Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Draw diagrams to show the refraction of light from glass to air. In diagram, label the incident ray, refracted ray, the angle of incidence (i) and the angle of refraction (r).
Solution
Diagram showing the refraction of light from Glass to Air
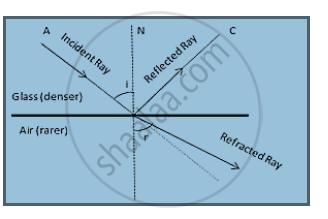
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
How is the reflection of light ray from a plane mirror different from the refraction of light ray as it enters a block of glass?
Light of a single colour is passed through a liquid having a piece of glass suspended in it. On changing the temperature of liquid, at a particular temperature the glass piece is not seen. When is the glass piece not seen?
Fill in the blanks to complete the following sentence
The refractive index of glass with respect to air is 3/2. The refractive index of air with respect to glass will be ……………….
A total reflecting right angled isosceles prism can be used to deviate a ray of light through:
(a) 30° (b) 60° (c) 75° (d) 90°.
While tracing the path of a ray of light passing through a rectangular glass slab a student tabulated his observations as given below:
|
S.NO. |
∠i |
∠r |
∠e |
|
I |
60° |
40° |
61° |
|
II |
50° |
36° |
51° |
|
III |
40° |
28° |
39° |
|
IV |
30° |
20° |
31° |
The correct observations is:
(A) I
(B) II
(C) III
(D) IV
A total reflecting equilateral prism can be used to deviate a ray of light through:
The refractive index of air with respect to glass is defined: as gµa = sin i/sin r
If r = 90°, what is the corresponding angle i called?
The diagram shows the path of a ray of light through a rectangular glass block placed in a liquid of uniform density.

What should be the rate of the speed of light through the liquid to the speed through the glass so that there is no refraction of light at the boundaries of the glass block when the system is illuminated by the light of one colour?
The diagram below shows two parallel rays A (Orange) & B (Blue) incident from air, on air-glass boundary.
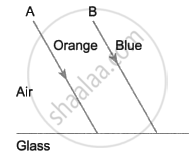
- Copy and complete the path of the rays A and B.
- How do the speeds of these rays differ in glass?
- Are the two refracted rays in glass parallel? Give a reason.
