Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain with the help of a diagram of how fish is able to see the objects above it.
उत्तर
A fish can see everything above it in clear water irrespective of its position in different depths. The critical angle for water is 48.5°. The angle of the cone of vision for the fish is twice this angle.
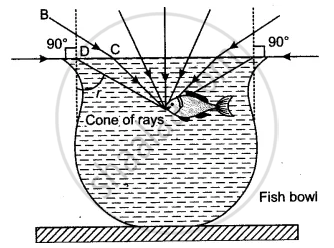
Hence it is 97°. All the objects outside water but in this cone of vision Will be seen by the fish. Outside this range, the fish will see all the objects in the surrounding area (see figure). Those objects which are at the bottom will be seen by the fish due to total internal reflection taking place at the water-air interface.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
On the basis of the experiment, "To trace the path of a ray of light through a rectangular glass slab", students of a class arrived at which one of the following conclusions?
(A) Angle of incidence is greater than the angle of emergence.
(B) Angle of emergence is smaller than the angle of refraction.
(C) Emergent ray is parallel to the refracted ray.
(D) Incident ray and emergent ray are parallel to each other.
Light passes through a rectangular glass slab and through a triangular glass prism. In what way does the direction of the two emergent beams differ and why?
When a ray of light from air enters a denser medium, it ______.
The diagram alongside shows the refraction of a ray of light from air to a liquid.
- Write the values of (i) angle of incidence, (ii) angle of refraction.
- Use Snell’s law to find the refractive index of liquid with respect to air.

An object is viewed through a glass prism with its vertex pointing upwards. It appears to be displaced upward. Explain the reason.
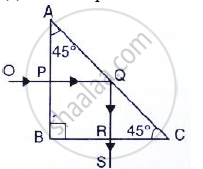
A ray of light OP passes through a right angles prism as shown in the adjacent diagram.
(a) State the angles of incidence at the faces AC and BC.
(b) Name the phenomenon which the ray suffers at the face AC.
“A ray of light incident on a rectangular glass slab immersed in any medium emerges parallel to itself.” Draw labelled ray diagram to justify the statement.
What is the refractive index of vacuum
What is the total reflecting prism?
A ray of monochromatic light is incident from air into a glass slab. Draw a labelled ray diagram indicating the change in its path till it emerges out of the slab. In the diagram, mark the angle of incidence (i) and the angle of refraction (r) at the first interface. How is the refractive index of glass related to the angles i and r?
