Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Observe the figure and name the ray AB, ray CD, ray GH.

Solution
- Ray AB - Incident ray
- Ray CD - Refracted ray
- Ray GH - Emergent ray
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Explain how the formation of a rainbow occurs.
Four students P, Q, R and S traced the path of a ray of light passing through a glass slab for an angle of incidence 40° and measured the angle of refraction. The values as measured them were 18°; 22°; 25° and 30° respectively. The student who has performed the experiment methodically is
(A) P
(B) Q
(C) R
(D) S
The following diagram shows a 60°, 30°, 90° glass prism of critical angle 42°, Copy the diagram and complete the path of incident ray AB emerging out of the prism marking the angle of incidence on each surface.
How is the reflection of light ray from a plane mirror different from the refraction of light ray as it enters a block of glass?
Write the relation between the angle of incidence and the angle of refraction for a medium.
For which colour of white light, is the refractive index of a transparent medium the most?
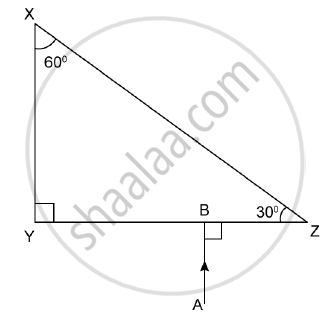
In the adjacent diagram, AO is a ray of light incident on a rectangular glass slab.
- Complete the path of the ray till it emerges out of the slab.
- In the diagram, mark the angle of incidence (i) and the angle of refraction (r) at the first interface. How is the refractive index of glass related to the angles i and r?
- Mark angles of emergence by the letter e. How are the angles i and e related?
- Which two rays are parallel to each other? Name them.
- Indicate in the diagram the lateral displacement between the emergent ray and the incident ray. State one factor that affects the lateral displacement.
A ray of light is passing from a transparent medium 1 to another transparent medium 2 (i) Speed up (ii) slows down. In each case, state whether the refractive index of medium 2 is equal to, less than or greater than the refractive index of medium 1.
The diagram alongside shows the refraction of a ray of light from air to a liquid.
- Write the values of (i) angle of incidence, (ii) angle of refraction.
- Use Snell’s law to find the refractive index of liquid with respect to air.

How is the angle of emergence related to the angle of incidence when prism is in the position of minimum deviation? Illustrate your answer with help of a labelled diagram using an equilateral prism?
Complete Fig. 4.32 to show the path of the ray of single colour as it enters the prism and emerges out of it. Mark the angles wherever necessary.
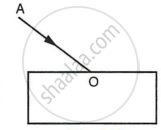
A Water pond appears to be 2.7 m deep. If the refractive index of water is 4/3, find the actual depth of the pond.
The refractive index of glass is 1.5. From a point P inside a glass block, draw rays PA, PB and PC incident on the glass air surface at an angle of incidence 30°, 42° and 60° respectively.
- In the diagram show the approximate direction of these rays as they emerge out of the block.
- What is the angle of refraction for the ray PB?
`("Take" sin 42° =2/3)`
Trace the path of a ray of light incident at an angle of 45° on a rectangular glass slab. Write the measure of the angle of refraction, the angle of emergence and the lateral displacement suffered by the ray as it passes through the slab.
“A ray of light incident on a rectangular glass slab immersed in any medium emerges parallel to itself.” Draw labelled ray diagram to justify the statement.
(i) What is the relation between the refractive index of water with respect to air `("_aμ_\text(w))` and the refractive index of air with respect to water `("_\text(w)μ_ a)` .
(ii) If the refractive index of water with respect to air `("_aμ_\text(w))` is`5/3`. Calculate the refractive index of air with respect to water `("_\text(w)μ_ a)` .
Which of the following has the highest refractive index:
Draw an í- `delta` graph for a mono chromatic raY through a glass prism of a plane and mark
(i) `delta` m, the angle of mínimum devíation
(íí) Any two values of i for which value of `delta` ís same.
The critical angle for glass-air interface is :
Rewrite the following statement by selecting the correct option:
If a ray of light strikes a glass slab at an angle of 600 with the surface of the slab, the angle of incidence must be __________________.
Name the phenomenon responsible in the following case:
Apparent bending of a stick in water
Why do the faces of persons sitting around campfire appear to shimmer?
A ray of light passes from water to air. How does the speed of light change?
Name one main factor on which the direction of bending of a ray of light depends.
Express the refractive index μ of a medium in terms of the velocity of light.
Why does the sun appear bigger during sunset or sunrise?
The refractive index of air with respect to glass is defined: as gµa = sin i/sin r
Write down a similar expression for aµg in terms of angle i and r.
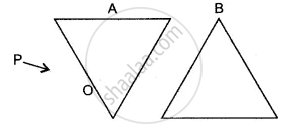
The figure shows two prisms A and B. A monochromatic ray of light PO is incident at the face of the prism A. Complete the diagram to show the path of the ray till it emerges out of the prism B.
The diagram shows the path of a ray of light through a rectangular glass block placed in a liquid of uniform density.

Show with the help of a ray diagram the path of the ray when incident ray normally falls on the first surface of the glass block and passes through the block and the liquid.
Trace a ray of light incident at 30° on a surface if travelling from air to glass. What is the angle of refraction in this case? (R.I. for glass = 3/2).
Explain with the help of a diagram of how fish is able to see the objects above it.
A ray of light PQ is incident normally on the hypotenuse of a right-angled prism ABC as shown in the diagram given below:
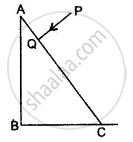
(i) Copy the diagram and complete the path of the ray PQ till it emerges from the prism.
(ii) What is the value of the angle of deviation of the ray?
(iii) Name an instrument where this action of the prism is used.
Write the approximate values of speed of light in (i) air and (ii) glass. Use these values to calculate the refractive index of glass with respect to air.
Draw the ray diagram of a glass slab having medium A and B for the velocity of light ray VA and VB respectively and define Snell's law.
- If VB = 1.5 VA, then which medium is denser?
- What is the refractive index of A with respect to B?
- What is the refractive index of B with respect to A?
