Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Draw the ray diagram of a glass slab having medium A and B for the velocity of light ray VA and VB respectively and define Snell's law.
- If VB = 1.5 VA, then which medium is denser?
- What is the refractive index of A with respect to B?
- What is the refractive index of B with respect to A?
Solution
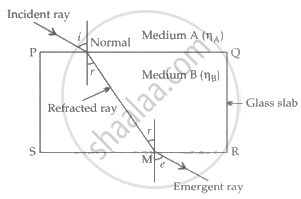
Where i = angle of incidence,
r = angle of refraction,
e = angle of emergence
At point N, using snell's law
AηB =
According to snell's law, the sin i of the angle of incidence to the sin r of the angle of refraction is always constant.
- Medium A is denser.
- Refractive index of A with respect to B is:
BηA = - Refractive index of B with respect to A is:
AηB =
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Select from the following the best experimental setup for tracing the path of a ray of light passing through a rectangular glass slab.
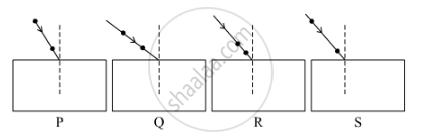
(a) P
(b) Q
(c) R
(d) S
Explain the term absolute refractive index of a medium and write an expression to relate it with the speed of light in vacuum.
Draw a ray diagram to show the refraction of a monochromatic ray through a prism when it suffers minimum deviation
Write a relationship between the angle of incidence and angle of refractions for a given pair of media
The speed of light in glass is 2 × 105 km/s. What is the refractive index of glass?
A ray of light strikes the surface of a rectangular glass block such that the angle of incidence in
air is 0°.
In each case, draw diagram to show the path taken by the ray as it passes through the glass block and emerges from it.
The diagram alongside shows the refraction of a ray of light from air to a liquid.
- Write the values of (i) angle of incidence, (ii) angle of refraction.
- Use Snell’s law to find the refractive index of liquid with respect to air.

An object is viewed through a glass prism with its vertex pointing upwards. It appears to be displaced upward. Explain the reason.
A postage stamp kept below a rectangular glass block of refractive index 1.5 when viewed from vertically above it, appears to be raised by 7.0 mm. Calculate the thickness of the glass slab.
What is meant by the statement the critical angle for diamond is 24°?
Four students showed the following traces of the path of a ray of light passing through a rectangular glass slab.
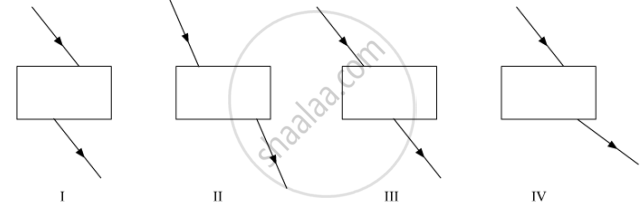
The trace most likely to be correct is that of student
(A) I
(B) II
(C) III
(D) IV
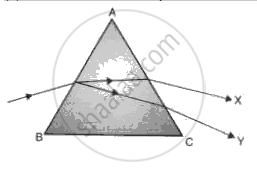
Fig. shows a ray of white light that passes through a prism and produces a spectrum.
(a) Name the phenomenon that is taking place.
(b) What colour would you see at X and Y?
(c) What radiation would you detect above X and below Y?
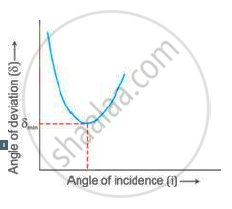
Using the curve, how do you infer that for given prism, the angle of minimum deviation δmin is unique for the given light?
Choose the correct alternative and rewrite the following:
A glass slab is placed in the path of convergent light. The point of convergence of light
A ray of light passes from water to air. How does the speed of light change?
Does the depth of a tank of water appear to change or remain the same when viewed normally from above?
What is the refractive index of water
How is the refractive index of a medium related to its real depth and apparent depth?
Express the refractive index μ of a medium in terms of the velocity of light.
Explain briefly what causes the twinkling of stars at night.
What is the total reflecting prism?
You are provided with a printed piece of paper. Using this paper how will you differentiate between a convex lens and a concave lens?
In the diagram below, PQ is a ray of light incident on a rectangular glass block.
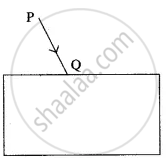
How are the angles ‘i’ and ‘e’ related to each other?
Draw ray of light bending towards the normal while passing from air to glass. Label your diagrams.
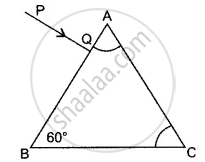
In the diagram alongside a ray of light, PQ is incident normally on one face AB of an equilateral glass prism. What is the angle of incidence at the faces AB and AC?
The diagram shows the path of a ray of light through a rectangular glass block placed in a liquid of uniform density.

(a) Does the light speed up or slow down in the glass,
(b) Give the reason for your answer.
The diagram shows the path of a ray of light through a rectangular glass block placed in a liquid of uniform density.

What is the angular, deviation of the emergent ray from the glass block with respect to the incident ray?
The diagram shows the path of a ray of light through a rectangular glass block placed in a liquid of uniform density.

What should be the rate of the speed of light through the liquid to the speed through the glass so that there is no refraction of light at the boundaries of the glass block when the system is illuminated by the light of one colour?
Trace a ray of light incident at 30° on a surface if travelling from air to glass. What is the angle of refraction in this case? (R.I. for glass = 3/2).
Trace a ray of light incident at 30° on a surface if travelling from glass to air. What is the angle of refraction in this case? (R.I. for glass = 3/2).
The velocity of light in diamond is 121000 kms-1. What is its refractive index?
Write the approximate values of speed of light in (i) air and (ii) glass. Use these values to calculate the refractive index of glass with respect to air.
A glass block is having refractive index 3/2, the light ray is incident at an angle 45°. Find the sine of the angle of, refraction inside the glass block.
A coin placed at the bottom of a beaker appears to be raised by 4.0 cm. If the refractive index of water is 4/3, find the depth of the water in the beaker.
