Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Choose the correct alternative and rewrite the following:
A glass slab is placed in the path of convergent light. The point of convergence of light
Options
moves away from the slab
moves towards the slab
remains at the same point
undergoes lateral shift
Solution
moves away from the slab
If the glass slab is placed in the path of convergent light, the point of convergence or focus will shift away from the glass slab as the light passing through glass will bend towards the normal and after coming out in the air, the light will converge out at a point away from the glass slab.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Explain how the formation of a rainbow occurs.
In your laboratory you trace the path of light rays through a glass slab for different values of angle of incidence (∠i) and in each case measure the values of the corresponding angle of refraction (∠r) and angle of emergence (∠e). On the basis of your observations your correct conclusion is:
(a) ∠i is more than ∠r, but nearly equal to ∠e
(b) ∠i is less then ∠r, but nearly equal to ∠e
(c) ∠i is more than ∠e, but nearly equal to ∠r
(d) ∠i is less than ∠e, but nearly equal to ∠r
Explain the term absolute refractive index of a medium and write an expression to relate it with the speed of light in vacuum.
State the dependence of angle of deviation On the wavelength of light
Which colour of light travels fastest in any medium except air?
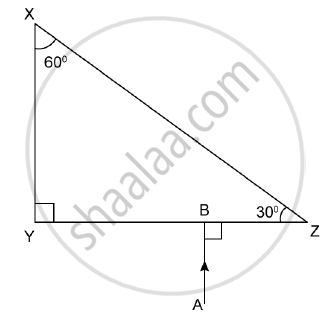
The following diagram shows a 60°, 30°, 90° glass prism of critical angle 42°, Copy the diagram and complete the path of incident ray AB emerging out of the prism marking the angle of incidence on each surface.
How is the refractive index of a medium related to the speed of light in it?
A ray of light strikes the surface of a rectangular glass block such that the angle of incidence in
air is 0°.
In each case, draw diagram to show the path taken by the ray as it passes through the glass block and emerges from it.
When light travels from a rarer to a denser medium, its speed ______.
The highest refractive index is of ______.
With the help of diagram of the principal section of a prism, indicate its refracting surfaces, refracting edge and base.
A light ray in passing from water to a medium
(a) speeds up
(b) slows down. In each case, give one example of the medium.
What do you understand by the statement the refractive index of glass is 1.5 for white light?
Fill in the blanks to complete the following sentence
The refractive index of glass with respect to air is 3/2. The refractive index of air with respect to glass will be ……………….
A coin is places at the bottom of a beaker containing water (refractive index = 4/3) to a depth of 12 cm. By what height the coin appears to be raised when seen from vertically above?
(i) What is the relation between the refractive index of water with respect to air `("_aμ_\text(w))` and the refractive index of air with respect to water `("_\text(w)μ_ a)` .
(ii) If the refractive index of water with respect to air `("_aμ_\text(w))` is`5/3`. Calculate the refractive index of air with respect to water `("_\text(w)μ_ a)` .
In the fig. name the ray which represents the correct path of light while passing through a glass block.
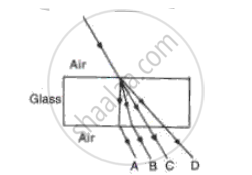
Fig shows a lens as a combination of a glass block and two prisms.
(i) Name the lens formed by the combination.
(ii) What is the line XX' called?
(iii) Complete the path of the incident ray PQ after passing through the lens.
(iv) The final emergent ray either meets XX' at a point or appears to come from a point on XX'. Label it as F, What is this point called?
Which colour of light travels fastest in any medium except air?
Rewrite the following statement by selecting the correct option:
If a ray of light strikes a glass slab at an angle of 600 with the surface of the slab, the angle of incidence must be __________________.
A ray of light passes from water to air. How does the speed of light change?
Write a relation between the angle of incidence (i), angle of emergence (e), angle of the prism (A), and angle of deviation (d) for a ray of light passing through an equilateral prism.
Name the material for which the refractive index is found to be maximum.
What should be the ratio of the speed of light through the liquid to the speed through the glass so that there is no refraction of light at the boundaries of the glass block when the system is illuminated by the light of one colour?
Can the absolute refractive index of a medium be less than one?
What is the total reflecting prism?
In what condition a prism is said to be in the position of minimum deviation? What is the direction of the refracted ray inside the prism in this condition?
How does the angle of deviation produced by a prism depend on the colour of light used? Which colour of white light is deviated (i) most, (ii) least, by a prism?
What do you understand by the deviation produced by a prism?
The refractive index of air with respect to glass is defined: as gµa = sin i/sin r
Write down a similar expression for aµg in terms of angle i and r.
The diagram shows the path of a ray of light through a rectangular glass block placed in a liquid of uniform density.

What should be the rate of the speed of light through the liquid to the speed through the glass so that there is no refraction of light at the boundaries of the glass block when the system is illuminated by the light of one colour?
Trace a ray of light incident at 30° on a surface if travelling from air to glass. What is the angle of refraction in this case? (R.I. for glass = 3/2).
A ray of light PQ is incident normally on the hypotenuse of a right-angled prism ABC as shown in the diagram given below:
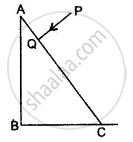
(i) Copy the diagram and complete the path of the ray PQ till it emerges from the prism.
(ii) What is the value of the angle of deviation of the ray?
(iii) Name an instrument where this action of the prism is used.
The diagram below shows two parallel rays A (Orange) & B (Blue) incident from air, on air-glass boundary.
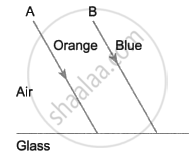
- Copy and complete the path of the rays A and B.
- How do the speeds of these rays differ in glass?
- Are the two refracted rays in glass parallel? Give a reason.
A ray of light strikes the surface of a rectangular glass slab such that the angle of incidence in air is
- 0°,
- 45°.
In each case, draw a diagram to show the path taken by the ray as it passes through the glass slab and emerges from it.
