Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
2: Simple Machines
▶ 3: Refraction of Light
4: Refraction through Lenses and Optical Instruments
5: Spectrum
6: Echoes and Vibrations of Sound
7: Electricity
8: Electric Power and House hold Circuits
9: Magnetic Effect of Current
10: Specific Heat Capacity and Latent Heat
11: Thermionic Emission and Radioactivity
![ICSE solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 chapter 3 - Refraction of Light ICSE solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 chapter 3 - Refraction of Light - Shaalaa.com](/images/physics-english-class-10_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 3: Refraction of Light
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 3 of CISCE ICSE for Physics [English] Class 10.
ICSE solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 3 Refraction of Light Short Answers
What is meant by the refraction of light?
Name the phenomenon responsible in the following case:
Apparent bending of a stick in water
Name the phenomenon responsible in the following case:
Twinkling of stars
Why do the faces of persons sitting around campfire appear to shimmer?
Why does a fisherman aim at the tail of fish during spearfishing?
During sunset and sunrise, the sun is seen when it is slightly below the horizon. Give reason.
Why upper surface of water contained in a beaker and above eye level appears silvery?
Glass is transparent in nature. Why does glass powder look opaque? When water is poured over it, it again becomes transparent. Why?
A ray of light passes from water to air. How does the speed of light change?
Which colour of light travels fastest in any medium except air?
Why is the colour red used as a sign of danger?
Does the depth of a tank of water appear to change or remain the same when viewed normally from above?
Mention one difference between reflection of light from a plane mirror and total internal reflection of light from a prism.
Name one main factor on which the direction of bending of a ray of light depends.
How does a ray of light bend when it travels from rarer to denser medium
How does a ray of light bend when it travels from denser to rarer medium.
How does a ray of light bend when it travels from when it is normal to the interface of the two media.
A fish swimming in a pond seems nearer than it really is. Explain.
Why do diamonds sparkle?
Can light be ‘piped’ like sound in a doctor’s stethoscope?
State the Snell’s laws of refraction of light.
Write a relation between the angle of incidence (i), angle of emergence (e), angle of the prism (A), and angle of deviation (d) for a ray of light passing through an equilateral prism.
A glass slab is placed over a page on which the word VIBGYOR is printed with each letter in its corresponding colour.
- Will the image of all the letters be in the same place?
- If not, the state which letter will be raised to the maximum. Give a reason for your answer.
State the factors on which the angle of deviation depends.
Name the material for which the refractive index is found to be maximum.
State the relation between the refractive index μ and the velocity of light (vm) in that medium.
What is the refractive index of vacuum
What is the refractive index of water
Write down the relationship between the critical angle and the refractive index of the medium.
For which colour of white light, is the refractive index of a transparent medium the most?
What should be the ratio of the speed of light through the liquid to the speed through the glass so that there is no refraction of light at the boundaries of the glass block when the system is illuminated by the light of one colour?
Comment on the statement ‘The refractive index of glass is 3/2.’
Define the term refractive index of a medium in terms of velocity of light.
How is the refractive index of a medium related to its real depth and apparent depth?
Express the refractive index μ of a medium in terms of the velocity of light.
Express the refractive index μ of a medium in terms of the angle of incidence i in air and the angle of refraction r in a denser medium.
If a ray of light passes from medium I to medium II without any change of direction, what can be said about the refractive indices of these media (angle I is not 0)?
Explain briefly what causes the twinkling of stars at night.
How are critical angles related to the refractive index of the medium?
Can the absolute refractive index of a medium be less than one?
Why does the sun appear bigger during sunset or sunrise?
Name a prism required for obtaining a spectrum of Ultraviolet light.
Name the radiation which can be detected by a thermopile.
What is the total reflecting prism?
Name two instruments of the total refracting prism in which is used.
State two advantages of using a right-angle prism as a reflector, rather than a plane mirror.
State three actions that a total reflecting prism can produce.
In what condition a prism is said to be in the position of minimum deviation? What is the direction of the refracted ray inside the prism in this condition?
How does the angle of deviation produced by a prism depend on the colour of light used? Which colour of white light is deviated (i) most, (ii) least, by a prism?
Images formed by totally reflecting prisms are brighter than the image formed by ordinary reflected light, why?
A ray of light incident at an angle of incidence ‘i’ passes through an equilateral glass prism such that the refracted ray inside the prism is parallel to its base and emerges from the prism at an angle of emergence ‘e’.
How is the angle of emergence ‘e’ related to the angle of incidence ‘i’?
A ray of light incident at an angle of incidence ‘i’ passes through an equilateral glass prism such that the refracted ray inside the prism is parallel to its base and emerges from the prism at an angle of emergence ‘e’.
What can you say about the value of the angle of deviation in such a situation?
What do you understand by the deviation produced by a prism?
Define the term angle of deviation.
State one factor on which a critical angle for a given pair of media depends. The critical angle for the glass-air interface is 45° for the yellow light. Will it be equal to, less than or greater than 45° for (i) red light, (ii) blue light?
Name the factors affecting the critical angle for the pair of media.
What is meant by the statement, ‘the critical angle for diamond is 24°’?
How is the critical angle of a material related to its refractive index?
What is meant by the term ‘critical angle’?
You are provided with a printed piece of paper. Using this paper how will you differentiate between a convex lens and a concave lens?
ICSE solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 3 Refraction of Light Long Answers
The refractive index of air with respect to glass is defined: as gµa = sin i/sin r
Write down a similar expression for aµg in terms of angle i and r.
The refractive index of air with respect to glass is defined: as gµa = sin i/sin r
If r = 90°, what is the corresponding angle i called?
ICSE solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 3 Refraction of Light Figure Based Short Answers
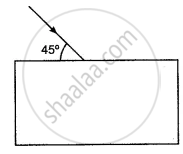
Draw the diagram given below and clearly show the path taken by the emergent ray.
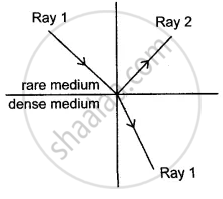
A ray of light moves from a rare medium to a dense medium as shown in the diagram below. Write down the number of the ray which represents the partially reflected ray.
In the diagram below, PQ is a ray of light incident on a rectangular glass block.
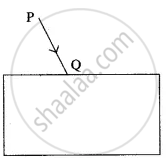
Copy the diagram and complete the path of the ray of light through the glass block. In your diagram, mark the angle of incidence by letter ‘i’ and the angle of emergence by the letter ‘e’.
In the diagram below, PQ is a ray of light incident on a rectangular glass block.

