Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
During sunset and sunrise, the sun is seen when it is slightly below the horizon. Give reason.
उत्तर
Light rays from the sun while coming towards earth suffers successive refractions from a rarer to a denser medium and so it bends towards the normal at each refraction. These rays on earth appear to be coming from an apparent position of the sun which is higher than its actual position. Thus, the sun is seen even when it is slightly below the horizon during sunset and sunrise.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
How is the reflection of light ray from a plane mirror different from the refraction of light ray as it enters a block of glass?
How is the angle of emergence related to the angle of incidence when prism is in the position of minimum deviation? Illustrate your answer with help of a labelled diagram using an equilateral prism?
An object is viewed through a glass prism with its vertex pointing upwards. It appears to be displaced upward. Explain the reason.
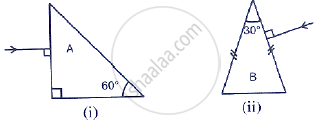
Fig 4.31 below shows a light ray of single colour incident normally on two prisms A and B. In each case draw the path of the ray of light as it enters and emerges out of the prism. Mark the angle wherever necessary.
A ray of light falls normally on the surface of a transparent glass slab. Draw a ray diagram to show its path and also mark angle of incidence and angle of emergence.
Make the correct for each of the following :
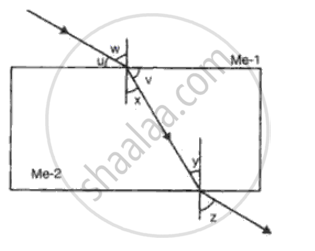
With reference to the fig, the refractive index of the glass block is
Which colour of light travels fastest in any medium except air?
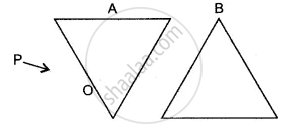
The figure shows two prisms A and B. A monochromatic ray of light PO is incident at the face of the prism A. Complete the diagram to show the path of the ray till it emerges out of the prism B.
How does the angle of deviation produced by a prism depend on the angle of incidence of light at the prism surface? Draw a graph to illustrate your answer.
The diagram shows the path of a ray of light through a rectangular glass block placed in a liquid of uniform density.

Show with the help of a ray diagram the path of the ray when incident ray normally falls on the first surface of the glass block and passes through the block and the liquid.
