Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
(a)A ray of light is incident at 45° on the face of
(i) A rectangular block of glass.
(ii) A 600 glass prism.
(b) Draw a sketch showing how the ray of monochromatic ray of light passes through glass in each case.
(c) With the aid of a diagram, explain how the face of a right angled prism may totally reflect incident on it.
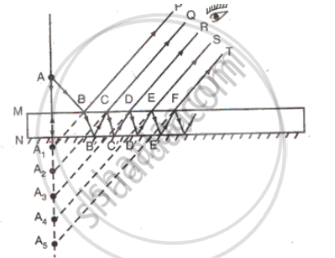
(d) A thick plane mirror produces several faint images in addition to a prominent one. Draw a ray diagram showing how reflection and refraction produce all these images.
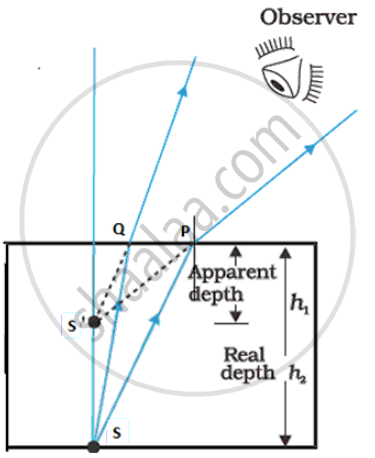
(e) Fig. represents a stone S at the bottom of a pond of water. Using the two rays, as shown, complete the ray diagram to show where the image of the stone appears when viewed from E.

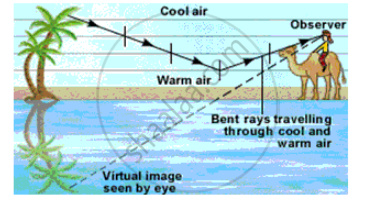
(f) What is a''mirage'? Explain with the help of a diagram.
(g) A man observes the bottom of a swimming pool of 3 m depth. If the refractive index of water is 1.3, what is the apparent depth of water?
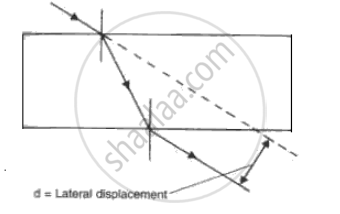
(h) When a ray of light undergoes refraction through a glass slab and when it emerges it is displaced laterally (Fig). What are the factors on which the lateral displacement depends?
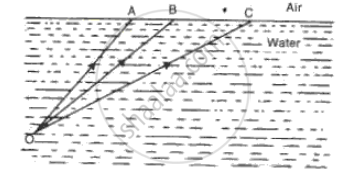
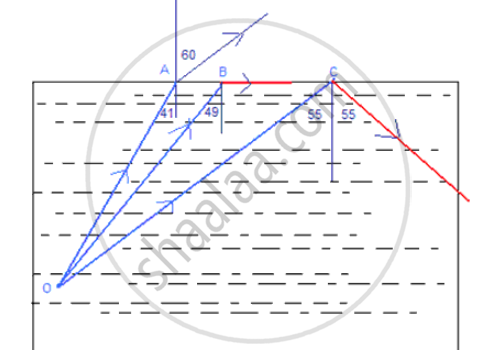
(i) Fig. shows three rays of light OA, OB and OC passing from water to air, making angles 490, 410 and 350 with the horizontal surface respectively. Draw an approximate path of the emergent ray for each. (Critical angle of water is 490.)