How are the angles ‘i’ and ‘e’ related to each other?
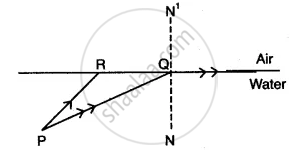
A ray of monochromatic light enters a liquid from the air as shown in the diagram given below:
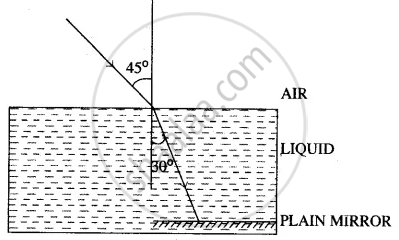
Copy the diagram and show in the diagram the path of the ray of light after it strikes the mirror and re-enters the medium of air.
A ray of monochromatic light enters a liquid from the air as shown in the diagram given below:

Mark in your diagram the two angles on the surface of separation when the ray of light moves out from the liquid to air.
A ray of monochromatic light is incident from air into a glass slab. Draw a labelled ray diagram indicating the change in its path till it emerges out of the slab. In the diagram, mark the angle of incidence (i) and the angle of refraction (r) at the first interface. How is the refractive index of glass related to the angles i and r?
Draw ray of light bending towards the normal while passing from air to glass. Label your diagrams.
Draw ray of light bending towards the normal while passing from glass to water. Label your diagrams.
Show the path of a ray of light when it travels from air into water, the angle of incidence being 30°. Mark the angle of incidence and the corresponding angle of refraction.
A ray of light is moving from a rarer medium to a denser medium and strikes a plane mirror placed at 90° to the direction of the ray as shown in the diagram.
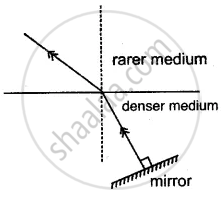
(i) Copy the diagram and mark arrows to show the path of the ray of light after it is reflected from the mirror.
(ii) Name the principle you have used to mark the arrows to show the direction of the ray.
After a robbery, if a window has been broken, there will be tiny particles of glass. Some of these will be found at the scene of the crime and some may be caught in the thief’s clothing. If the police can prove that these particles are identical, they have a strong case.
A method of doing this is to suspend the particles of glass in a special liquid. Light of a single colour is thrown through the liquid and the particles viewed through a microscope. The temperature of the liquid is then slowly altered. This alters the speed of light through the liquid (i.e., it alters the refractive index). At one particular temperature, the particles of glass disappear. It this happens at the same temperature for both sets of glass particles, they probably came from the same broken pane of glass.
Complete and copy the diagram to show how light bends when it travels from the liquid to the glass and back to the liquid, If the light slows down in the glass.
After a robbery, if a window has been broken, there will be tiny particles of glass. Some of these will be found at the scene of the crime and some may be caught in the thief’s clothing. If the police can prove that these particles are identical, they have a strong case.
A method of doing this is to suspend the particles of glass in a special liquid. Light of a single colour is thrown through the liquid and the particles viewed through a microscope. The temperature of the liquid is then slowly altered. This alters the speed of light through the liquid (i.e., it alters the refractive index). At one particular temperature, the particles of glass disappear. It this happens at the same temperature for both sets of glass particles, they probably came from the same broken pane of glass.
Complete and copy the diagram to show how light bends when it travels from the liquid to the glass and back to the liquid, If the light speeds up in the glass.
Show with the help of a diagram how a total reflecting prism can be used to turn a ray of light through 90°. Name one instrument in which such a prism is used.
Draw a diagram, properly labelled, to illustrate the use of a total reflecting prism (a right-angled isosceles prism) to turn a ray of light through 180°. Name an instrument in which this device is used.
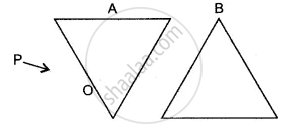
The figure shows two prisms A and B. A monochromatic ray of light PO is incident at the face of the prism A. Complete the diagram to show the path of the ray till it emerges out of the prism B.
Draw a diagram to show the refraction of a monochromatic light ray through an equilateral prism. On the diagram, label the incident, refracted, and emergent rays. It also indicates the angle of deviation by the letter δ.
How does the angle of deviation produced by a prism depend on the angle of incidence of light at the prism surface? Draw a graph to illustrate your answer.
In the diagram alongside a ray of light, PQ is incident normally on one face AB of an equilateral glass prism. What is the angle of incidence at the faces AB and AC?
Complete the ray diagram showing its emergence into the air after passing through the prism.
A ray of light enters a glass slab ABDC as shown in figure and strikes at the centre O of the circular part AC of the slab. The critical angle of glass is 42°. Complete the path of the ray till it emerges out from the slab. Mark the angles in the diagram wherever necessary.

