Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Explain how the formation of a rainbow occurs.
Solution
(i) The formation of a rainbow in the sky is a combined result of refraction, dispersion and reflection of sunlight by water droplets present in the atmosphere after it has rained.

(ii) Sunlight is a mixture of seven colours: Violet, indigo, blue, green, yellow, orange and red. After it has stopped raining, the atmosphere contains a large number of water droplets. When sunlight is incident on a water droplet, there is
- Refraction and dispersion of light as it passes from air to water
- Internal reflection of light inside the droplet
- Refraction of light as it passes from water to air
(iii) The refractive index of water is different for different colours, being maximum for violet and minimum for red. Hence, there is dispersion of light (separation into different colours) as it passes from air to water.
(iv) The combined action of different water droplets (acting like tiny prisms) produces a rainbow with red colour on the outer side and violet colour on the inner side. The remaining five colours lie between these two colours. The rainbow is seen when the Sun is behind the observer and the water droplets are in the front.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
When rays of light are incident on a glass slab then the incident ray and emergent ray are _________ each other.
- perpendicular
- parallel
- opposite
- concurrent
A student traces the path of a ray of light through a rectangular glass slab for the different values of angle of incidence. He observes all possible precautions at each step of the experiment. At the end of the experiment, on analyzing the measurements, which of the following conclusions is he likely to draw?
(A) ∠i = ∠e < ∠r
(B) ∠i < ∠e < ∠r
(C) ∠i > ∠e > ∠r
(D) ∠i = ∠e > ∠r
Name a prism required for obtaining a spectrum of Ultraviolet light.
How can you bend light away from the normal?
For which colour of white light, is the refractive index of a transparent medium the most?
A ray of light strikes the surface of a rectangular glass block such that the angle of incidence in
air is 0°.
In each case, draw diagram to show the path taken by the ray as it passes through the glass block and emerges from it.
When light travels from a rarer to a denser medium, its speed ______.
When a ray of light from air enters a denser medium, it ______.
How does the angle of minimum deviation produces by a prism change with increase in :
the wavelength of incident light
Fill in the blanks to complete the following sentence
When light travels from a denser to a rarer medium, its speed ……………….
The critical angle for glass-air is 45° for the light of yellow colour. State whether it will be less than, equal to, or more than 45° for (i) ref light, (ii) blue light?
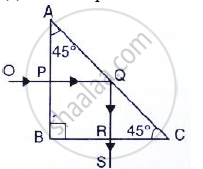
A ray of light OP passes through a right angles prism as shown in the adjacent diagram.
(a) State the angles of incidence at the faces AC and BC.
(b) Name the phenomenon which the ray suffers at the face AC.
Trace the path of a ray of light incident at an angle of 45° on a rectangular glass slab. Write the measure of the angle of refraction, the angle of emergence and the lateral displacement suffered by the ray as it passes through the slab.
Select from the following the best set-up for tracing the path of a ray of light through a rectangular glass slab:
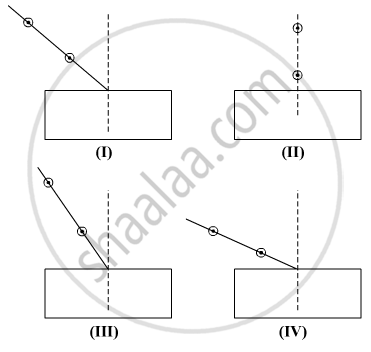
(A) I
(B) II
(C) III
(D) IV
While tracing the path of a ray of light passing through a rectangular glass slab a student tabulated his observations as given below:
|
S.NO. |
∠i |
∠r |
∠e |
|
I |
60° |
40° |
61° |
|
II |
50° |
36° |
51° |
|
III |
40° |
28° |
39° |
|
IV |
30° |
20° |
31° |
The correct observations is:
(A) I
(B) II
(C) III
(D) IV
Four students showed the following traces of the path of a ray of light passing through a rectangular glass slab.
