Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Observe the following figure and answer the questions given under it:
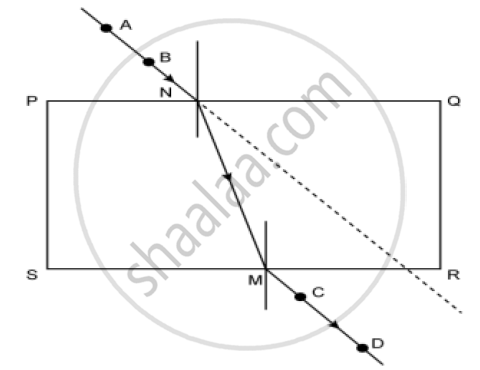
1) How many times does refraction take place in the above figure?
2) What happens to the ray of light when it passes from air to glass?
3) What happens to the ray of light when it passes from glass to air?
4) What are the rays AB and CD in the figure called?
5) Define refraction.
उत्तर
An expression for heat produced in a conductor by using Joule's experiment:
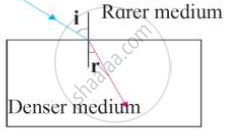
1) Refraction occurs twice, once at Point N and the second time at Point M.
2) Air is rarer than glass. So, when light passes from the rarer medium to the denser medium, it bends towards the normal.
3) When light passes from the denser (glass) medium to the rarer (air) medium, it bends away from the normal.
4) Ray AB is called the incident ray, and ray CD is called the emergent ray.
5) Refraction of light is the phenomenon of change in the direction of propagation of light when it passes obliquely from one transparent medium to another.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
After tracing the path of a ray of light passing through a rectangular glass slab for four different values of the angle of incidence, a student reported his observations in tabular form as given below:
| S.No | ∠ i | ∠ r | ∠ e |
| I | 30° | 19° | 29° |
| II | 40° | 28° | 40° |
| III | 50° | 36° | 50° |
| IV | 60° | 40° | 59° |
The best observation is
(A) I
(B) II
(C) III
(D) IV
Select from the following the best experimental setup for tracing the path of a ray of light passing through a rectangular glass slab.
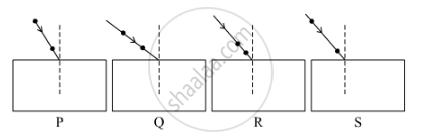
(a) P
(b) Q
(c) R
(d) S
Draw a ray diagram to show the refraction of light through a glass slab and mark angle of refraction and the lateral shift suffered by the ray of light while passing through the slab.
Draw the diagram given below and clearly show the path taken by the emergent ray.
Which colour of light travels fastest in any medium except air?
Draw the diagram of refraction of light in the glass slab
How can you bend light away from the normal?
How must light travel out of a substance if it is not going to be refracted?
How is the refractive index of a medium related to the speed of light in it?
When a lighted candle is held in front of a thick plane glass mirror, several images can be seen, but the second image is the brightest, give reason.
When light travels from a rarer to a denser medium, its speed ______.
The highest refractive index is of ______.
How does the angle of deviation produced by a prism change with increase in the angle of incidence. Draw a curve showing the variation in the angle of deviation with the angle of incidence at a prism surface.
Fill in the blanks to complete the following sentence
When light travels from a denser to a rarer medium, its speed ……………….
How is the angle of emergence related to the angle of incidence when prism is in the position of minimum deviation? Illustrate your answer with help of a labelled diagram using an equilateral prism?
Name the colour of white light which is deviated the most on passing through a prism.
Select from the following the best experimental set-up for tracing the path of a ray of light through a glass slab: (A) I
(A) I
(B) II
(C) III
(D) IV
A student traces the path of a ray of white light through a rectangular glass slab and marks, the angles of incidence (∠i) , refraction (∠r) and emergence (∠e) as shown. Which angle or angles has he not marked correctly?
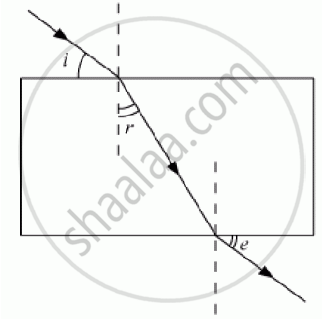
(A) ∠i only
(B) ∠i and ∠r
(C) ∠i and ∠e
(D) ∠r and ∠e
While tracing the path of a ray of light passing through a rectangular glass slab a student tabulated his observations as given below:
|
S.NO. |
∠i |
∠r |
∠e |
|
I |
60° |
40° |
61° |
|
II |
50° |
36° |
51° |
|
III |
40° |
28° |
39° |
|
IV |
30° |
20° |
31° |
The correct observations is:
(A) I
(B) II
(C) III
(D) IV
Observe the figure and write accurate conclusion regarding refraction of light.
In the fig., PO is a ray of light incident on a rectangular glass block.
(a) Complete the path of the ray through the block.
(b) In the diagram, mark the angle of incidence (i) and the angle of refraction (r) at the first interface. How is the refractive index of glass related to the angles I and r?
(c) Mark angle of emergence by the letter e. How are the angles i and e related?
(d) Which two rays are parallel to each other? Name them.
(e) Indicate in the diagram the lateral displacement between the emergent ray and the incident ray.
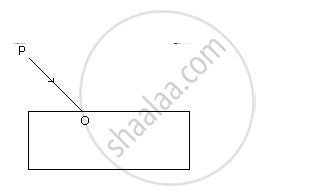
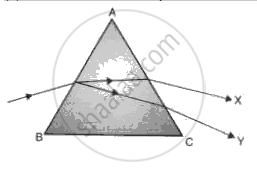
Fig. shows a ray of white light that passes through a prism and produces a spectrum.
(a) Name the phenomenon that is taking place.
(b) What colour would you see at X and Y?
(c) What radiation would you detect above X and below Y?
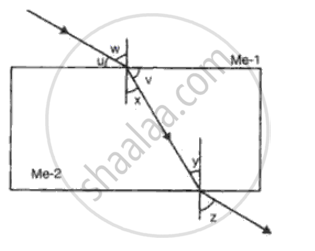
Make the correct for each of the following :
With reference to the fig, the refractive index of the glass block is
How does the deviation produced by a prism depend on the refraction index of its material.
Why is the colour red used as a sign of danger?
What is the refractive index of water
What should be the ratio of the speed of light through the liquid to the speed through the glass so that there is no refraction of light at the boundaries of the glass block when the system is illuminated by the light of one colour?
Explain briefly what causes the twinkling of stars at night.
Why does the sun appear bigger during sunset or sunrise?
The refractive index of air with respect to glass is defined: as gµa = sin i/sin r
Write down a similar expression for aµg in terms of angle i and r.
The refractive index of air with respect to glass is defined: as gµa = sin i/sin r
If r = 90°, what is the corresponding angle i called?
A ray of monochromatic light is incident from air into a glass slab. Draw a labelled ray diagram indicating the change in its path till it emerges out of the slab. In the diagram, mark the angle of incidence (i) and the angle of refraction (r) at the first interface. How is the refractive index of glass related to the angles i and r?
A ray of light is incident at an angle of 45° on one face of a rectangular glass slab of thickness 10 cm and refractive index 3/2. Calculate the lateral shift produced ______.
Which colour of white light travels fastest in any medium except air?
A ray of light strikes the surface of a rectangular glass slab such that the angle of incidence in air is
- 0°,
- 45°.
In each case, draw a diagram to show the path taken by the ray as it passes through the glass slab and emerges from it.
What is lateral displacement?