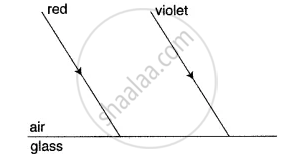
Two parallel rays of Red and Violet travelling through the air, meet the air-glass boundary as shown in the above figure. Will their paths inside the glass be parallel? Give a reason for your answer.
Light passes through a rectangular glass slab and through a triangular glass prism. In what way does the direction of the two emergent beams differ and why?
A ray of monochromatic light is incident from the air on a glass slab:
(i) Draw a labelled ray diagram showing the change in the path of the ray till it emerges from the glass slab.
(ii) Name the two rays that are parallel to each other.
(iii) Mark the lateral displacement in your diagram.
With the help of a well-labelled diagram show that the apparent depth of an object, such as a coin, in water is less than its real depth.
How are the refractive index of water-related to the real depth and the apparent depth of a column of water?
ICSE solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 3 Refraction of Light Figure Based Long Answers
How will you verify the laws of refraction or how the refractive index of glass is determined in the laboratory?
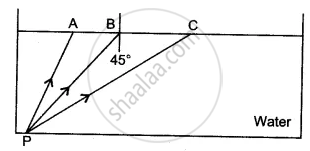
The diagram shows a point source P inside a water container. Three rays A, B, and C starting from P are shown up to the water surface. Show in the diagram the path of these rays after striking the water surface. The critical angle for the water-air pair is 48°.
The diagram shows the path of a ray of light through a rectangular glass block placed in a liquid of uniform density.

(a) Does the light speed up or slow down in the glass,
(b) Give the reason for your answer.
The diagram shows the path of a ray of light through a rectangular glass block placed in a liquid of uniform density.

What is the angular, deviation of the emergent ray from the glass block with respect to the incident ray?
The diagram shows the path of a ray of light through a rectangular glass block placed in a liquid of uniform density.

Show with the help of a ray diagram the path of the ray when incident ray normally falls on the first surface of the glass block and passes through the block and the liquid.
The diagram shows the path of a ray of light through a rectangular glass block placed in a liquid of uniform density.

What should be the rate of the speed of light through the liquid to the speed through the glass so that there is no refraction of light at the boundaries of the glass block when the system is illuminated by the light of one colour?
Trace a ray of light incident at 30° on a surface if travelling from air to glass. What is the angle of refraction in this case? (R.I. for glass = 3/2).
Trace a ray of light incident at 30° on a surface if travelling from glass to air. What is the angle of refraction in this case? (R.I. for glass = 3/2).
Explain with the help of a diagram of how fish is able to see the objects above it.
Draw a diagram of a prism and label:
(i) the base,
(ii) the refracting surfaces,
(iii) the refracting edge,
(iv) the refracting angle in it.
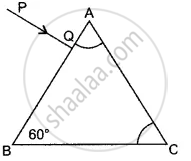
A ray of light passes through a right-angled prism as shown in the figure. State the angles of incidence at the faces AC and BC.
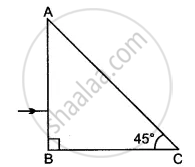
Calculate the velocity of light in a glass block of refractive index 1.5. (Velocity of light in air = 3 × 108 m/s)
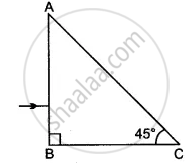
Complete the following diagram to show the path of the ray of a single colour in the diagram as if enters in and emerges out of the prism. Mark the angles wherever necessary. (Critical angle for glass = 42°).

