Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
During sunset and sunrise, the sun is seen when it is slightly below the horizon. Give reason.
उत्तर
Light rays from the sun while coming towards earth suffers successive refractions from a rarer to a denser medium and so it bends towards the normal at each refraction. These rays on earth appear to be coming from an apparent position of the sun which is higher than its actual position. Thus, the sun is seen even when it is slightly below the horizon during sunset and sunrise.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State the dependence of angle of deviation On the refractive index of the material of the prism.
State the dependence of angle of deviation On the wavelength of light
In the adjacent diagram, AO is a ray of light incident on a rectangular glass slab.
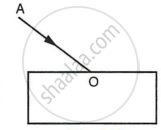
- Complete the path of the ray till it emerges out of the slab.
- In the diagram, mark the angle of incidence (i) and the angle of refraction (r) at the first interface. How is the refractive index of glass related to the angles i and r?
- Mark angles of emergence by the letter e. How are the angles i and e related?
- Which two rays are parallel to each other? Name them.
- Indicate in the diagram the lateral displacement between the emergent ray and the incident ray. State one factor that affects the lateral displacement.
Light of a single colour is passed through a liquid having a piece of glass suspended in it. On changing the temperature of liquid, at a particular temperature the glass piece is not seen. When is the glass piece not seen?
How does the speed of light change when it passes from glass to water?
Select from the following the best experimental set-up for tracing the path of a ray of light through a glass slab: (A) I
(A) I
(B) II
(C) III
(D) IV
Draw a ray diagram showing the lateral displacement of a ray of light when it passes through a parallel sided glass slab.
Draw a diagram to show the refraction of a monochromatic light ray through an equilateral prism. On the diagram, label the incident, refracted, and emergent rays. It also indicates the angle of deviation by the letter δ.
