Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Observe the following figure and answer the questions given under it:
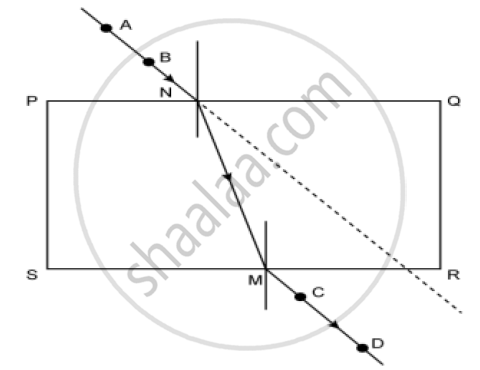
1) How many times does refraction take place in the above figure?
2) What happens to the ray of light when it passes from air to glass?
3) What happens to the ray of light when it passes from glass to air?
4) What are the rays AB and CD in the figure called?
5) Define refraction.
Solution
An expression for heat produced in a conductor by using Joule's experiment:
1) Refraction occurs twice, once at Point N and the second time at Point M.
2) Air is rarer than glass. So, when light passes from the rarer medium to the denser medium, it bends towards the normal.
3) When light passes from the denser (glass) medium to the rarer (air) medium, it bends away from the normal.
4) Ray AB is called the incident ray, and ray CD is called the emergent ray.
5) Refraction of light is the phenomenon of change in the direction of propagation of light when it passes obliquely from one transparent medium to another.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A student traces the path of a ray of light passing through a rectangular glass slab and marks the angle of incidence i, angle of refraction r and angle of emergence e, as shown.
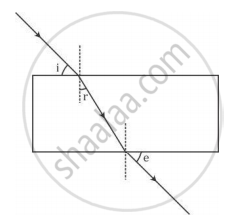
The correctly marked angle(s) is/are
(A) ∠ i only
(B) ∠ e only
(C) ∠ r only
(D) ∠ i and ∠ e
Select from the following the best experimental setup for tracing the path of a ray of light passing through a rectangular glass slab.
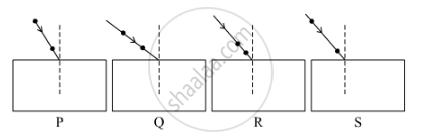
(a) P
(b) Q
(c) R
(d) S
On the basis of the experiment, "To trace the path of a ray of light through a rectangular glass slab", students of a class arrived at which one of the following conclusions?
(A) Angle of incidence is greater than the angle of emergence.
(B) Angle of emergence is smaller than the angle of refraction.
(C) Emergent ray is parallel to the refracted ray.
(D) Incident ray and emergent ray are parallel to each other.
Why is the ratio of the velocities of light of wavelengths 4000Å and 8000Å in vacuum 1: 1?
Draw diagrams to show the refraction of light from glass to air. In diagram, label the incident ray, refracted ray, the angle of incidence (i) and the angle of refraction (r).
How is the refractive index of a medium related to the speed of light in it?
A monochromatic ray of light passes from air to glass. The wavelength of light in air is λ, the speed of light in air is c and in glass is V. If the absolute refractive index of glass is 1.5, write down
- the relationship between c and V,
- the wavelength of light in glass.
A ray of light of wavelength 6600 Å suffer refraction from air to glass. Taking \[\ce{_a\mu_g = \frac{3}{2}}\], find the wavelength of light in glass.
A light ray in passing from water to a medium
(a) speeds up
(b) slows down. In each case, give one example of the medium.
An object is viewed through a glass prism with its vertex pointing upwards. It appears to be displaced upward. Explain the reason.
Complete Fig. 4.32 to show the path of the ray of single colour as it enters the prism and emerges out of it. Mark the angles wherever necessary.
The refractive index of air with respect to glass is expressed as `""_g μ_a=sin i /sin r`.
- Write down a similar expression for aμg in terms of the angles i and r.
- If angle r = 90°, what is the corresponding angle i called?
- What is the physical significance of the angle i in part (b)?
“A ray of light incident on a rectangular glass slab immersed in any medium emerges parallel to itself.” Draw labelled ray diagram to justify the statement.