Complete the following diagram to show the path of the ray of a single colour in the diagram as if enters in and emerges out of the prism. Mark the angles wherever necessary. (Critical angle for glass = 42°).
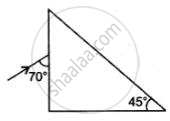
The adjacent diagram shows two right-angled isosceles prisms A and B. Complete the diagram to show the path of rays P and Q emerging out of the prism B. What principles have you used to complete the diagram?
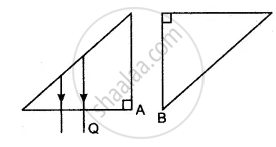
A ray of light PQ is incident normally on the hypotenuse of a right-angled prism ABC as shown in the diagram given below:
(i) Copy the diagram and complete the path of the ray PQ till it emerges from the prism.
(ii) What is the value of the angle of deviation of the ray?
(iii) Name an instrument where this action of the prism is used.
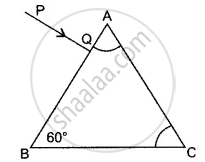
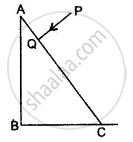
PQ and PR are two light rays emerging from the object as shown in the figure below:
(i) What is the special name given to the angle of incidence (∠PQN) of ray PQ?
(ii) Copy the ray diagram and complete it to show the position of the image of the object P when seen obliquely from above.
(iii) Name the phenomenon that occurs if the angle of incidence ∠PQN is increased still further.
ICSE solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 3 Refraction of Light Short Numerical
The speed of light in air is 3 × 108 ms-1. Calculate the speed of light in water. The refractive index of water is 4/3.
The velocity of light in diamond is 121000 kms-1. What is its refractive index?
Write the approximate values of speed of light in (i) air and (ii) glass. Use these values to calculate the refractive index of glass with respect to air.
The refractive index of glass with respect to air is 3/2. What is the refractive index of air with respect to glass?
A glass block is having refractive index 3/2, the light ray is incident at an angle 45°. Find the sine of the angle of, refraction inside the glass block.
A coin placed at the bottom of a beaker appears to be raised by 4.0 cm. If the refractive index of water is 4/3, find the depth of the water in the beaker.
A ray of light is incident on a glass surface at an angle of 50° with the corresponding angle of refraction 30°. Find the value of the R.I. of glass.
The refractive index of glass with respect to air is 1.5. What is the value of the refractive index of air with respect to glass?
A ray of light is incident as a normal ray on the surface of separation of two different mediums. What is the value of the angle of incidence in this case?
Solutions for 3: Refraction of Light
![ICSE solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 chapter 3 - Refraction of Light ICSE solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 chapter 3 - Refraction of Light - Shaalaa.com](/images/physics-english-class-10_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
ICSE solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 chapter 3 - Refraction of Light
Shaalaa.com has the CISCE Mathematics Physics [English] Class 10 CISCE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. ICSE solutions for Mathematics Physics [English] Class 10 CISCE 3 (Refraction of Light) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. ICSE textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Physics [English] Class 10 chapter 3 Refraction of Light are Introduction to Refraction of Light, Speed of Light, Relationship Between Refractive Index and Speed of Light (µ = C/V), Refraction of Light Through a Rectangular Glass Slab, Prism, Principle of Reversibility of the Path of Light, Experimental Verification of Law of Refraction and Determination of Refractive Index of Glass, Critical Angle, Relationship Between the Critical Angle and the Refractive Index (µ = 1/ Sin C), Total Internal Reflection in a Prism, Some Consequences of Refraction of Light, Use of a Total Internal Reflecting Prism in Place of a Plane Mirror, Consequences of Total Internal Refraction, Multiple Images in a Thick Plane Glass Plate Or Thick Mirror, Refraction of Light Through a Prism, Real and Apparent Depth, Apparent Bending of a Stick Under Water, Transmission of Light from a Denser Medium (Glass Or Water) to a Rarer Medium (Air) at Different Angles of Incidence, Total Internal Reflection.
Using ICSE Physics [English] Class 10 solutions Refraction of Light exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in ICSE Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CISCE Physics [English] Class 10 students prefer ICSE Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 3, Refraction of Light Physics [English] Class 10 additional questions for Mathematics Physics [English] Class 10 CISCE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
