Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The diagram below shows two parallel rays A (Orange) & B (Blue) incident from air, on air-glass boundary.
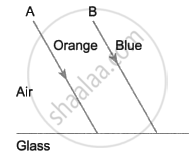
- Copy and complete the path of the rays A and B.
- How do the speeds of these rays differ in glass?
- Are the two refracted rays in glass parallel? Give a reason.
Solution

- In glass, speed of orange (A) light is more than that of blue light (B).
- No, the two refracted rays are not parallel to each other as their speeds vary in the glass.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Draw a ray diagram to show the refraction of light through a glass slab and mark angle of refraction and the lateral shift suffered by the ray of light while passing through the slab.
Write the relation between the angle of incidence and the angle of refraction for a medium.
Fill in the blanks to complete the following sentence
When light travels from a denser to a rarer medium, its speed ……………….
Fig shows a lens as a combination of a glass block and two prisms.
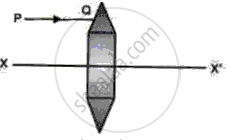
(i) Name the lens formed by the combination.
(ii) what is the XX' called?
(iii) Complete the ray diagram and show the path of the incident ray PQ after passing through the lens.
(iv) The final emergent ray will either meet XX' at a point or appear to come from a point on XX'. what is the point called?
Name the phenomenon responsible in the following case:
Apparent bending of a stick in water
Why is the colour red used as a sign of danger?
How is the refractive index of a medium related to its real depth and apparent depth?
Draw a diagram to show the refraction of a monochromatic light ray through an equilateral prism. On the diagram, label the incident, refracted, and emergent rays. It also indicates the angle of deviation by the letter δ.
Calculate the velocity of light in a glass block of refractive index 1.5. (Velocity of light in air = 3 × 108 m/s)