After tracing the path of rays of light through a glass slab for three different angles of incidence, a student measured the corresponding values angle of refraction r and angle of emergence e and recorded them in the table given below:
|
S. No. |
∠i |
∠i |
∠e |
|
I |
30° |
20° |
31° |
|
II |
40° |
25° |
40° |
|
III |
50° |
31° |
49° |
The correct observations are:
(A) I and II
(B) II and III
(C) I and III
(D) I, II and III
While tracing the path of a ray of light passing through a rectangular glass slab a student tabulated his observations as given below:
|
S.NO. |
∠i |
∠r |
∠e |
|
I |
60° |
40° |
61° |
|
II |
50° |
36° |
51° |
|
III |
40° |
28° |
39° |
|
IV |
30° |
20° |
31° |
The correct observations is:
(A) I
(B) II
(C) III
(D) IV
Four students showed the following traces of the path of a ray of light passing through a rectangular glass slab.
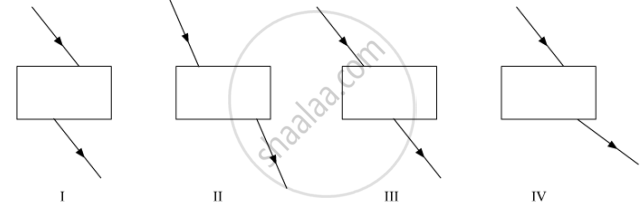
The trace most likely to be correct is that of student
(A) I
(B) II
(C) III
(D) IV
While performing the experiment on tracing the path of a ray of light through a rectangular glass slab, in which of the following experimental set-ups is a student likely to get best results? P1 and P2 are the positions of pins fixed by him.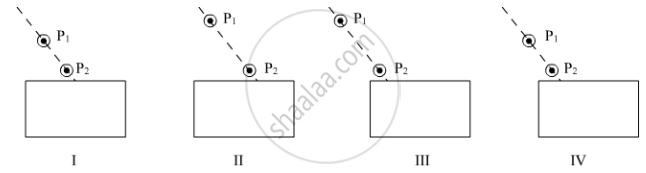
(A) I
(B) II
(C) III
(D) IV
(i) What is the relation between the refractive index of water with respect to air `("_aμ_\text(w))` and the refractive index of air with respect to water `("_\text(w)μ_ a)` .
(ii) If the refractive index of water with respect to air `("_aμ_\text(w))` is`5/3`. Calculate the refractive index of air with respect to water `("_\text(w)μ_ a)` .
In the fig. name the ray which represents the correct path of light while passing through a glass block.
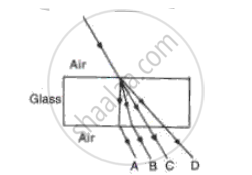
Fig shows a lens as a combination of a glass block and two prisms.
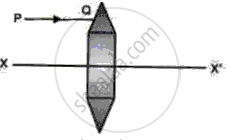
(i) Name the lens formed by the combination.
(ii) what is the XX' called?
(iii) Complete the ray diagram and show the path of the incident ray PQ after passing through the lens.
(iv) The final emergent ray will either meet XX' at a point or appear to come from a point on XX'. what is the point called?
Write a relation between the angle of incidence (i), angle of emergence (e), angle of the prism (A), and angle of deviation (d) for a ray of light passing through an equilateral prism.
Name the material for which the refractive index is found to be maximum.
What is the refractive index of vacuum
How is the refractive index of a medium related to its real depth and apparent depth?
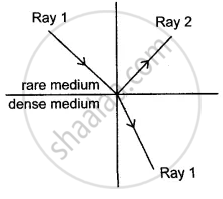
A ray of light moves from a rare medium to a dense medium as shown in the diagram below. Write down the number of the ray which represents the partially reflected ray.
Draw ray of light bending towards the normal while passing from glass to water. Label your diagrams.
Draw a diagram to show the refraction of a monochromatic light ray through an equilateral prism. On the diagram, label the incident, refracted, and emergent rays. It also indicates the angle of deviation by the letter δ.
Light passes through a rectangular glass slab and through a triangular glass prism. In what way does the direction of the two emergent beams differ and why?
A ray of monochromatic light is incident from the air on a glass slab:
(i) Draw a labelled ray diagram showing the change in the path of the ray till it emerges from the glass slab.
(ii) Name the two rays that are parallel to each other.
(iii) Mark the lateral displacement in your diagram.
The diagram shows the path of a ray of light through a rectangular glass block placed in a liquid of uniform density.

What is the angular, deviation of the emergent ray from the glass block with respect to the incident ray?
Draw a diagram of a prism and label:
(i) the base,
(ii) the refracting surfaces,
(iii) the refracting edge,
(iv) the refracting angle in it.
