Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A person is unable to see clearly a poster fixed on a distant wall. He however sees it clearly when standing at a distance of about 2 m from the wall.
- Draw ray diagram to show the formation of image by his eye lens when he is far away from the wall.
- List two possible reasons of this defect of vision.
- Draw ray diagram to show the correction of this defect using appropriate lens.
उत्तर
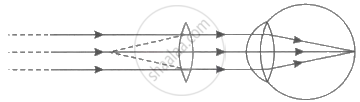
(a)

Myopic eye
(b) In a myopic eye, rather than at the retina itself, the image of a distant object is created in front of the retina. This flaw may result from (i) an excessively curved eye lens or (ii) an elongated eyeball. With the use of a concave lens of the appropriate power, this flaw can be fixed. The flaw is fixed by returning the picture to the retina with a concave lens of the proper power.
(c)
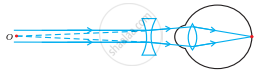
Correction for myopic
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What is myopia?
List three common refractive defects of vision. Suggest the way of correcting these defects.
A student sitting in the last row of the class-room is not able to read clearly the writing on the blackboard.
How can this defect by corrected?
An eye has a far point of 2 m. What type of lens in spectacles would be needed to increase the far point to infinity? Also calculate the power of lens required. Is this eye long-sighted or short-sighted?
The defect of vision which cannot be corrected by using spectacles is:
(a) myopia
(b) presbyopia
(c) cataract
(d) hypermetropia
Distinguish between the following pair of words:
Myopia and hypermetropia
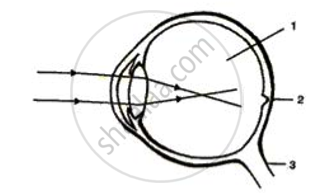
Given alongside is a diagram depicting a defect of the human eye. Study the same and then answer the questions that follow:
(i) Identify the defect.
(ii) Name the parts labelled 1, 2 and 3.
(iii) Give labelled two possible reasons for this eye defect.
(iv) Draw a labelled diagram to show how the above mentioned defect is rectified.
Differentiate between:
Short-sightedness and Long-sightedness.
Observe the given below the figure, correct it and explain and write about the concept depicted in this figure.
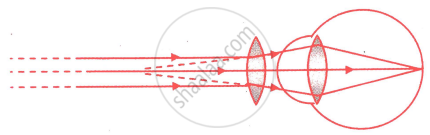
Observe the figure whether it is correct or not and explain the phenomenon.