Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain how the formation of a rainbow occurs.
उत्तर
(i) The formation of a rainbow in the sky is a combined result of refraction, dispersion and reflection of sunlight by water droplets present in the atmosphere after it has rained.

(ii) Sunlight is a mixture of seven colours: Violet, indigo, blue, green, yellow, orange and red. After it has stopped raining, the atmosphere contains a large number of water droplets. When sunlight is incident on a water droplet, there is
- Refraction and dispersion of light as it passes from air to water
- Internal reflection of light inside the droplet
- Refraction of light as it passes from water to air
(iii) The refractive index of water is different for different colours, being maximum for violet and minimum for red. Hence, there is dispersion of light (separation into different colours) as it passes from air to water.
(iv) The combined action of different water droplets (acting like tiny prisms) produces a rainbow with red colour on the outer side and violet colour on the inner side. The remaining five colours lie between these two colours. The rainbow is seen when the Sun is behind the observer and the water droplets are in the front.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
When rays of light are incident on a glass slab then the incident ray and emergent ray are _________ each other.
- perpendicular
- parallel
- opposite
- concurrent
A student traces the path of a ray of light through a rectangular glass slab for the different values of angle of incidence. He observes all possible precautions at each step of the experiment. At the end of the experiment, on analyzing the measurements, which of the following conclusions is he likely to draw?
(A) ∠i = ∠e < ∠r
(B) ∠i < ∠e < ∠r
(C) ∠i > ∠e > ∠r
(D) ∠i = ∠e > ∠r
A student traces the path of a ray of light passing through a rectangular glass slab and marks the angle of incidence i, angle of refraction r and angle of emergence e, as shown.
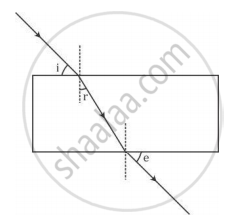
The correctly marked angle(s) is/are
(A) ∠ i only
(B) ∠ e only
(C) ∠ r only
(D) ∠ i and ∠ e
Four students P, Q, R and S traced the path of a ray of light passing through a glass slab for an angle of incidence 40° and measured the angle of refraction. The values as measured them were 18°; 22°; 25° and 30° respectively. The student who has performed the experiment methodically is
(A) P
(B) Q
(C) R
(D) S
Draw the diagram of refraction of light in the glass slab
How is the reflection of light ray from a plane mirror different from the refraction of light ray as it enters a block of glass?
When a ray of light from air enters a denser medium, it ______.
How does the speed of light change when it passes from glass to water?
Fill in the blanks to complete the following sentence
The refractive index of glass with respect to air is 3/2. The refractive index of air with respect to glass will be ……………….
The critical angle for glass-air is 45° for the light of yellow colour. State whether it will be less than, equal to, or more than 45° for (i) ref light, (ii) blue light?
While tracing the path of a ray of light passing through a rectangular glass slab a student tabulated his observations as given below:
|
S.NO. |
∠i |
∠r |
∠e |
|
I |
60° |
40° |
61° |
|
II |
50° |
36° |
51° |
|
III |
40° |
28° |
39° |
|
IV |
30° |
20° |
31° |
The correct observations is:
(A) I
(B) II
(C) III
(D) IV
-
- the angle of refraction and
- the angle of deviation for the ray?
Draw an í- `delta` graph for a mono chromatic raY through a glass prism of a plane and mark
(i) `delta` m, the angle of mínimum devíation
(íí) Any two values of i for which value of `delta` ís same.
Fig shows a lens as a combination of a glass block and two prisms.
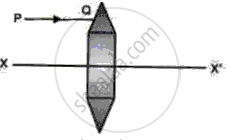
(i) Name the lens formed by the combination.
(ii) what is the XX' called?
(iii) Complete the ray diagram and show the path of the incident ray PQ after passing through the lens.
(iv) The final emergent ray will either meet XX' at a point or appear to come from a point on XX'. what is the point called?
Make the correct for each of the following :
With reference to the fig, the refractive index of the glass block is
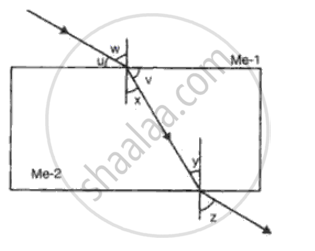
What is meant by the refraction of light?
Glass is transparent in nature. Why does glass powder look opaque? When water is poured over it, it again becomes transparent. Why?
What is the refractive index of vacuum
Comment on the statement ‘The refractive index of glass is 3/2.’
Name two instruments of the total refracting prism in which is used.
In what condition a prism is said to be in the position of minimum deviation? What is the direction of the refracted ray inside the prism in this condition?
How does the angle of deviation produced by a prism depend on the colour of light used? Which colour of white light is deviated (i) most, (ii) least, by a prism?
In the diagram below, PQ is a ray of light incident on a rectangular glass block.
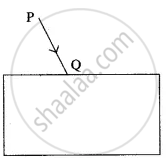
How are the angles ‘i’ and ‘e’ related to each other?
Complete the ray diagram showing its emergence into the air after passing through the prism.
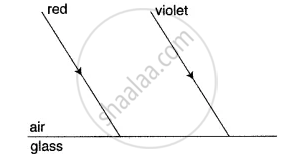
Two parallel rays of Red and Violet travelling through the air, meet the air-glass boundary as shown in the above figure. Will their paths inside the glass be parallel? Give a reason for your answer.
How will you verify the laws of refraction or how the refractive index of glass is determined in the laboratory?
Trace a ray of light incident at 30° on a surface if travelling from air to glass. What is the angle of refraction in this case? (R.I. for glass = 3/2).
A coin placed at the bottom of a beaker appears to be raised by 4.0 cm. If the refractive index of water is 4/3, find the depth of the water in the beaker.
The refractive index of glass with respect to air is 1.5. What is the value of the refractive index of air with respect to glass?
Draw the ray diagram of a glass slab having medium A and B for the velocity of light ray VA and VB respectively and define Snell's law.
- If VB = 1.5 VA, then which medium is denser?
- What is the refractive index of A with respect to B?
- What is the refractive index of B with respect to A?
Which colour of white light travels fastest in any medium except air?
What is lateral displacement?
