for the ray?
In the fig. name the ray which represents the correct path of light while passing through a glass block.
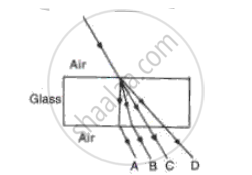
Fig shows a lens as a combination of a glass block and two prisms.
(i) Name the lens formed by the combination.
(ii) What is the line XX' called?
(iii) Complete the path of the incident ray PQ after passing through the lens.
(iv) The final emergent ray either meets XX' at a point or appears to come from a point on XX'. Label it as F, What is this point called?
Draw a diagram to show the splitting of white light into its constituent colours.
Choose the correct alternative and rewrite the following:
A glass slab is placed in the path of convergent light. The point of convergence of light
Glass is transparent in nature. Why does glass powder look opaque? When water is poured over it, it again becomes transparent. Why?
What should be the ratio of the speed of light through the liquid to the speed through the glass so that there is no refraction of light at the boundaries of the glass block when the system is illuminated by the light of one colour?
Comment on the statement ‘The refractive index of glass is 3/2.’
Define the term refractive index of a medium in terms of velocity of light.
Name two instruments of the total refracting prism in which is used.
You are provided with a printed piece of paper. Using this paper how will you differentiate between a convex lens and a concave lens?
A ray of light moves from a rare medium to a dense medium as shown in the diagram below. Write down the number of the ray which represents the partially reflected ray.
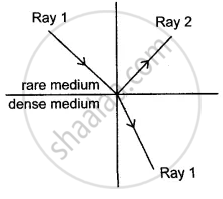
Draw ray of light bending towards the normal while passing from air to glass. Label your diagrams.
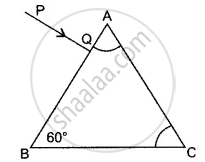
In the diagram alongside a ray of light, PQ is incident normally on one face AB of an equilateral glass prism. What is the angle of incidence at the faces AB and AC?
The diagram shows the path of a ray of light through a rectangular glass block placed in a liquid of uniform density.

What should be the rate of the speed of light through the liquid to the speed through the glass so that there is no refraction of light at the boundaries of the glass block when the system is illuminated by the light of one colour?
Explain with the help of a diagram of how fish is able to see the objects above it.
The velocity of light in diamond is 121000 kms-1. What is its refractive index?
