Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain how the formation of a rainbow occurs.
उत्तर
(i) The formation of a rainbow in the sky is a combined result of refraction, dispersion and reflection of sunlight by water droplets present in the atmosphere after it has rained.

(ii) Sunlight is a mixture of seven colours: Violet, indigo, blue, green, yellow, orange and red. After it has stopped raining, the atmosphere contains a large number of water droplets. When sunlight is incident on a water droplet, there is
- Refraction and dispersion of light as it passes from air to water
- Internal reflection of light inside the droplet
- Refraction of light as it passes from water to air
(iii) The refractive index of water is different for different colours, being maximum for violet and minimum for red. Hence, there is dispersion of light (separation into different colours) as it passes from air to water.
(iv) The combined action of different water droplets (acting like tiny prisms) produces a rainbow with red colour on the outer side and violet colour on the inner side. The remaining five colours lie between these two colours. The rainbow is seen when the Sun is behind the observer and the water droplets are in the front.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Draw a ray diagram to show the refraction of light through a glass slab and mark angle of refraction and the lateral shift suffered by the ray of light while passing through the slab.
Which of the above wavelengths has a higher frequency?
Observe the following figure and answer the questions given under it:
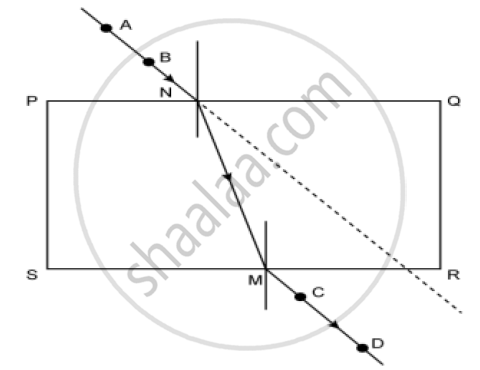
1) How many times does refraction take place in the above figure?
2) What happens to the ray of light when it passes from air to glass?
3) What happens to the ray of light when it passes from glass to air?
4) What are the rays AB and CD in the figure called?
5) Define refraction.
Draw diagrams to show the refraction of light from
- air to glass, and
- glass to air. In each diagram, label the incident ray, refracted ray, the angle of incidence
- and the angle of refraction (r).
A ray of light strikes the surface of a rectangular glass block such that the angle of incidence in
air is 0°.
In each case, draw diagram to show the path taken by the ray as it passes through the glass block and emerges from it.
In the adjacent diagram, AO is a ray of light incident on a rectangular glass slab.
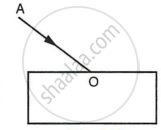
- Complete the path of the ray till it emerges out of the slab.
- In the diagram, mark the angle of incidence (i) and the angle of refraction (r) at the first interface. How is the refractive index of glass related to the angles i and r?
- Mark angles of emergence by the letter e. How are the angles i and e related?
- Which two rays are parallel to each other? Name them.
- Indicate in the diagram the lateral displacement between the emergent ray and the incident ray. State one factor that affects the lateral displacement.
The critical angle for glass-air is 45° for the light of yellow colour. State whether it will be less than, equal to, or more than 45° for (i) ref light, (ii) blue light?
The refractive index of glass is 1.5. From a point P inside a glass block, draw rays PA, PB and PC incident on the glass air surface at an angle of incidence 30°, 42° and 60° respectively.
- In the diagram show the approximate direction of these rays as they emerge out of the block.
- What is the angle of refraction for the ray PB?
`("Take" sin 42° =2/3)`
A ray of light enters a glass slab ABDC as shown in figure and strikes at the centre O of the circular part AC of the slab. The critical angle of glass is 42°. Complete the path of the ray till it emerges out from the slab. Mark the angles in the diagram wherever necessary.

