Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Trace a ray of light incident at 30° on a surface if travelling from air to glass. What is the angle of refraction in this case? (R.I. for glass = 3/2).
उत्तर

aμg = `sin"i"/sin"r"`
∴ `3/2=(sin30°)/sin"r"`
∴ Sin r = `2/3xxsin30°`
But sin 30° = `1/2`
∴ sin r = `2/3xx1/2`
= `1/3`
∴ sin r = 0.3334
∴ sin r = 19°30′.
Angle of refraction for air to glass = 19°30′.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State the dependence of angle of deviation On the wavelength of light
Observe the following figure and answer the questions given under it:
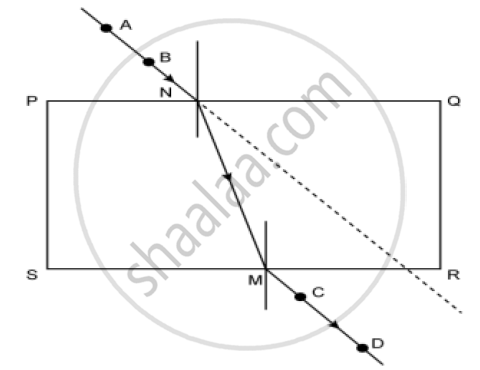
1) How many times does refraction take place in the above figure?
2) What happens to the ray of light when it passes from air to glass?
3) What happens to the ray of light when it passes from glass to air?
4) What are the rays AB and CD in the figure called?
5) Define refraction.
Draw diagrams to show the refraction of light from glass to air. In diagram, label the incident ray, refracted ray, the angle of incidence (i) and the angle of refraction (r).
When a lighted candle is held in front of a thick plane glass mirror, several images can be seen, but the second image is the brightest, give reason.
-
- the angle of refraction and
- the angle of deviation for the ray?
Which colour of light travels fastest in any medium except air?
Choose the correct alternative and rewrite the following:
A glass slab is placed in the path of convergent light. The point of convergence of light
State the relation between the refractive index μ and the velocity of light (vm) in that medium.
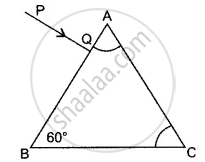
In the diagram alongside a ray of light, PQ is incident normally on one face AB of an equilateral glass prism. What is the angle of incidence at the faces AB and AC?
The diagram shows the path of a ray of light through a rectangular glass block placed in a liquid of uniform density.

What is the angular, deviation of the emergent ray from the glass block with respect to the incident ray?
