Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
-
- the angle of refraction and
- the angle of deviation for the ray?
Solution
The ray of light which is incident normally on a plane glass slab passes undeviated. That is such a ray suffers no bending at the surface because here the angle of incidence is 0°. Thus if angle of incidence ∠i= 0°, then the angle of refraction ∠r = 0°. And the angle of deviation of the ray will also be 0°.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
When rays of light are incident on a glass slab then the incident ray and emergent ray are _________ each other.
- perpendicular
- parallel
- opposite
- concurrent
For which colour of white light, is the refractive index of a transparent medium the most?
Light of a single colour is passed through a liquid having a piece of glass suspended in it. On changing the temperature of liquid, at a particular temperature the glass piece is not seen. When is the glass piece not seen?
A student traces the path of a ray of white light through a rectangular glass slab and marks, the angles of incidence (∠i) , refraction (∠r) and emergence (∠e) as shown. Which angle or angles has he not marked correctly?
(A) ∠i only
(B) ∠i and ∠r
(C) ∠i and ∠e
(D) ∠r and ∠e
Define the term refractive index of a medium. What do you understand by the statement 'the refractive index of glass is 1.5 for white light'?
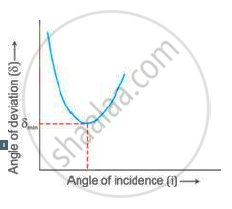
Using the curve, how do you infer that for given prism, the angle of minimum deviation δmin is unique for the given light?
Comment on the statement ‘The refractive index of glass is 3/2.’
How does the angle of deviation produced by a prism depend on the angle of incidence of light at the prism surface? Draw a graph to illustrate your answer.
A ray of monochromatic light is incident from the air on a glass slab:
(i) Draw a labelled ray diagram showing the change in the path of the ray till it emerges from the glass slab.
(ii) Name the two rays that are parallel to each other.
(iii) Mark the lateral displacement in your diagram.
Explain with the help of a diagram of how fish is able to see the objects above it.