Select from the following the best experimental set-up for tracing the path of a ray of light through a glass slab: (A) I
(A) I
(B) II
(C) III
(D) IV
Trace the path of a ray of light incident at an angle of 45° on a rectangular glass slab. Write the measure of the angle of refraction, the angle of emergence and the lateral displacement suffered by the ray as it passes through the slab.
After tracing the path of rays of light through a glass slab for three different angles of incidence, a student measured the corresponding values angle of refraction r and angle of emergence e and recorded them in the table given below:
|
S. No. |
∠i |
∠i |
∠e |
|
I |
30° |
20° |
31° |
|
II |
40° |
25° |
40° |
|
III |
50° |
31° |
49° |
The correct observations are:
(A) I and II
(B) II and III
(C) I and III
(D) I, II and III
Rahim recorded the following sets of observations while tracing the path of a ray of light passing through a rectangular glass slab for different angles of incidence.
|
S. No. |
Angle of incidence |
Angle of refraction |
Angle of emergence |
|
I |
45° |
41° |
45° |
|
II |
40° |
38° |
38° |
|
III |
45° |
41° |
40° |
|
IV |
41° |
45° |
41° |
The correct observation is recorded at serial number:
(1) I
(2) II
(3) III
(4) IV
A ray of light passes from air to water. In fig. 39, which of the ray A, B, C and D is the correct refracted ray?
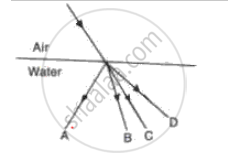
Fig shows a lens as a combination of a glass block and two prisms.
(i) Name the lens formed by the combination.
(ii) What is the line XX' called?
(iii) Complete the path of the incident ray PQ after passing through the lens.
(iv) The final emergent ray either meets XX' at a point or appears to come from a point on XX'. Label it as F, What is this point called?
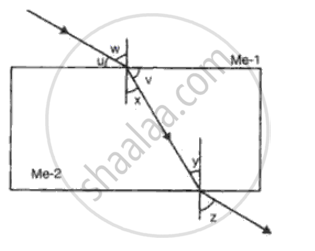
Make the correct for each of the following :
With reference to the fig, the refractive index of the glass block is
Draw a ray diagram showing the lateral displacement of a ray of light when it passes through a parallel sided glass slab.
The critical angle for glass-air interface is :
A ray of light passes from water to air. How does the speed of light change?
Why is the colour red used as a sign of danger?
State the factors on which the angle of deviation depends.
What is the refractive index of water
State the relation between the refractive index μ and the velocity of light (vm) in that medium.
Express the refractive index μ of a medium in terms of the velocity of light.
Explain briefly what causes the twinkling of stars at night.
Name two instruments of the total refracting prism in which is used.
In the diagram below, PQ is a ray of light incident on a rectangular glass block.
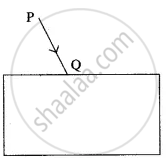
How are the angles ‘i’ and ‘e’ related to each other?
A ray of monochromatic light is incident from air into a glass slab. Draw a labelled ray diagram indicating the change in its path till it emerges out of the slab. In the diagram, mark the angle of incidence (i) and the angle of refraction (r) at the first interface. How is the refractive index of glass related to the angles i and r?
Draw ray of light bending towards the normal while passing from glass to water. Label your diagrams.
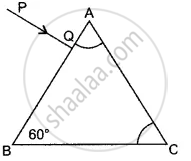
In the diagram alongside a ray of light, PQ is incident normally on one face AB of an equilateral glass prism. What is the angle of incidence at the faces AB and AC?
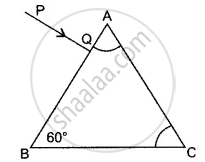
Complete the ray diagram showing its emergence into the air after passing through the prism.
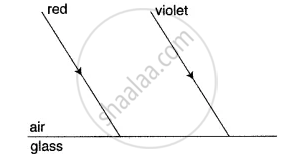
Two parallel rays of Red and Violet travelling through the air, meet the air-glass boundary as shown in the above figure. Will their paths inside the glass be parallel? Give a reason for your answer.
The diagram shows the path of a ray of light through a rectangular glass block placed in a liquid of uniform density.

Show with the help of a ray diagram the path of the ray when incident ray normally falls on the first surface of the glass block and passes through the block and the liquid.
The diagram shows the path of a ray of light through a rectangular glass block placed in a liquid of uniform density.

What should be the rate of the speed of light through the liquid to the speed through the glass so that there is no refraction of light at the boundaries of the glass block when the system is illuminated by the light of one colour?
The velocity of light in diamond is 121000 kms-1. What is its refractive index?
A ray of light strikes the surface of a rectangular glass slab such that the angle of incidence in air is
- 0°,
- 45°.
In each case, draw a diagram to show the path taken by the ray as it passes through the glass slab and emerges from it.
