Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
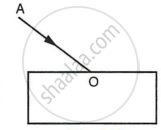
A ray of light enters a glass slab ABDC as shown in figure and strikes at the centre O of the circular part AC of the slab. The critical angle of glass is 42°. Complete the path of the ray till it emerges out from the slab. Mark the angles in the diagram wherever necessary.

उत्तर
Inside the slab at K ∠i = 48° = ∠r
KL incident ray strikes at L, ∠i = 42° = ∠C and emergent ray LM is parallel to BD, i.e. ∠r = 90°

APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Name a prism required for obtaining a spectrum of Ultraviolet light.
In the adjacent diagram, AO is a ray of light incident on a rectangular glass slab.
- Complete the path of the ray till it emerges out of the slab.
- In the diagram, mark the angle of incidence (i) and the angle of refraction (r) at the first interface. How is the refractive index of glass related to the angles i and r?
- Mark angles of emergence by the letter e. How are the angles i and e related?
- Which two rays are parallel to each other? Name them.
- Indicate in the diagram the lateral displacement between the emergent ray and the incident ray. State one factor that affects the lateral displacement.
An object is viewed through a glass prism with its vertex pointing upwards. It appears to be displaced upward. Explain the reason.
Select from the following the best set-up for tracing the path of a ray of light through a rectangular glass slab:
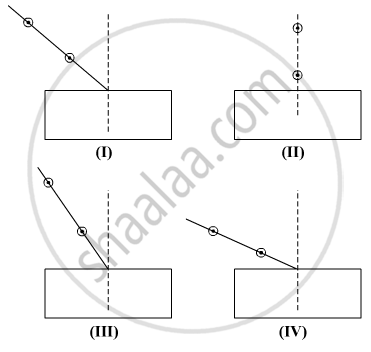
(A) I
(B) II
(C) III
(D) IV
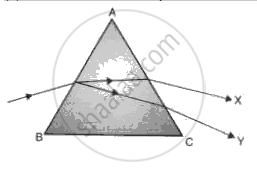
Fig. shows a ray of white light that passes through a prism and produces a spectrum.
(a) Name the phenomenon that is taking place.
(b) What colour would you see at X and Y?
(c) What radiation would you detect above X and below Y?
Why is the colour red used as a sign of danger?
During sunset and sunrise, the sun is seen when it is slightly below the horizon. Give reason.
The refractive index of air with respect to glass is defined: as gµa = sin i/sin r
If r = 90°, what is the corresponding angle i called?
A ray of light strikes the surface of a rectangular glass slab such that the angle of incidence in air is
- 0°,
- 45°.
In each case, draw a diagram to show the path taken by the ray as it passes through the glass slab and emerges from it.
