Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Write any three properties of magnetic lines of force.
List the properties of magnetic lines of force.
state two properties of magnetic lines of force.
उत्तर
Properties of magnetic lines of force:-
- Magnetic lines of force (or magnetic field lines) are closed continuous curves. They start from the North Pole and end at the South Pole.
- The tangent at any point on a magnetic line of force gives the direction of the magnetic field at that point.
- No two magnetic lines of force can intersect each other.
- Magnetic lines of force are crowded where the magnetic field is strong, and they are far from each other where the field is weak.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Magnetic lines of force are closed continuous curves.
An iron needle is attracted to the ends of a bar magnet but not to the middle region of the magnet. Is the material making up the ends of a bare magnet different from that of the middle region?
A bar magnet of length 1 cm and cross-sectional area 1.0 cm2 produces a magnetic field of 1.5 × 10−4 T at a point in end-on position at a distance 15 cm away from the centre. (a) Find the magnetic moment M of the magnet. (b) Find the magnetisation I of the magnet. (c) Find the magnetic field B at the centre of the magnet.
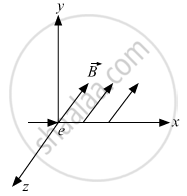
An electron moves along +x direction. It enters into a region of uniform magnetic field. `vecB` directed along –z direction as shown in fig. Draw the shape of the trajectory followed by the electron after entering the field.
A short bar magnet placed with its axis at 30° with a uniform external magnetic field of 0.25 T experiences a torque of magnitude equal to 4.5 × 10–2 J. What is the magnitude of magnetic moment of the magnet?
A closely wound solenoid of 2000 turns and area of cross-section 1.6 × 10-4 m2 , carrying a current of 4.0 A, is suspended through its centre allowing it to turn in a horizontal plane.
What is the force and torque on the solenoid if a uniform horizontal magnetic field of 7.5 × 10-2 T is set up at an angle of 30° with the axis of the solenoid?
Which of the following statements about bar magnet is correct?
Which of the following statement about magnetic field lines is true?
Magnetic field at far axial point due to solenoid as well as bar magnet varies ______.
According to the dipole analogy 1/ε0 corresponds to ______.
Magnetic moment for solenoid and corresponding bar magnet is ______.
A bar magnet of magnetic moment 3.0 Am is placed in a uniform magnetic field of 2 × 10-5T. If each pole of the magnet experience a force of 6 × 10-4 N, the length of the magnet is ______.
Magnetic dipole moment is a ______
A toroid of n turns, mean radius R and cross-sectional radius a carries current I. It is placed on a horizontal table taken as x-y plane. Its magnetic moment m ______.
A proton has spin and magnetic moment just like an electron. Why then its effect is neglected in magnetism of materials?
A bar magnet of magnetic moment m and moment of inertia I (about centre, perpendicular to length) is cut into two equal pieces, perpendicular to length. Let T be the period of oscillations of the original magnet about an axis through the midpoint, perpendicular to length, in a magnetic field B. What would be the similar period T′ for each piece?
Use (i) the Ampere’s law for H and (ii) continuity of lines of B, to conclude that inside a bar magnet, (a) lines of H run from the N pole to S pole, while (b) lines of B must run from the S pole to N pole.
There are two current carrying planar coils made each from identical wires of length L. C1 is circular (radius R) and C2 is square (side a). They are so constructed that they have same frequency of oscillation when they are placed in the same uniform B and carry the same current. Find a in terms of R.
