Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
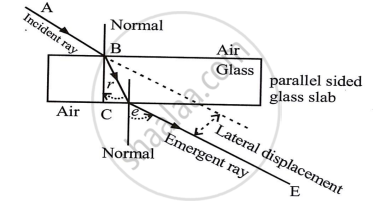
Draw a ray diagram showing the lateral displacement of a ray of light when it passes through a parallel sided glass slab.
उत्तर
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A student very cautiously traces the path of a ray through a glass slab for different values of the angle of incidence (∠i). He then measures the corresponding values of the angle of refraction (∠r) and the angle of emergence (∠e) for every value of the angle of incidence. On analysing these measurements of angles, his conclusion would be
(A) ∠i > ∠r > ∠e
(B) ∠i = ∠e > ∠r
(C) ∠i < ∠r < ∠e
(D) ∠i = ∠e < ∠r
Light passes through a rectangular glass slab and through a triangular glass prism. In what way does the direction of the two emergent beams differ and why?
Observe the following figure and answer the questions given under it:
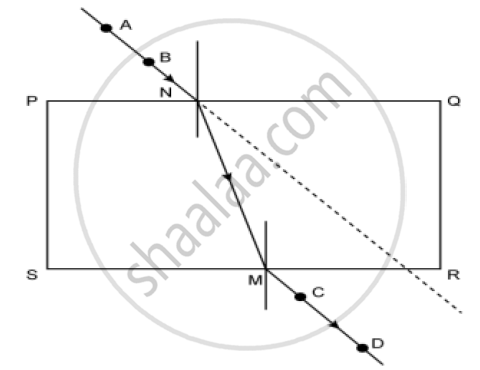
1) How many times does refraction take place in the above figure?
2) What happens to the ray of light when it passes from air to glass?
3) What happens to the ray of light when it passes from glass to air?
4) What are the rays AB and CD in the figure called?
5) Define refraction.
Why does a fisherman aim at the tail of fish during spearfishing?
Glass is transparent in nature. Why does glass powder look opaque? When water is poured over it, it again becomes transparent. Why?
Why is the colour red used as a sign of danger?
Write a relation between the angle of incidence (i), angle of emergence (e), angle of the prism (A), and angle of deviation (d) for a ray of light passing through an equilateral prism.
Explain briefly what causes the twinkling of stars at night.
Draw a diagram to show the refraction of a monochromatic light ray through an equilateral prism. On the diagram, label the incident, refracted, and emergent rays. It also indicates the angle of deviation by the letter δ.
