Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Solution
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Name one factor that affects the lateral displacement of light as it passes through a rectangular glass slab.
The refractive index of air with respect to glass is expressed as `""_g μ_a=sin i /sin r`.
- Write down a similar expression for aμg in terms of the angles i and r.
- If angle r = 90°, what is the corresponding angle i called?
- What is the physical significance of the angle i in part (b)?
Fig shows a lens as a combination of a glass block and two prisms.
(i) Name the lens formed by the combination.
(ii) What is the line XX' called?
(iii) Complete the path of the incident ray PQ after passing through the lens.
(iv) The final emergent ray either meets XX' at a point or appears to come from a point on XX'. Label it as F, What is this point called?
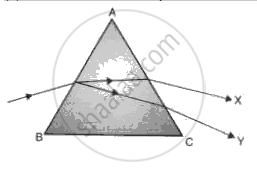
Fig. shows a ray of white light that passes through a prism and produces a spectrum.
(a) Name the phenomenon that is taking place.
(b) What colour would you see at X and Y?
(c) What radiation would you detect above X and below Y?
Draw a ray diagram showing the lateral displacement of a ray of light when it passes through a parallel sided glass slab.
State the relation between the refractive index μ and the velocity of light (vm) in that medium.
A ray of monochromatic light is incident from air into a glass slab. Draw a labelled ray diagram indicating the change in its path till it emerges out of the slab. In the diagram, mark the angle of incidence (i) and the angle of refraction (r) at the first interface. How is the refractive index of glass related to the angles i and r?
Draw ray of light bending towards the normal while passing from glass to water. Label your diagrams.
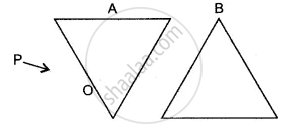
The figure shows two prisms A and B. A monochromatic ray of light PO is incident at the face of the prism A. Complete the diagram to show the path of the ray till it emerges out of the prism B.
Consider these indices of refraction: glass: 1.52; air: 1.0003; water: 1.333. Based on the refractive indices of three materials, arrange the speed of light through them in decreasing order.
