Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Name the phenomenon responsible in the following case:
Twinkling of stars
उत्तर
Refraction of light
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A student traces the path of a ray of light through a rectangular glass slab for the different values of angle of incidence. He observes all possible precautions at each step of the experiment. At the end of the experiment, on analyzing the measurements, which of the following conclusions is he likely to draw?
(A) ∠i = ∠e < ∠r
(B) ∠i < ∠e < ∠r
(C) ∠i > ∠e > ∠r
(D) ∠i = ∠e > ∠r
How can you bend light away from the normal?
In the adjacent diagram, AO is a ray of light incident on a rectangular glass slab.
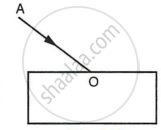
- Complete the path of the ray till it emerges out of the slab.
- In the diagram, mark the angle of incidence (i) and the angle of refraction (r) at the first interface. How is the refractive index of glass related to the angles i and r?
- Mark angles of emergence by the letter e. How are the angles i and e related?
- Which two rays are parallel to each other? Name them.
- Indicate in the diagram the lateral displacement between the emergent ray and the incident ray. State one factor that affects the lateral displacement.
A ray of light is passing from a transparent medium 1 to another transparent medium 2 (i) Speed up (ii) slows down. In each case, state whether the refractive index of medium 2 is equal to, less than or greater than the refractive index of medium 1.
The critical angle for glass-air is 45° for the light of yellow colour. State whether it will be less than, equal to, or more than 45° for (i) ref light, (ii) blue light?
“A ray of light incident on a rectangular glass slab immersed in any medium emerges parallel to itself.” Draw labelled ray diagram to justify the statement.
What is meant by the refraction of light?
The diagram shows the path of a ray of light through a rectangular glass block placed in a liquid of uniform density.

What is the angular, deviation of the emergent ray from the glass block with respect to the incident ray?
Calculate the velocity of light in a glass block of refractive index 1.5. (Velocity of light in air = 3 × 108 m/s)
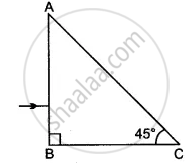
Write the approximate values of speed of light in (i) air and (ii) glass. Use these values to calculate the refractive index of glass with respect to air.