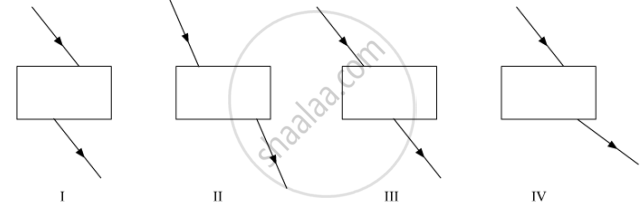
The trace most likely to be correct is that of student
(A) I
(B) II
(C) III
(D) IV
Rahim recorded the following sets of observations while tracing the path of a ray of light passing through a rectangular glass slab for different angles of incidence.
|
S. No. |
Angle of incidence |
Angle of refraction |
Angle of emergence |
|
I |
45° |
41° |
45° |
|
II |
40° |
38° |
38° |
|
III |
45° |
41° |
40° |
|
IV |
41° |
45° |
41° |
The correct observation is recorded at serial number:
(1) I
(2) II
(3) III
(4) IV
Four students A, B, C and D traced the paths of incident ray and the emergent ray by fixing pins P and Q for incident ray and pins R and S for emergent ray for a ray of light passing through a glass slab.
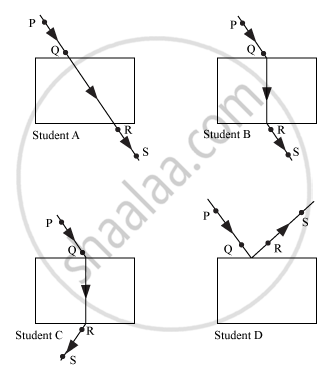
The correct emergent ray was traced by the student:
(1) A
(2) B
(3) C
(4) D
Observe the figure and write accurate conclusion regarding refraction of light.
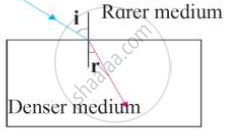
-
- the angle of refraction and
- the angle of deviation for the ray?
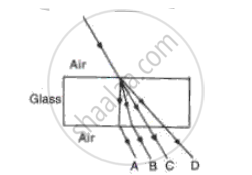
In the fig. name the ray which represents the correct path of light while passing through a glass block.
Draw a diagram to show the splitting of white light into its constituent colours.
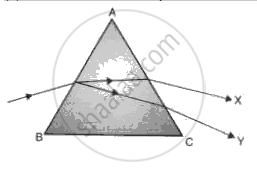
Fig. shows a ray of white light that passes through a prism and produces a spectrum.
(a) Name the phenomenon that is taking place.
(b) What colour would you see at X and Y?
(c) What radiation would you detect above X and below Y?
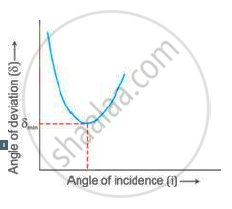
Using the curve, how do you infer that for given prism, the angle of minimum deviation δmin is unique for the given light?
Name one main factor on which the direction of bending of a ray of light depends.
During sunset and sunrise, the sun is seen when it is slightly below the horizon. Give reason.
What is the refractive index of vacuum
Define the term refractive index of a medium in terms of velocity of light.
Explain briefly what causes the twinkling of stars at night.
What do you understand by the deviation produced by a prism?
Draw ray of light bending towards the normal while passing from glass to water. Label your diagrams.
After a robbery, if a window has been broken, there will be tiny particles of glass. Some of these will be found at the scene of the crime and some may be caught in the thief’s clothing. If the police can prove that these particles are identical, they have a strong case.
A method of doing this is to suspend the particles of glass in a special liquid. Light of a single colour is thrown through the liquid and the particles viewed through a microscope. The temperature of the liquid is then slowly altered. This alters the speed of light through the liquid (i.e., it alters the refractive index). At one particular temperature, the particles of glass disappear. It this happens at the same temperature for both sets of glass particles, they probably came from the same broken pane of glass.
Complete and copy the diagram to show how light bends when it travels from the liquid to the glass and back to the liquid, If the light slows down in the glass.
A ray of light PQ is incident normally on the hypotenuse of a right-angled prism ABC as shown in the diagram given below:
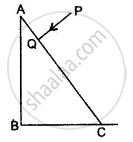
(i) Copy the diagram and complete the path of the ray PQ till it emerges from the prism.
(ii) What is the value of the angle of deviation of the ray?
(iii) Name an instrument where this action of the prism is used.
The speed of light in air is 3 × 108 ms-1. Calculate the speed of light in water. The refractive index of water is 4/3.
The velocity of light in diamond is 121000 kms-1. What is its refractive index?
Write the approximate values of speed of light in (i) air and (ii) glass. Use these values to calculate the refractive index of glass with respect to air.
The refractive index of glass with respect to air is 3/2. What is the refractive index of air with respect to glass?
