Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Draw a diagram to show the splitting of white light into its constituent colours.
Solution
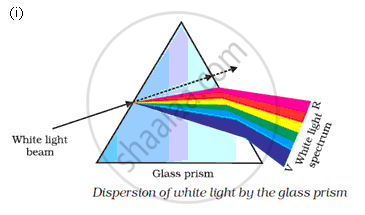
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A monochromatic ray of light passes from air to glass. The wavelength of light in air is λ, the speed of light in air is c and in glass is V. If the absolute refractive index of glass is 1.5, write down
- the relationship between c and V,
- the wavelength of light in glass.
A ray of light of wavelength 6600 Å suffer refraction from air to glass. Taking \[\ce{_a\mu_g = \frac{3}{2}}\], find the wavelength of light in glass.
How does the angle of deviation produced by a prism change with increase in the angle of incidence. Draw a curve showing the variation in the angle of deviation with the angle of incidence at a prism surface.
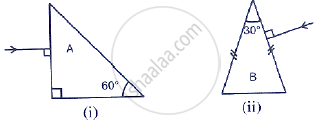
Fig 4.31 below shows a light ray of single colour incident normally on two prisms A and B. In each case draw the path of the ray of light as it enters and emerges out of the prism. Mark the angle wherever necessary.
A ray of light enters a glass slab ABDC as shown in figure and strikes at the centre O of the circular part AC of the slab. The critical angle of glass is 42°. Complete the path of the ray till it emerges out from the slab. Mark the angles in the diagram wherever necessary.

What is meant by the refraction of light?
What should be the ratio of the speed of light through the liquid to the speed through the glass so that there is no refraction of light at the boundaries of the glass block when the system is illuminated by the light of one colour?
What do you understand by the deviation produced by a prism?
The diagram shows the path of a ray of light through a rectangular glass block placed in a liquid of uniform density.

Show with the help of a ray diagram the path of the ray when incident ray normally falls on the first surface of the glass block and passes through the block and the liquid.
The diagram below shows two parallel rays A (Orange) & B (Blue) incident from air, on air-glass boundary.
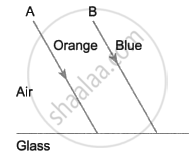
- Copy and complete the path of the rays A and B.
- How do the speeds of these rays differ in glass?
- Are the two refracted rays in glass parallel? Give a reason.
