Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
When a ray of light travels from air to glass slab and strikes the surface of separation at 90°, then it …………….
(a) bends towards normal
(b) bends away from normal
(c) passes unbent
(d) passes in zigzag way
Solution
(c) passes unbent
In this case, the angle of incidence (i) is zero and so also the angle of refraction.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
When rays of light are incident on a glass slab then the incident ray and emergent ray are _________ each other.
- perpendicular
- parallel
- opposite
- concurrent
A student very cautiously traces the path of a ray through a glass slab for different values of the angle of incidence (∠i). He then measures the corresponding values of the angle of refraction (∠r) and the angle of emergence (∠e) for every value of the angle of incidence. On analysing these measurements of angles, his conclusion would be
(A) ∠i > ∠r > ∠e
(B) ∠i = ∠e > ∠r
(C) ∠i < ∠r < ∠e
(D) ∠i = ∠e < ∠r
The speed of light in glass is 2 × 105 km/s. What is the refractive index of glass?
Name a prism required for obtaining a spectrum of Ultraviolet light.
How is the angle of emergence related to the angle of incidence when prism is in the position of minimum deviation? Illustrate your answer with help of a labelled diagram using an equilateral prism?
In the fig. name the ray which represents the correct path of light while passing through a glass block.
Draw an í- `delta` graph for a mono chromatic raY through a glass prism of a plane and mark
(i) `delta` m, the angle of mínimum devíation
(íí) Any two values of i for which value of `delta` ís same.
Fig shows a lens as a combination of a glass block and two prisms.
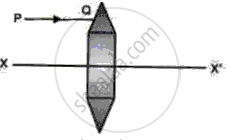
(i) Name the lens formed by the combination.
(ii) what is the XX' called?
(iii) Complete the ray diagram and show the path of the incident ray PQ after passing through the lens.
(iv) The final emergent ray will either meet XX' at a point or appear to come from a point on XX'. what is the point called?
Which colour of light travels fastest in any medium except air?
Rewrite the following statement by selecting the correct option:
If a ray of light strikes a glass slab at an angle of 600 with the surface of the slab, the angle of incidence must be __________________.
What is meant by the refraction of light?
Name the phenomenon responsible in the following case:
Twinkling of stars
Why upper surface of water contained in a beaker and above eye level appears silvery?
Glass is transparent in nature. Why does glass powder look opaque? When water is poured over it, it again becomes transparent. Why?
A ray of light passes from water to air. How does the speed of light change?
Which colour of light travels fastest in any medium except air?
Why is the colour red used as a sign of danger?
Name one main factor on which the direction of bending of a ray of light depends.
During sunset and sunrise, the sun is seen when it is slightly below the horizon. Give reason.
A glass slab is placed over a page on which the word VIBGYOR is printed with each letter in its corresponding colour.
- Will the image of all the letters be in the same place?
- If not, the state which letter will be raised to the maximum. Give a reason for your answer.
How is the refractive index of a medium related to its real depth and apparent depth?
You are provided with a printed piece of paper. Using this paper how will you differentiate between a convex lens and a concave lens?
The refractive index of air with respect to glass is defined: as gµa = sin i/sin r
Write down a similar expression for aµg in terms of angle i and r.
A ray of monochromatic light is incident from air into a glass slab. Draw a labelled ray diagram indicating the change in its path till it emerges out of the slab. In the diagram, mark the angle of incidence (i) and the angle of refraction (r) at the first interface. How is the refractive index of glass related to the angles i and r?
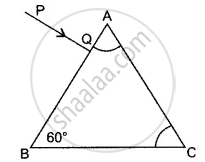
In the diagram alongside a ray of light, PQ is incident normally on one face AB of an equilateral glass prism. What is the angle of incidence at the faces AB and AC?
A ray of monochromatic light is incident from the air on a glass slab:
(i) Draw a labelled ray diagram showing the change in the path of the ray till it emerges from the glass slab.
(ii) Name the two rays that are parallel to each other.
(iii) Mark the lateral displacement in your diagram.
The diagram shows the path of a ray of light through a rectangular glass block placed in a liquid of uniform density.

(a) Does the light speed up or slow down in the glass,
(b) Give the reason for your answer.
Explain with the help of a diagram of how fish is able to see the objects above it.
Calculate the velocity of light in a glass block of refractive index 1.5. (Velocity of light in air = 3 × 108 m/s)
The refractive index of glass with respect to air is 1.5. What is the value of the refractive index of air with respect to glass?
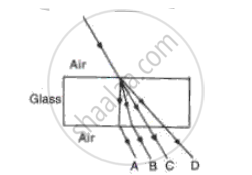
The path of a ray of light coming from air passing through a rectangular glass slab traced by four students are shown as A, B, C and D in the figure. Which one of them is correct?
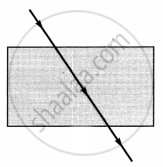 |
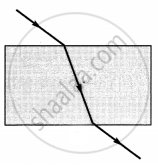 |
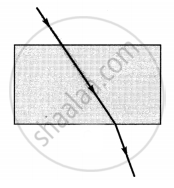 |
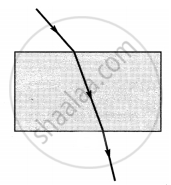 |
| A | B | C | D |
A ray of light strikes the surface of a rectangular glass slab such that the angle of incidence in air is
- 0°,
- 45°.
In each case, draw a diagram to show the path taken by the ray as it passes through the glass slab and emerges from it.