Solution
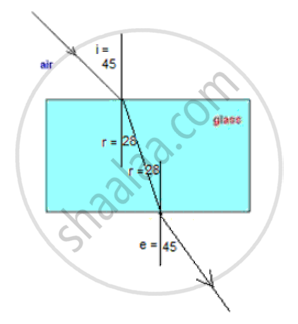
(a) For the glass block,
Given i = 45
Using μ = sin i / sin r
Taking μ = 1.5 for a glass, we get r = 28°
The ray diagram of parallel glass slab will look like this:
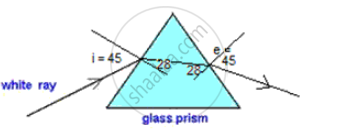
(b) For triangular glass prism:
Given i = 45
Using μ = sin i / sin r
Taking μ = 1.5 for a glass, we get r = 28°
The ray diagram of parallel glass slab will look like this:
(c)
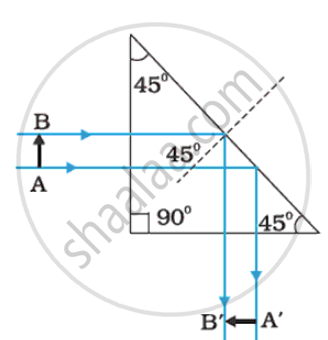
In the above diagram, light rays from the object AB are incident normally on a right angled glass prism and hence they pass undeviated. These rays fall on the other surface of the prism at 45°, Which is greater than the critical angle for the glss air interface (42°). Here, no refraction takes places but the ray of light is totally reflected back in the glass and finally it emerges out through the third surface of the prism normally forming the image A'B' of the object AB.
(d)
(e)
(f)
Mirage is a naturally occuring optical phenomenon caused due to total internal reflection light wherein and image some distant object appears displaced from its true position often observed in deserts and coal tarred roads on hot summer days.
In the desert, the air is very hot. The air near the surface of the earth is hot and is less dense. Thus, air can be considered aslayers of medium with higher density in the vertical upward direction. Rays of light from an object, say, a tree bend away from the normal as successive layer. At a certain point, When the angle of incidence becomes greater than the critical angle, The rays of light will undergo total internal reflection. The ray now starts traveling from rarer to denser medium. When the light reaches the eye of a weary dese traveler,to him, the light will appear to emerge in a straight line in the backward direction. Thus creating an impression of water pool or oasis.
(g) μ = `"Real depyh"/"apparent depth"`
`therefore " Apparent depth" = "Real depth"/μ = 3/1.3 = 2.3"m"`
(h) Factors on which lateral displacement depends are:
1. Thickness of the slab
2. Angle of incidence
3. Refractive index of the glass
(i) Given the angles with horizontal surface as:
OA making an angle of 49° with horizontal, hence iA = 90 - 49 = 41
OB making an angle of 41 with horizontal, hence ig = 90 - 41 = 49
OC making an angle of 35 with horizontal, hence ic = 90 - 35 = 55
Given critical angle = 49
So all incident angles is denser media, more than 49,will undergo total internal reflection, (Ray OC)
i = critical angle will graze through the interface (Ray Ob)
i = less than critical angle will emergent out into rare meium due to refraction (Ray OA).
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
What is a lens?
A ray of light incident on a lens parallel to its principal axis, after refraction passes through or appears to come from ______.
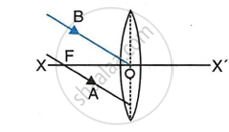
In the diagram below, XX’ represents the principal axis, O the optical centre and F the focus of the lens. Complete the path of rays A and B as they emerge out of the lens.
 |
 |
| (a) | (b) |
The diagram given below shows the position of an object OA in relation to a converging lens whose foci are at F1 and F2.
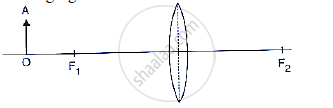
Describe three characteristic of the image.
The diagram given below shows the position of an object OA in relation to a converging lens whose foci are at F1 and F2.
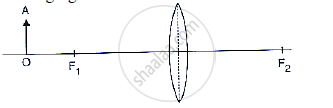
Describe how the distance of the image from the lens and the size of the image change as the object is moved towards F1.
Fig shows an object PQ placed on the principle axis of a lens L. The two foci of the kens are F1 and f2. The image formed by the lens is erect, Virtual and dimnished.
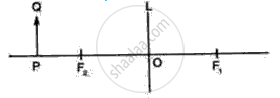
(i) Draw the outline ofthe lens L used and Named it.
(ii) Draw a ray of light starting from Q and passing through O. show the same ray after refraction by the lens.
(iii) Draw another ray from Q Which is incident parallel to the principle axis and show how it emerges after refraction from the lens.
(iv) Locate the final image formed.
In the following diagram ., the object and the image formed by the respective lenses are shown. Complete the ray diagram, and locate the focus. Find the focal length of the lens.

Make the correct choices in the following items :
A lens used as a magnifying glass
(i) ls a diverging lens
(ii) Produces a virtual image
(iii) ls placed with the object nearer the lens than the principle focus
