Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What is myopia?
उत्तर
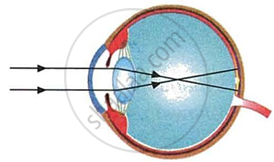
Myopia or near-sightedness is the defect of vision in which a human eye can see nearby objects distinctly but is unable to see distant objects clearly. In this case, the image of a distant object is formed in front of the retina instead of on the retina.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Which defect of vision can be rectified:
by using a convex lens?
What is the other name for
hypermetropia
What is the scientific name of
short-sightedness
Name the defect of vision which makes the eye-lens cloudy resulting in blurred vision.
Where is the near point of a person suffering from hypermetropia (or long-sightedness)?
A student sitting in the last row of the class-room is not able to read clearly the writing on the blackboard.
How can this defect by corrected?
Differentiate between myopia and hypermetropia. What type of spectacles should be worn by a person having the defects of myopia as well as hypermetropia? How does it help?
What is short-sightedness? State the two causes of short-sightedness (or myopia). With the help of ray diagrams, show:
(i) the eye-defect short-sightedness.
(ii) correction of short-sightedness by using a lens.
A person having short-sight cannot see objects clearly beyond a distance of 1.5 m. What would be the nature and power of the corrective lens to restore proper vision?
A person cannot see the distant objects clearly (though he can see the nearby objects clearly). He is suffering from the defect of vision called:
(a) cataract
(b) hypermetropia
(c) myopia
(d) presbyopia
Name the following:
The eye defect caused due to shortening of the eye ball from front to back.
Differentiate between members of the following pair with reference to what is asked in the bracket.
Rods and cones (sensitivity).
Explain the terms ‘adaptation’ and ‘accommodation’ with reference to the eye.
What eye defect is hypermetropia? Describe with a ray diagram how this defect of vision can be corrected by using an appropriate lens.
A student has difficulty reading the blackboard while sitting in the last row. What could be the defect the child is suffering from? How can it be corrected?
State the main functions of the following:
Tears
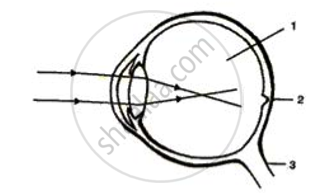
Given alongside is a diagram depicting a defect of the human eye. Study the same and then answer the questions that follow:
(i) Identify the defect.
(ii) Name the parts labelled 1, 2 and 3.
(iii) Give labelled two possible reasons for this eye defect.
(iv) Draw a labelled diagram to show how the above mentioned defect is rectified.
Given below is a diagram depicting a defect of the human eye? Study the same and answer the question that follow:
Give two possible reasons for this defect of the eye in human beings.
Have a look at the posture of this woman who is reading a book and answer the questions which follow:
What kind of looking glasses she needs?
A person is unable to see objects distinctly placed within 50 cm from his eyes.
(a) Name the defect of vision the person is suffering from and list its two possible causes.
(b) Draw a ray diagram to show the defect in the above case.
(c) Mention the type of lens used by him for the correction of the defect and calculate its power. Assume that the near point for the normal eye is 25 cm.
(d) Draw a labeled diagram for the correction of the defect in the above case.
Give Reason:
Older people require glasses to read and write.
Give Reason:
Deficiency of vitamin A causes night blindness.
Give Reason:
When you enter into a dark room from bright because of sunlight, you can not see things for a few seconds.
Explain the Term: Hypermetropia
Explain the Term: Cataract
Give Technical Term:
The type of lens used to correct myopia is
With respect to human eye explain:
(i) How is the image formed on the retina?
(ii) How is the amount of light entering the eye-controlled?
(iii) What type of lens is used for the correction of ‘Long sight’ defect?
(iv) With the help of a ray, diagram show the defect of the eye and then its correction after the use of a lens.
Choose the Odd One Out:
Choose the Odd One Out:
Nearsightedness: elongated eyeball : : farsightedness: _______
Myopia and hypermetropia can be corrected by:
Correlate the given sequence:
Hypermetropia : Convex lens : ______ : Concave lens
Observe the figure and answer the following questions:
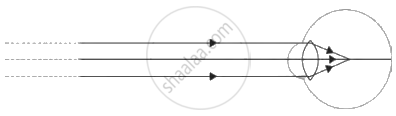
- Name the defect of vision represented in the above figure.
- State the reasons for this defect.
- How is it corrected?
- Draw the diagram to show the correction of this defect.
A person is unable to see clearly a poster fixed on a distant wall. He however sees it clearly when standing at a distance of about 2 m from the wall.
- Draw ray diagram to show the formation of image by his eye lens when he is far away from the wall.
- List two possible reasons of this defect of vision.
- Draw ray diagram to show the correction of this defect using appropriate lens.
Complete the following table by observing the given figures:
| Figure → | 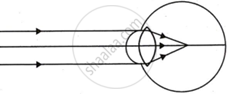 |
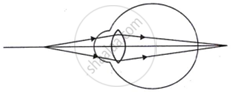 |
| Points ↓ | ||
| (a) Name of the defect | ______ | ______ |
| (b) Position of the image | ______ | ______ |
| (c) Lens used to correct the defect | ______ | ______ |
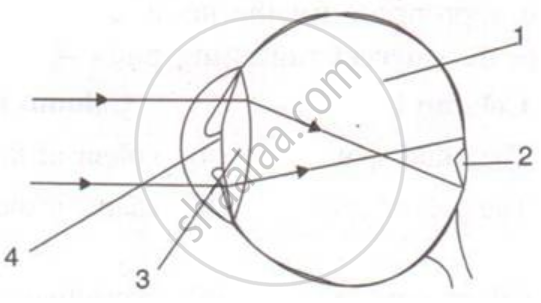
Given alongside is a diagram depicting a defect of the human eye. Study the same and answer the questions that follow:
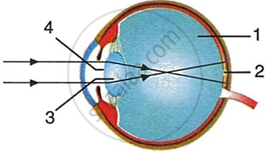 |
- Name the defect shown in the diagram.
- Give two possible reasons for this defect.
- Name the parts labelled 1 to 4.
- Name the type of lens used to correct this eye defect.
- Draw a labelled diagram to show how the above mentioned defect is rectified using the lens named above.
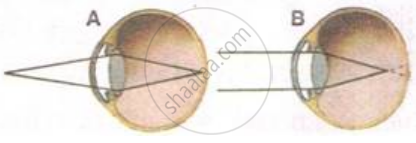
Have a look at the posture of this girl who is reading a book and answer the questions which follow:
 |
- Name the problem she is facing.
- What are the two conditions shown in sections A and B of the eye as applicable to her.
- What kind of reading glasses does she need?
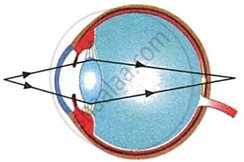 |
 |
| A | B |
